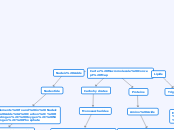
Carter Macromolecule Concept Map
Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides
Elements found in Carbohydrates: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
Carbs Functions: Give us quick and stored energy, make up plant structure,
Examples of Carbohydrates: glucose, fructose, lactose, sucrose, starch, galactose
Unique characteristics: A simple carbohydrate is a chain of sugar molecules called monosaccharides if you combine these sugars you get

Subtopic
Lipids
Triglyceride
Elements found in Lipids: Hydrogen, Oxygen, Carbon
Lipid Functions: Energy storage, cushions organs, insulates body
Lipids Examples: Saturated Fats-butter, coconut oil. Unsaturated fats-plant and fish fats, vegetable oils, liquid at room temp, phospholipids
Unique characteristics: Lipids are non-polar, and they are hydrophobic meaning they don't like water

Subtopic
Subtopic
Proteins
Amino Acids
Elements found in Lipids: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen
Protein Functions: Give us structure, hormones, muscle, strengthen immune system
Examples of Proteins: Muscle, fingernails, skin, hair, enzymes, hormones
Unique characteristics: There are 20 essential amino acids in proteins, there are four layers in protein structure

Subtopic
Nucleic Acids
Nucleotide
Elements found in Nucleic Acids: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphate
Functions of Nucleic Acids: Make up DNA and RNA, store information in the body, transferred from parents to offspring
Examples of Nucleic Acids: RNA and DNA
Unique characteristics: nucleotides are the monomers of nucleic acids. Nucleotides have three parts; phosphate group, pentose sugar, and a nucleotide

Subtopic