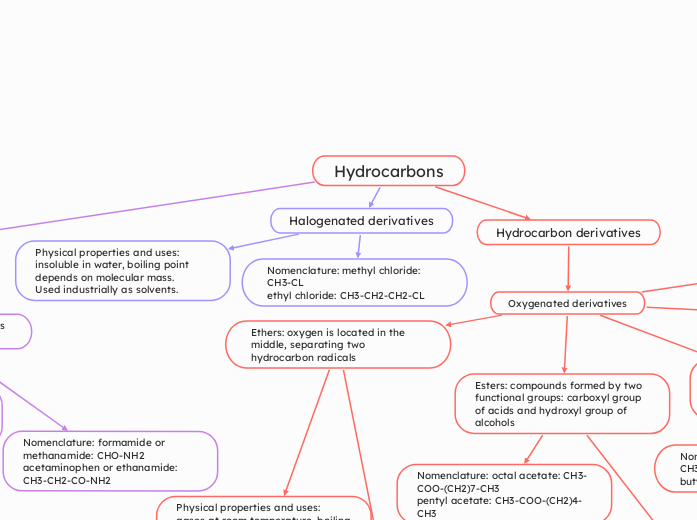
Hydrocarbons
Halogenated derivatives
Nomenclature: methyl chloride: CH3-CL
ethyl chloride: CH3-CH2-CH2-CL
Physical properties and uses: insoluble in water, boiling point depends on molecular mass.
Used industrially as solvents.
Nitrogenated derivatives
Amides: considered derivatives
of carboxylic acids
Physical properties and uses: similar to amines, also employed in textil dye and polymer synthesis industries.
Nomenclature: formamide or methanamide: CHO-NH2
acetaminophen or ethanamide: CH3-CH2-CO-NH2
Amines: derived
from ammonia
Nomenclature: athylmethilamine: CH3-CH2-NH-CH3
triethylamine: CH3-CH2-N-CH2-CH3
CH2-CH3
Physical properties and uses: unpleasant odors.
Used in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals.
Hydrocarbon derivatives
Oxygenated derivatives
Esters: compounds formed by two functional groups: carboxyl group of acids and hydroxyl group of alcohols
Nomenclature: octal acetate: CH3-COO-(CH2)7-CH3
pentyl acetate: CH3-COO-(CH2)4-CH3
Carboxylic acids: the functional group is a combination of carbonyl and hydroxyl groups called carboxyl group
Nomenclature: propionic acid: CH3CH2COOH
butyric acid: CH3CH2CH2COOH
Physical properties and uses: up to 9 carbon atoms are liquids, more than 9 are solids.
Used to manufacture soaps.
Aldehydes and Ketones: two families of derivatives share the same functional group called carbonyl
Nomenclature: methane: CH4
ethane: CH3-CH3
Physical properties and uses: up to12 carbon atoms are liquids, used as starting points for the synthesis of other compounds.
Alcohol: hydrogens are
replaced by hydroxyl groups
Nomenclature: methanol: CH3-OH
ethanol: CH3-CH2-OH
Physical properties and uses: with 5 to 12 carbon atoms are oily liquids, with more than 12, they are insoluble solids.
Used as an industrial solvent and for polymer manufacturing.
Ethers: oxygen is located in the middle, separating two hydrocarbon radicals
Nomenclature: methyl ether: CH3-O-CH3
ethyl methyl: CH3-O-CH2-CH3
Physical properties and uses: gases at room temperature, boiling points are lower than of alcohols of similar molecular masses, solubility similar to alcohols.
Used as a additive and to manufacture ethylene glycol, also for liquid detergents.