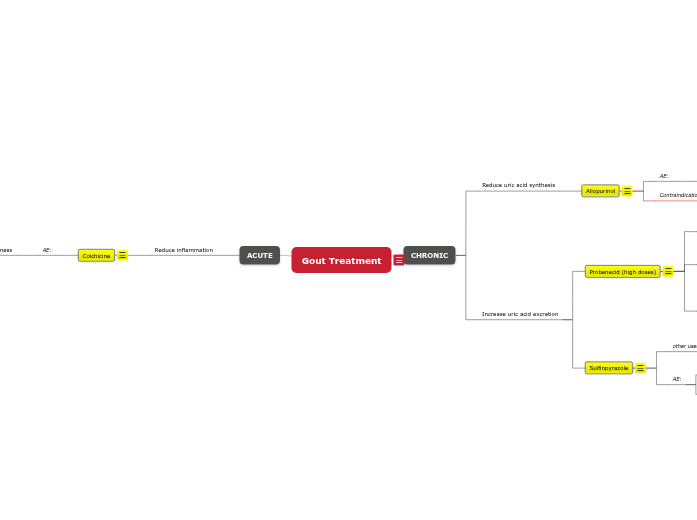
Gout Treatment
ACUTE
Reduce inflammation
Colchicine
AE:
severe n/v, limits effectiveness
CHRONIC
Reduce uric acid synthesis
Allopurinol
AE:
may worsen an acute gouty attack if used as 1st tx
Contraindications
acute gouty attack
Increase uric acid excretion
Probenecid (high doses)
other uses
uncomplicated gonoccocal infxn
AE:
GI disurbances
predisposes to kidney stone
complications
aspirin prevents its action
it antagonizes diuretics
Sulfinpyrazole
other uses:
antithrombic (like aspirin)
AE:
GI side effects
hypersensitivity not common