BIO311D Extra Credit Assignment (Levin)
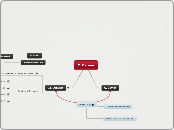
Extinction
Island Size
Large
higher immigration rates
more resources
Small
extinction rate is higher
Process
Fragmentation
think lightbulb
habitat corridor - reduces population fragmentation
single populations in range going out
Contraction
think deflating baloon
Major Causes
Genetic Contributions
Hybridization
minor species always dislves
results in loss of genetic variation
less reproduction
includes homozygosity
Species Introduction
bringing a species to a different country
predation
Overexploitation/Hunting
Habitat Destruction
farmland/asphalt
deforestation
species are not found in all habitats
Speciation
evolutionary process by which new biological species arise
Species
all species arise from previously existing species
groups of actually/potentially interbreeding individuals
Allopatric (geographical)
Models
dumb-bell
ancestral species is divided into two roughly equal halves, each of which forms a new species
peripheral
in which new species forms from a population isolated at edge of an ancestral species range
Series
two populations experience gene flow
gene flow interrupted variant types appear
selection causes divergence in gene pools
reproductive isolation present without geographical barrier. speciation is complete
Global Warming
rise in the average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans since the late 19th century and its projected continuation
Biological Impacts of Climate Change
Responses to Climate Change
Northern range shifts
The spread of parasites and vectors as they’ve shifted northward.
50% of species show a response. (Exists on every continent/every ocean)
Species Extinction
Coral Bleaching
Earlier Spring Events
Altitudinal/poleward shift in species range
The faster global warming, the faster range shifts
Increase in malaria and other subtropical diseases
More intense hurricanes/storms
Increase in ocean temperatures
Atmosphere
Greenhouse effect
the trapping of heat in the atmosphere by certain (so-called "greenhouse") gases.
Examples: heat trapped in car, glass greenhouse for plants
Projected Emissions
All the greenhouse gases will increase:
CFC’s
Water Vapo
Nitrous oxide – from fossil fuels
Methane – from wet agriculture (rice paddies), cows, and ocean bottom
Carbon dioxide
Biomagnification
The increase in the concentration of alien substances from one trophic level to the next. (The substances can not be metabolized.)
Carbon Dioxide
Relationship between CO2 and temperature over time
Predicted that temperatures will increase by 4°C by the end of the century
Positive correlation
not a prevention but a reduction of heat escaping into space
more radiant energy stays in the earth’s atmosphere
but burning fossil fuels contributes to increased CO2 levels in atmosphere
usually in a balanced concentration
Aerosol
DDT - used to kill insects (crop pests)
Invented in WWII to suppress crop pests. (Mosquitos)
DDT has a 95% breakdown time of 10 years.
Population Growth
Resourece
less
decrease in population
more
increase in population
Biological Control
reproductive control
release of incompatible pest strains
use of chemical sterilants
release of sterile insects
Equal amounts of the two factors results in an population equilibrium.
Environmental resistance
bad weather
space
competition
redation
disease
low nutrients, food, water
Biotic potential
Defense mechanisms
ability to withstade adverse conditions
rate of reproduction
Selection
Natural Selction
Sexual Selection
females choosing males and males compete and females choose
Mating Systems
Asexual reproduction
offspring of asexual reproduction are genetically identical to the last generation
Assortative
phenotypic similarities
Consequences
mating for eye color does not change p or q
the rest of the genome is not affected
if ppl with blue eyes mate with others with blue eyes, homozygosity for eye color would increase
Random Mating
independent of genotype and phenotype
Positve Assortative
phenotypically similar
Negative Assortative
phenotypically dissimilar
Inbreeding
mating between relatives
products of inbreeding are inferior than products of non-related individuals
every generation of self-fertilization (“selfing”), heterozygous decreases by half
self-fertilization is the most extreme form of inbreeding
properties
Stabilizing
favors the mean
Heterozygote Advantage
genes in the heterozygous state are superior to the homozygous state
Directional
will skew the distribution in one direction
Disruptive
favors the extremes
Main topic
Organization of Genetic Variation
Subtopic
Decrease in Variation
Intergradation
members of different populations mating with each other
gene flow: movement of individuals between established, existing populations
Founder Effect: loss of genetic variation when a new population is established by a small number of individuals from a larger population (chance deviation)
Geographical Isolation
races evolve separately because the distance between them is too great
race: groups of populations with similar allele frequencies that are different from other related populations
Reproductive Isolation
Mechanisms
Postzygotic barriers
reduce viability or fertility of hybrid
Hybrid Breakdown
F1 hybrid viable and fertile, but F2 and backcross generations aren't
Hybrid Inviability
hybrid dies prior to reproductive maturity
Hybrid Sterility
hybrid is viable, but sterile
Zygotic Mortality
fertilized egg, but no zygote development
Gametic Isolation
cross incompatibility. sperm transfer, but no fertilization
Prezygotic barriers
prevents fertiliztion
Mechanical Isolation
structural differences in reproductive organs
Behavioral Isolation
species isolation. potential mates choose to mate with own species
Ecological Isolation
organisms mate at different locations
Temporal Isolation
organisms mate at different times
Increase in Variation
Adaptive Differentiation
development of different phenotypes from a common ancestor due to adaptations to different environments
adaptation: a trait that enhances survivorship and reproduction
Mutation
random change in genetic code
for men, mutation is age dependent
95% of all homozygous mutations are harmful
ultimate source of genetic variation
generates new alleles