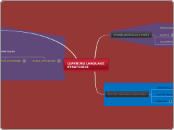
LEARNING LANGUAGE STRATEGIES
Oxford (1990)
TWO major classes:
2).INDIRECT STRATEGIES
SOCIAL STRATEGIES
actions which learners choose to take in order to interact with other learners and with native speakers.
eg.asking question for clarifications.
b). AFFECTIVE STRATEGIES
involve regulating of emotion, motivation and attitudes.
eg.taking your emotional temperature.
a).METACOGNITIVE STRATEGIES
deal with pre-assesment and pre-planning, online-planning and evaluation of langauge use events. such events allow learners to control their own cognition by coordinatingthe planning, organising, and evaluating of the learning process.
eg. centering your learning
1).DIRECT STRATEGIES
c).COMPENSATION STRATEGIES
for using the language despite knowledge gaps.
eg.guessing inteligently,overcoming limititations in speaking and writing.
b).COGNITIVE STRATEGIES
used for understanding and producing teh language. it involve identification,retention, storage or retrieval of words, phrases and other elements of the language.
eg. practicing,receiving and sending message.
a).MEMORY STRATEGIES
involve remembering important things we hear or read in the target language and retrieving of new information.
eg. applying images and sounds, reviewing well.
Prof.Dr. Mohamed Amin Embi
Exam LLS
reading over notes/exercises, studying grammar books, memorising essay formats, doing previous exam papers.
Out-of-Class LLS
conversing in English with friends out side of school, conversing with teachers in school, looking for opportunities to learn English.
Classroom LLS
paying attention in class, listening to teacher's speech, reading over class work, asking friends to clarify, discussing with friends.
O'Malley&Chamot (1985)
socioeffective
part of cooperative learning, which involves peer interaction to achieve a common goal in learning .
cognitive
more direct manipulation of the learning material itselfsuch as repetition,resourcing,translation,grouping,note taking, deduction, recombination, imagery,auditory representation, key word, contextualization,elobaration,transfer and inferencing are among the most important cognitive strategies.
metacognitive
help learners to regulate their own cognition and focus,plan and evaluate their progress as they move towards communicative competence.