Overview of Macroeconomics
To name your story, you have to think about the overall message and what you want your audience to understand from the story. Also, make it relevant and easy to remember.
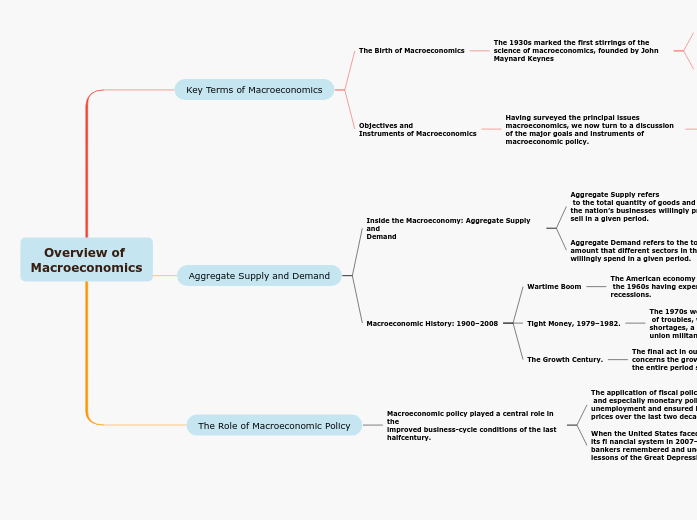
The Role of Macroeconomic Policy
Macroeconomic policy played a central role in the
improved business-cycle conditions of the last halfcentury.
When the United States faced a major shock to its fi nancial system in 2007–2009, central bankers remembered and understood the lessons of the Great Depression
The application of fiscal policy,
and especially monetary policy, helped lower unemployment and ensured largely stable prices over the last two decades.
Aggregate Supply and Demand
Macroeconomic History: 1900–2008
The Growth Century.
The final act in our macroeconomic drama concerns the growth of output and prices over the entire period since 1900
Tight Money, 1979–1982.
The 1970s were a time
of troubles, with rising oil prices, grain shortages, a sharp increase in import prices, union militancy, and accelerating wages.
Wartime Boom
The American economy entered
the 1960s having experienced multiple recessions.
Inside the Macroeconomy: Aggregate Supply and
Demand
Aggregate Demand refers to the total
amount that different sectors in the economy willingly spend in a given period.
Fiscal policy
Monetary policy
Aggregate Supply refers
to the total quantity of goods and services that the nation’s businesses willingly produce and sell in a given period.
Capital, labor, technology
Potential output
Price level and costs
Key Terms of Macroeconomics
In the beginning of the story (or the exposition), you will need to introduce the setting and characters. You might also want to introduce the main conflict. This part of the story is important because it gives the reader necessary background information and maybe even a first insight into a character’s personality.
Objectives and
Instruments of Macroeconomics
The setting (time & place) of a story can change throughout the plot.
Having surveyed the principal issues macroeconomics, we now turn to a discussion of the major goals and instruments of macroeconomic policy.
Your story can take place wherever your imagination will take you to.
For example: in an elevator, in an enchanted forest, etc. Don't forget to give details of the environment each time the setting changes, otherwise, the story can be confusing. Also, mention the seasons as each of them has unique weather and events.
Measuring
Economic Success
The major macroeconomic goals are a high level and
rapid growth of output, low unemployment, and stable prices
Inflation
Price index
Unemployment rate
Gross Domestic Product
Output
The Birth of Macroeconomics
Characters are essential to a good story. Usually, the protagonist(s) is/are the most affected by the plot. Introduce a character by focusing on their actions, interests, and occupation, as the physical appearance doesn't make a difference in most cases.
The 1930s marked the first stirrings of the science of macroeconomics, founded by John Maynard Keynes
Type in the name of your character.
The U.S. Congress formally proclaimed
federal responsibility for macroeconomic performance
Which traits best describe the character's personality? Choose more if necessary:
introvertedloyalkindindependentquick-thinkingadventuresomeidealisticsweet-naturedcalmrisk-takercreativewittystrictfussyweirdclumsyharshaggressivecarelessclingingcowardlycrueldeceitfulimpulsiveOther
Keynes
(1883–1946) was a many-sided genius who
won eminence in the fields of mathematics, philosophy, and literature.
Choose the type of your chacter:
Protagonist (main character)Antagonist (main character's opponent)Flat (stereotypical character)Round (his/ her personality develops throughout the story)Static (doesn't evolve as a person throughout the story)Dynamic (dramatical change in personality)Confidant (the main character trusts him/ her)Foil (contrasting character who enhances the personality of another character)Other