Sampling (Trochim)
Probability Sampling
Simple
Stratified
how?
homogenous subgroup
sample
homogenous subgroup
sample
homogenous subgroup
sample
advantages
able to represent key subgroups in population, especially minority groups
more statistical precision (when subgroups are homogenous)
sampling fraction between strata
same
proportionate stratified random sample
different
disproportionate stratifed random sample
Cluster (AREA)
how?
1. divide population into clusters (usually geographically)
2. randomly sample clusters
3. measure all units withing sampled clusters
Systematic
how?
1. number units in population
2. decide on sample size (n)
3. calculate interval size (K = N/n)
4. randomly select integer between 1 and K
5. Take every Kth unit
advantages
easy to do
may be more precise than simple random sampling
Multistage
Non-probability Sampling
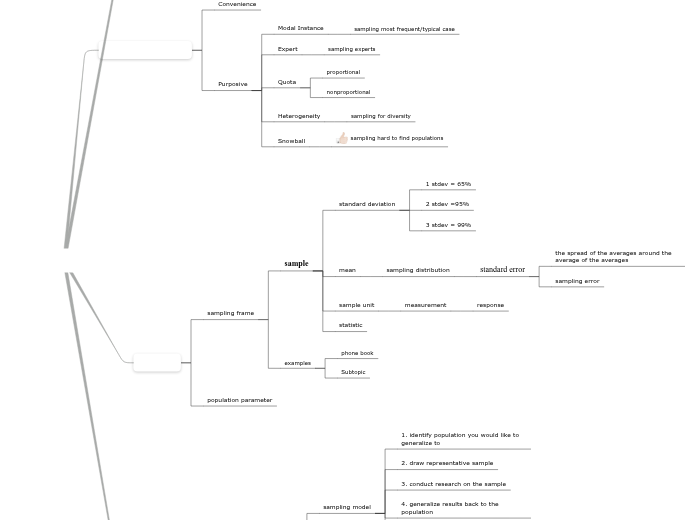
Convenience
Purposive
Modal Instance
sampling most frequent/typical case
Expert
sampling experts
Quota
proportional
nonproportional
Heterogeneity
sampling for diversity
Snowball
sampling hard to find populations
population
sampling frame
sample
standard deviation
1 stdev = 65%
2 stdev =95%
3 stdev = 99%
mean
sampling distribution
standard error
the spread of the averages around the average of the averages
sampling error
sample unit
measurement
response
statistic
examples
phone book
Subtopic
population parameter
external validity
generalization
sampling model
1. identify population you would like to generalize to
2. draw representative sample
3. conduct research on the sample
4. generalize results back to the population
problems
don't know what part of population you want to generalize to
not able to draw fair or representative sample
impossible to sample across all times you want to generalize to
proximal similarity model
gradient of similarity
dimension along which your study context can be related to other potential contexts to which you might wish to generalize
contexts
people
places
times
threats to
ways to improve
draw good sample
keep dropout rates low
use theory of proximal similarity effectively
provide data/descriptions
similarities
differences
do study in a variety of places