Photosynthesis
Sunlight enters the leaf cells and
Moves through the epidermis and mesophyll, captured by the chloroplast
This energy
causes the oxidation reaction of water into H+, O2, and 2 electrons. This occurs when photosystem II loses its original electrons and needs to fill that spot.
oxygen is released into the air as a product
These hydrogen ions are carried to the stroma
These electrons move into photosystem II
moves into the thylakoid and
Hits photosystem II as a photon. This excites the electrons (photoexcitation)
These electrons move down the electron transport chain through a mobile electron carrier
these electrons move into the cytochrome complex and it uses energy from the electrons to carry over 2 hydrogen ions from the stroma to the thylakoid space
This creates a proton gradient, and the hydrogen will normally move from an area of high to low concentration by diffusion.
These hydrogen ions only have one passage to the other side and it is ATP synthase.
As the hydrogen ion moves through ATP synthase, the diffusion allows for the protein to rotate. This action pushes together ADP and Pi
This produces ATP, a product that is used in the next reaction
The electrons continue to move through the electron transport chain until they reach photosystem I
Once these electrons get re-excited, they move onto another mobile electron carrier and the energy they create is used to help make NADPH from NADP+, 1 hydrogen ion, and 2 electrons.
The NADPH is a product of this reaction, used in the next reaction.
Diagram of the light dependant reaction
ADP and Pi enter the cell, into the stroma
The first step in the light independent reaction (calvin cycle) is carbon fixation. In this step a protein called RuBisCo (ribulose 1,5 bisphosphate carboxylase oxidase) is used to attach three molecules of carbon dioxide and three molecules of RuBP (ribulose bisphosphate)
This produces a molecule with a 6 carbon chain but this structure is very unstable. Due to this, each 6 carbon chain, breaks apart into 2 molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate. When all molecules of CO2 and RuBP have reacted, it produces 6 molecules of 3-Phoshoglycerate
Each molecule of 3-phosphoglycerate reacts with one molecule of ATP and one molecule of NADPH. This is the reduction phase.
The two electrons from the NADPH attach to the 3-phosphoglycerate and produce a molecule of G3P (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate). Plants can convert this compound into virtually any carbohydrate.
When all molecules have reacted with the ATP and NADPH, 6 molecules of G3P are produced.
One molecule of G3P leaves the reaction to be used by the cell
The remaining 5 molecules of G3P react with 3 molecules of ATP, producing RuBP so that the calvin cycle can start again. This is the third and final stage called regeneration
The ATP breaks apart into ADP and Pi and it leaves the calvin cycle.
Three molecules of RuBP are ready to be used to repeat the cycle

Stage 3: Regeneration
NADP+, ADP and Pi are products of ths reaction
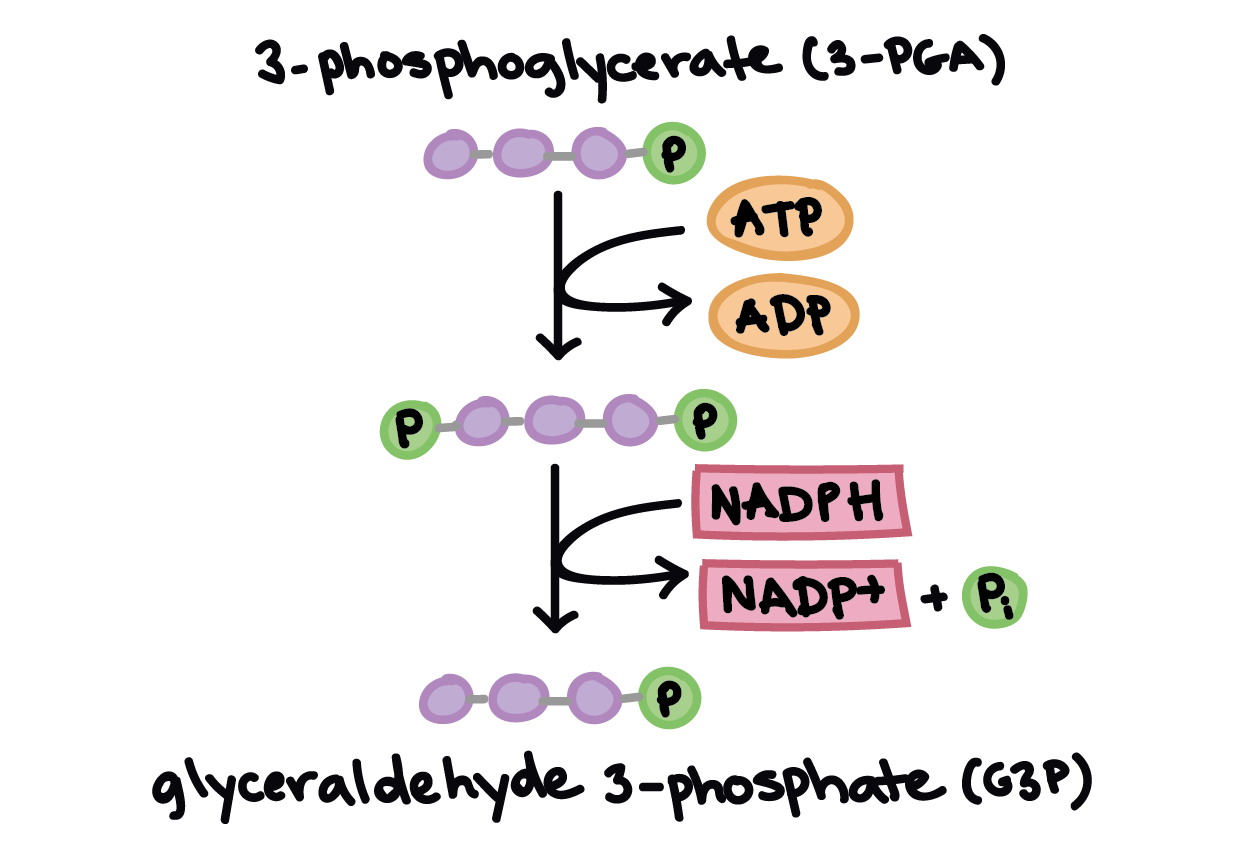
Stage 2: Reduction
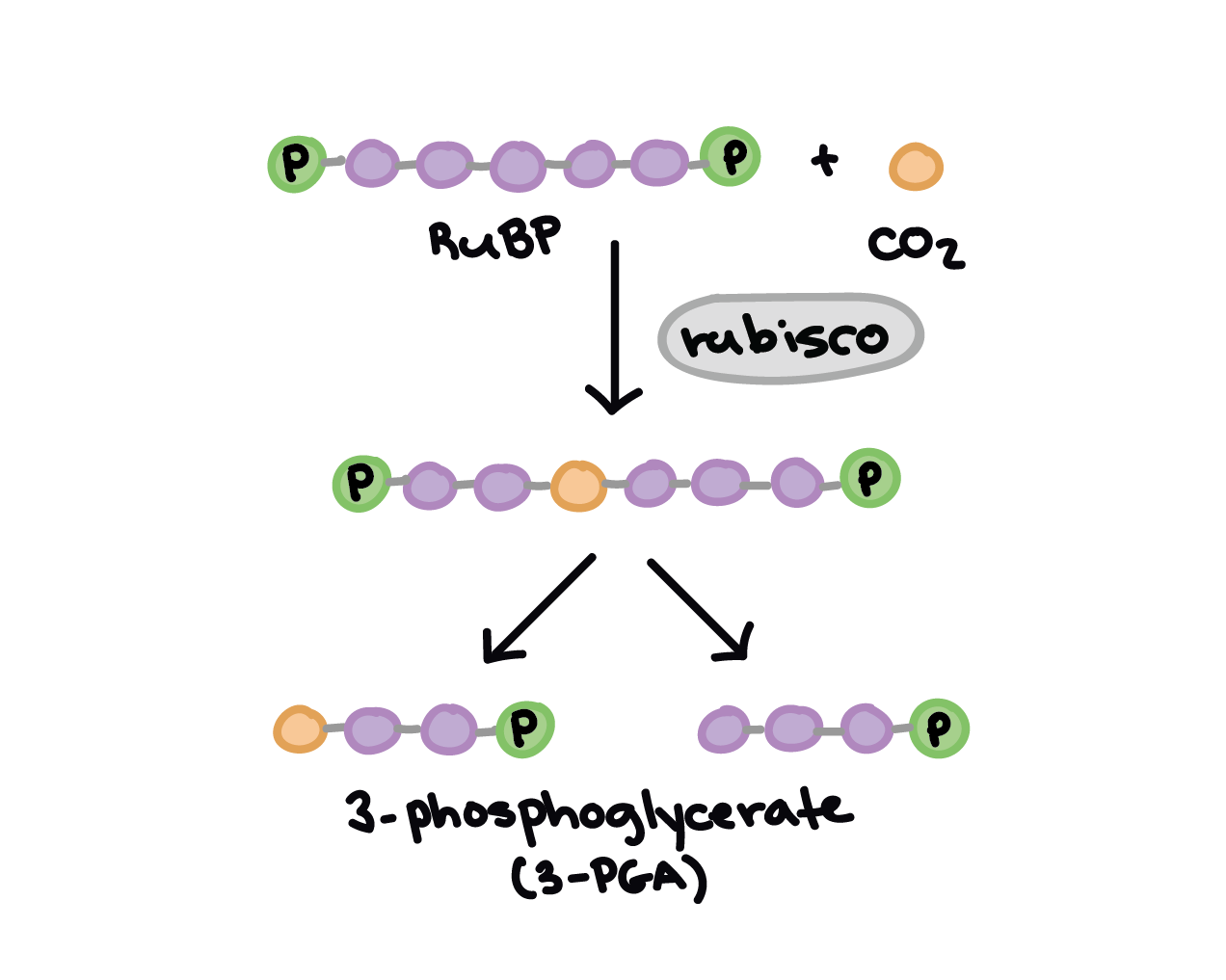
Stage 1: Carbon Fixation
