Epithelial
simple
simple squamous
flat and thin
diffusion and filtration
air sacs in the lungs and capillaries
single layer
simple cuboidal
secretion and absorption
kidneys, tubules,ducts, and covering the ovaries
simple columnar
secretion and absorption
digestive tract and uterus
scattered goblet cells to secrete mucus

simple

simple squamous

simple cubodial
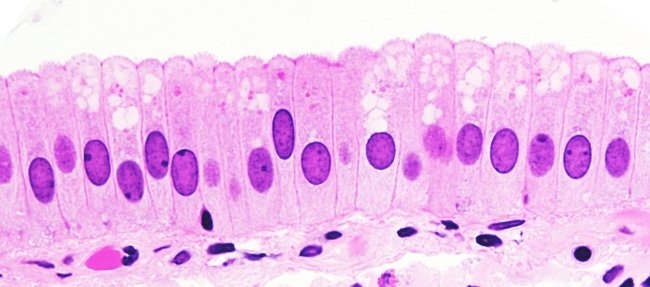
simple columnar
stratified squamous
multi layer squamous functions in protection
lining body cavities and skin and the mouth
stratified cuboidal
stratified Columnar
inside the eyelids and areas of tissue transition
used for protection and mucous secretion

Subtopic


stratified cubodial
Pseudostratified columnar
appear stratified, single layer of cells, nuclei different levels
can have cillia, goblet cellls, and secrete mucus
secreation and cillia aided movement
lining air passages and tubes of reproductive system

pseudostratified columnar
Transitional Epithelium
stretchable
blocks diffusion
urinary bladder
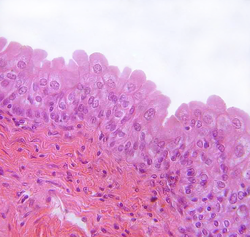
Subtopic
transitional Epithelium
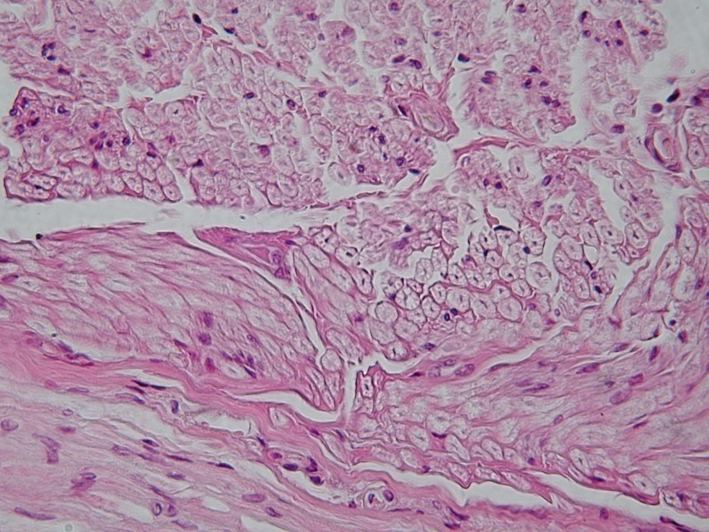
Glandular Epithelium
cells are specialized to secrete substances
make up glands
saliva

Glandular Epithelium
Connective
Loose tissue or Areolar tissue
binds underlying organs to skin and to each other
forms delicate thin membranes throughout the body

Subopic
Loose Tissue
Adipose Tissue(fat)
protective tisssue
stores energy
insulation to preserve body heat

Adipose
Fibrous Tissue
Tendons= muscles to bones
Ligaments= bones to bones
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dense_connective_tissue-56a09aee3df78cafdaa32ca1.jpg)
Fibrous
cartilage
cells are called chondrocytes
Hyaline
Elastic
External ear and larynx

Fibro
tough, shock absorbing
between the vertebrate

Subtopic
Fibro
Blood Tissue
Subtopic
bone

Subtopic
Muscle Tissue
smooth tissue

cardiac Muscle

skeletal

Nerve Tissue
Neurons transmit signals
support the cells