visual representations of bonds
Polar molecules will have a slightly negative pole (with higher
density of electrons) and a slightly positive pole
Higher electronegativity = stronger pull on electrons = slightly
negative end
"δ" delta symbol signifies a partial charge
sodium transfers its electron to chlorine to fill its valence shell
covalent bonding
molecular compound
compound formed by two non-metals (2 anions)
The overall charge of a molecular compound
is not always neutral
write the names of each element in the same order as the chemical formula, change the ending of the second element to "ide.", add prefixes (di, tri, mono, etc...) to match the subscripts for each element, never add MONO to the first name .
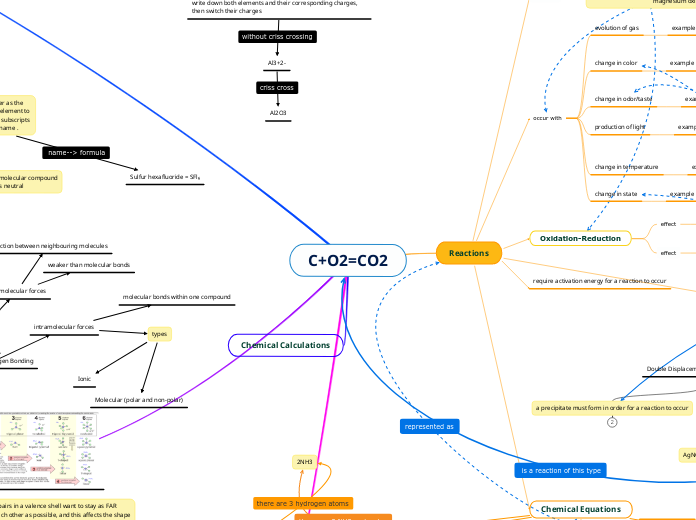
Sulfur hexafluoride = SFl₆
H2O (water)
hydrogen atoms sharing electrons
unstable
atoms share electrons to form a stable outer shell of 8
when electrons are
shared between two or more atoms
how to measure?
electronegativity
difference in electronegativity (∆EN) can be used to determine
ionic compound- ∆EN > 1.7, transferred completely
Na - Cl
bond polarity
molecular polarity
If the central atom has any lone pairs (nonbonding), the molecule is POLAR.
Linear and square planar are exceptions.
A molecule can have polar bonds, but be
non-polar overall depending on the shape
Partial charges can be assigned to atoms or regions
of the molecule
Evaluating all of the bond polarities and overall
shape of the molecule
how do we find the structure?
VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory)
Molecules have different physical and chemical
properties based on their bond and molecular
polarity.
intramolecular forces
Molecular (polar and non-polar)
Ionic
molecular bonds within one compound
intermolecular forces
types
Hydrogen Bonding
Dipole-Dipole
London Dispersion
weaker than molecular bonds
attraction between neighbouring molecules
Electron pairs in a valence shell want to stay as FAR
APART from each other as possible, and this affects the shape
of the entire molecule
allows us to predict the geometry (structure) and molecule
polarity of individual molecules based on the number of
electron pairs that surround the central atom
polar molecule- 0 < ∆EN ≤ 1.7, shared unequally
O - H
non-polar molecule- ∆EN = 0, electrons shared equally
Cl - Cl, N - CL
trend
types of trends
the periodic table of elements reveals unique patterns in the properties of chemical elements.
electronegativity generally increases as you move from left to right across a period and decreases as you move down a group
how do you find the electronegativity of an element?
measure of an atom’s ability to attract a shared
pair of electrons within a molecular bond
transferred between two or more atoms
ionic
elements being held together by
a bond in a fixed ratio
Name-->Chemical Formula
Chemical Formula--> Name
polyatomic group
when there are more than 2 elements, the compound is polyatomic, have to use the back of the periodic table to identify names, criss cross using brackets
Name the metal normally,
and then use the name from
the polyatomic chart on the
back of the periodic table.
Crisscross the charge of the metal
(found on the periodic table) with
the charge on the polyatomic
(found on the back of the periodic
table). Use brackets when the
number of the polyatomic > 1.
multivalent metals
transition metals
capable of having different charges and forming compounds in different proportions are called multivalent metals
rule: roman numerals represent the charge on the multivalent metal ion. Ex Cu⁺² ---> copper (II), can backwards criss cross to find the charge, include roman numerals in word equation and continue to change the ending of the non-metal to "ide"
formula ---> name
Al2O3
aluminum oxide
Name → Formula: CRISS CROSS METHOD
write down both elements and their corresponding charges, then switch their charges
Al3+2-
The non-metal goes second, and you change the ending to “ide”
The full name of the metal goes first
the overall charge of an ionic compound is neutral
the
bond
an attraction that holds two or more
atoms together
is formed by a transfer of electrons
a compound formed between a metal and a non-metal
instability of an atom's nucleus may result from an excess of either neutrons or protons
different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei
isotope
-Atoms of an element that have the same atomic number but different atomic masses
-Isotopes have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons
-Most elements in nature are a mixture of two or more isotopes, which is why the atomic mass is represented as a weighted average
Bronsted-Lowry Theory
when an acid and base are mixed together, the acid will transfer a proton to the base
a base's strength is measured by its ability to receive protons
an acid's strength is measured by its ability to donate protons
HCl+NH3=ClNH4
C+O2=CO2
Solubility
Main topic
Chemical Calculations
Periodic Table
Pure Substance
elements
formed by
Atoms
Parts
nucleus
neutrons
neutral particles found in the nucleus of an atom
protons
positively charged particles found in the nucleus of an atom
crust
electrons
negatively charged particles found in the shell of an atom (outside of the nucleus)
valence electrons
stable
atoms are at their most stable when their outermost energy level is either empty of electrons or filled with electrons.
Models
Bohr Rutherford Diagram
Lewis Diagram
Properties
mass number
isotopes
atomic mass
are classified on
periodic table
by
Periodic Properties
Macroscopic
types of compounds formed
brightness
metallic or non-metallic character
density
boiling point
melting point
Submicroscopic
capacity to capture or lose electrons
electric conductivity
ions
loses an electron
anion
gains an electron
cation
An ion is a charged atom or molecule. It is charged because the number of electrons do not equal the number of protons in the atom or molecule.
atomic volume
Families
according to
atomic number
compound
Reactions
Chemical Equations
A word equation should state the reactants (starting materials), products (ending materials), and direction of the reaction in a form that could be used to write a chemical equation.
Iron and sodium nitrate produce iron (II) nitrate and sodium
Fe(s) + NaNO3 (aq) → Fe(NO3)2 (aq) + Na(s)
Coefficients
The coefficient tells us how many molecules of a given formula are present and is shown preceding the elements
Subscripts
2NH3
indication to the number of atoms of the preceding element
include
Products
the substance(s) to the left of the arrow that is present at the beginning of a chemical reaction
Reactants
the substance(s) to the right of the arrow, this is what is produced from the reactants' reaction with each other and is present at the end of the chemical equation.
Fe(s) + S(s) → FeS(s)
states
HCH3CO2(aq)+NaHCO3(s)→CH3CO2Na(aq)+H2O(l)+CO2(g)
liquid (l)
gas (g)
solid (s)
aqueous (aq)
Types of Reactions
Neutralization
Acid + Base = Salt + Water
acids and bases are determined by their pH levels
Bases
a substance that produces HYDROXIDE IONS (OH⁻) in a solution/take a proton from another compound
most bases contain ions/are ionic compounds that contain a metal and a hydroxide polyatomic group
NaOH = sodium hydroxide, Al(OH)3 = aluminum hydroxide
"__________hydroxide"
corrosive, denature protein and digest fats, react with acids to make neutral solutions.
conduct electricity, slippery touch, water soluble, bitter taste.
Acids
substances that produce HYDROGEN IONS (H⁺) in a solution/they give a proton to another compound
types of acids
oxyacids
contains hydrogen and a polyatomic group that contains oxygen
H3PO4 = phosphoric acid, H2SO4 = sulfuric acid
"__________ic acid (no hydro)"
binary acids
contains 2 elements only: hydrogen and another non-metal
HCl = hydrochloric acid, HBr = hydrobromic acid
naming rule
"hydro_________ic acid"
chemical properties
corrosive, react with metals to produce hydrogen gas (H2), react with bases to produce a neutral solution
physical properties
conduct electricity, taste sour, water soluble.
pH scale
ranges from
very strong base
very strong acid
7.1-14.0
base
7.0
neutral
can be determined by
indicators
universal indicator
full color range
>11
indigo-violet
strong base
ammonia solution (11)
8-11
blue
weak base
baking soda (9)
7
green
pure water (7)
3-6
orange-yellow
weak acid
black coffee (5)
< 3
red
strong acid
vinegar (2)
red cabbage water
litmus paper
0.0-6.9
acid
to measure how
basic
acidic
a substance is
Precipitation
when an aqueous compound reacts to form an insoluble salt called a precipitate. Whether or not a reaction will form a precipitate is dictated by solubility rules ionic compounds.
Combustion (CxHy + O2 = CO2 + H2O + heat energy)
complete combustion
when a fuel reacts quickly with oxygen (O2) and produces carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O)- when there is a good supply of air.
incomplete combustion
when the supply of air or oxygen is poor. H2O is still produced, but carbon monoxide and carbon are produced instead of carbon dioxide.
Single Displacement (A+BC=AC+B)
when one element displaces another in a compound
reaction will occur when the more active metal displaces the metal that is less active
no reaction: Zn+Mg(MnO4)2
no reaction occurs because zinc's reactivity level is lower than that of magnesium's, so it cannot displace it.
reaction: Mg(s)+Cu(NO3)2(aq)→Mg(NO3)2(aq)+Cu(s)
reaction occurs because magnesium is more active than copper, thus displacing it.
activity chart allows us to predict if there were to be a reaction
2AgNO3(aq)+Cu(s)→Cu(NO3)2(aq)+2Ag(s)
a balanced chemical equation
An ERP chart
to accurately reflect the law of conservation, that matter is neither created or destroyed
the number of atoms for each element in the reaction and the total charge is the same for both the reactants and products.
Decomposition (AB=A+B)
when 1 reactant breaks down (decomposes) to form
multiple products
CaCO3→CaO+CO2
Synthesis (A+B=AB)
when 2 or more reactants combine to form one new
product
2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl
Double Displacement (AB+CD=AD+CB)
when two elements in different compounds switch places, forming two new compounds
AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO
a precipitate must form in order for a reaction to occur
reaction indicator
require activation energy for a reaction to occur
Oxidation-Reduction
rancidity
when butter is kept in the open atmosphere than its smell and taste change
effect
corrosion
rusting
occur with
change in state
Subtopic
change in temperature
quick lime with water: CaO + H₂0 = Ca(OH)₂ + Heat
production of light
when oxygen combines with calcium, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and the chemical luciferin in the presence of luciferase, a bioluminescent enzyme, light is produced.
change in odor/taste
rotting food
change in color
when iron reacts with oxygen and develops an orange-red color from rusting
evolution of gas
when zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid, hydrogen gas is evolved with formation of zinc chloride
example
magnesium ribbon when burnt in oxygen is converted into magnesium oxide