Personality Testing

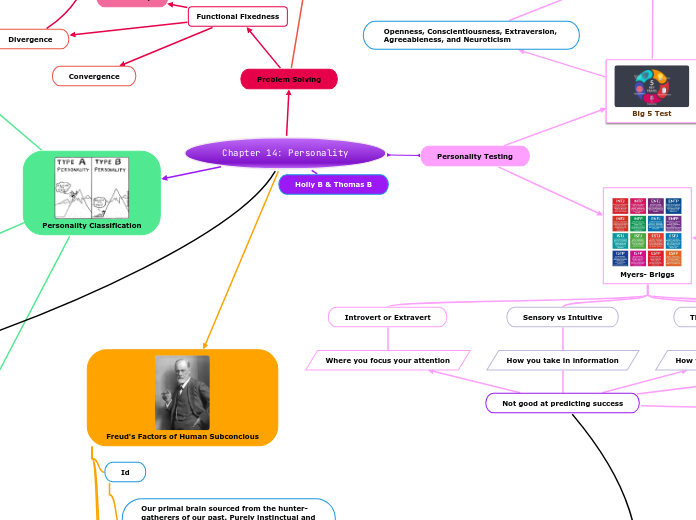
Myers- Briggs
Introvert or Extravert
Where you focus your attention
Sensory vs Intuitive
How you take in information
Not good at predicting success
Thinker vs Feeler
How you make decisions
Judging vs Perceiving
How you structure yourself in the world

Big 5 Test
Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, and Neuroticism
Often considered the most accurate
and diverse form of personality testing currently available
Not defined personality "types", but more broad personality groups that form a gradient between people
Chapter 14: Personality

Personality Classification
Type A vs Type B
Type A: Anal, attentive, work-minded. Tend to prioritize hard work and gain satisfaction from accomplishing tasks that require logical thinking.
Very general and not applicable to all people. Actual humans may lean to one personality type other but the classifications are far to general to provide any concrete psychological evaluation or predict success.
Type B: Relaxed, steady-headed, creative. Tend to gain satisfaction from tasks involving creativity and abstract thinking. Generally laid-back and less engaged with mathematics and similar topics than type A personalities.
IQ and EQ
IQ: Quantified through standardized testing. Score of the test taker's affinity for spatial awareness, math, and analytics.
EQ: Tested through various personality tests and evaluations. Score of the test taker's ability to understand other people's emotions and interact with social situations in positive ways.
Numerically quantifying systems are limited and do not provide reliable way to determine intellect and success.
Growth vs Fixed Mindset
Growth Mindset: A willingness to take failure and turn it into success - exhibits an active desire to improve. Generally sees improvements, even when failure occurs.
Growth mindsets help improve productivity and mood
Fixed Mindset: Lacks initiative or confidence to make improvements. Essentially the doomer mindset - setbacks often can feel like the end of the world, like the person is in question is in quicksand and can't get out.
Problem Solving
4 Stages
1. Problem identified

Freud's Factors of Human Subconcious
Id
Our primal brain sourced from the hunter-gatherers of our past. Purely instinctual and societally unacceptable in the current day, but important for survival nonetheless. Regulated by the superego and its direct opposite.
Ego
The ego acts as a center point between the superego and the id, controlling the Id's animalistic urges to make them more acceptable to the world while also stopping the superego from completely repressing the urges.
Superego
The idealized version of an individual's personality - the segment that manages the ego's behavior and forms complex moral standpoints and beliefs.
Holly B & Thomas B
Less accurate
More accurate
Often considered antiquated due to its questionably racist origins and new research into intellect and its inherent multifactededness
3. Solutions evaluated
2. Potential solutions generated
Functional Fixedness
Creativity
Thinking "outside of the box"
"Name as many things as you can with wheels"
1. Flexibility - how many categories
2. Fluency - How many answers
3. Originality - did anyone else come up with the same answer
4. Elaboration - does it require explanation