af Garrett Sieger 5 år siden
279
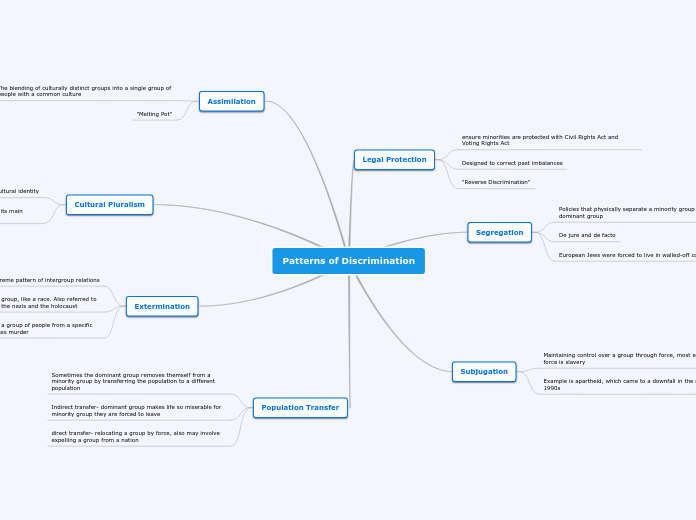
Patterns of Discrimination
Different forms of social and political policies shape the interactions between dominant and minority groups. Discrimination and protection frameworks, like the Civil Rights Act and Voting Rights Act, aim to address past inequities and ensure minority rights.