Eukarya
Protista
Animal-Like
Autotrophic
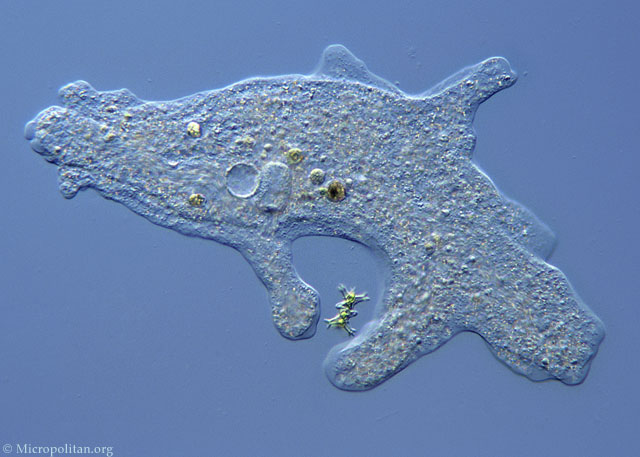
Sarcodines
Pseudopods stretch towards
prey
Ameoba Proteus
Subtopic
Ciliates
Tiny hair around
organism called Cilia
Propel It
Paramedcium

Zooflagellates
Move by beating
a long whip like Flagella
Trypansoma Gambiense

Sporozoan
Do not move
Plasmodium

Fungi-Like
Saprophytic Heterotrophic
Acelluar Slime Molds
Red Raspberry Slime Mold
Water Molds
Pernonosporales

Cellular Slime Molds
Dictyostelium
Plant-Like
Heterotrophic
Rhodophyta
Red Algae

Dinoflageliates
Gonyaulax Catenella
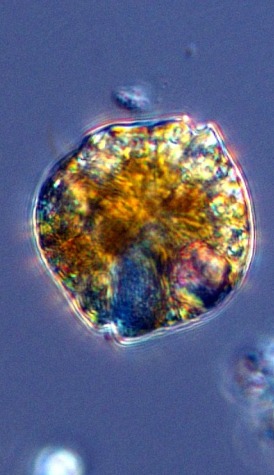
Eugenoids
Euglena

Fungi
Ascomycota
Reproduces asexually or sexually.
in asexual, the fungus undergoes
fission, the cells splits apart to create
a copy of the fungus which can split apart.
In sexual, the two gametes have to combine
Pezizomycotina

Zygomycota
Reproduces asexually or sexually.
In asexual, hyphae produce sporangium,
which then burst to release spores,
which then germinate and produce more fungi.
In sexual, gametes form at the top of hyphae,
and combine with each other to reproduce
Rhizopus Stolonifer

Deutermycota
They do reproduce asexually
and undergoes sporogenesis
like other fungi. When the cell splits apart,
and creates a copy of the fungus
Aspergillus Niger
Basidiomycota
Reproduces asexually and sexually,
during sexual reproduction, Mycelia of
different mating strains combine to create
Mycelium. It reproduces asexually like other fungi
Agaricomycetes

Plantae
Bryophytes
Schreberi
Adaption:
- Found in fresh water,
they begin to adapt in that environment
- Grow in the water

Pterophyta
Pteropus
Adaption:
- contains a stem, allows for structural
support, and to give nutrients
- Reproduce by using haploid spores

Gymnosperms
Melinjo
Adaption:
- Contains roots, that help gather nutrients
- By using the xylem and phloem tissues

Angiosperms
Albosetulosa
Adaption:
- Have their own way of bringing nutrients
around the plant
- Live on land
- Produce flowers and covered seeds

Animalia
Porifera
Demosponge
It developed a stomach and
and flagellated cells to create
the flow of water

Cnidaria
Hydrozoans
Developed defense
mechanisms, as well
as, a nervous system

Platyhelminthes
Taenia
Developed body segmentation

Nematoda
Tubeaform
Developed two
opening, which
helps in digesting
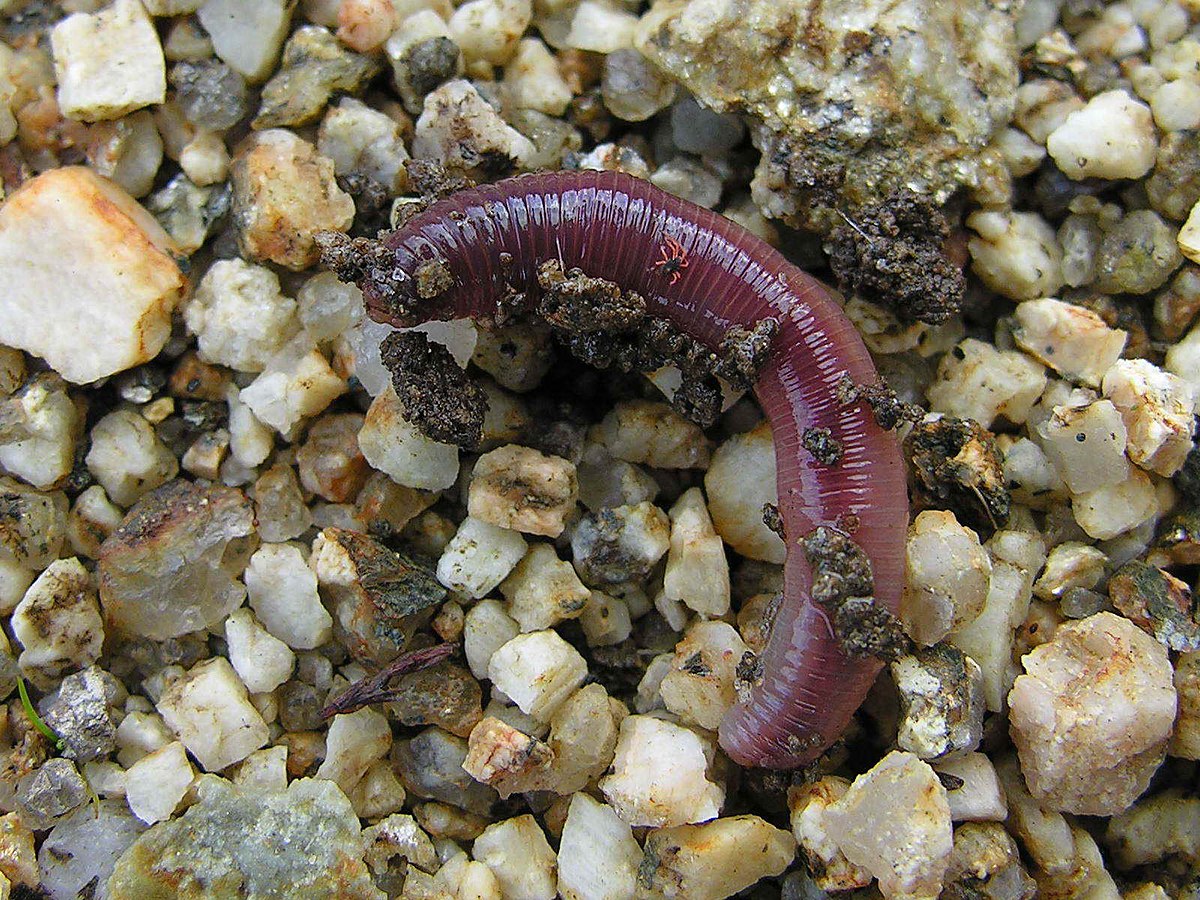
Annelida
Clitellata
Developed a circulatory
system, and digestive
system
system and digestv

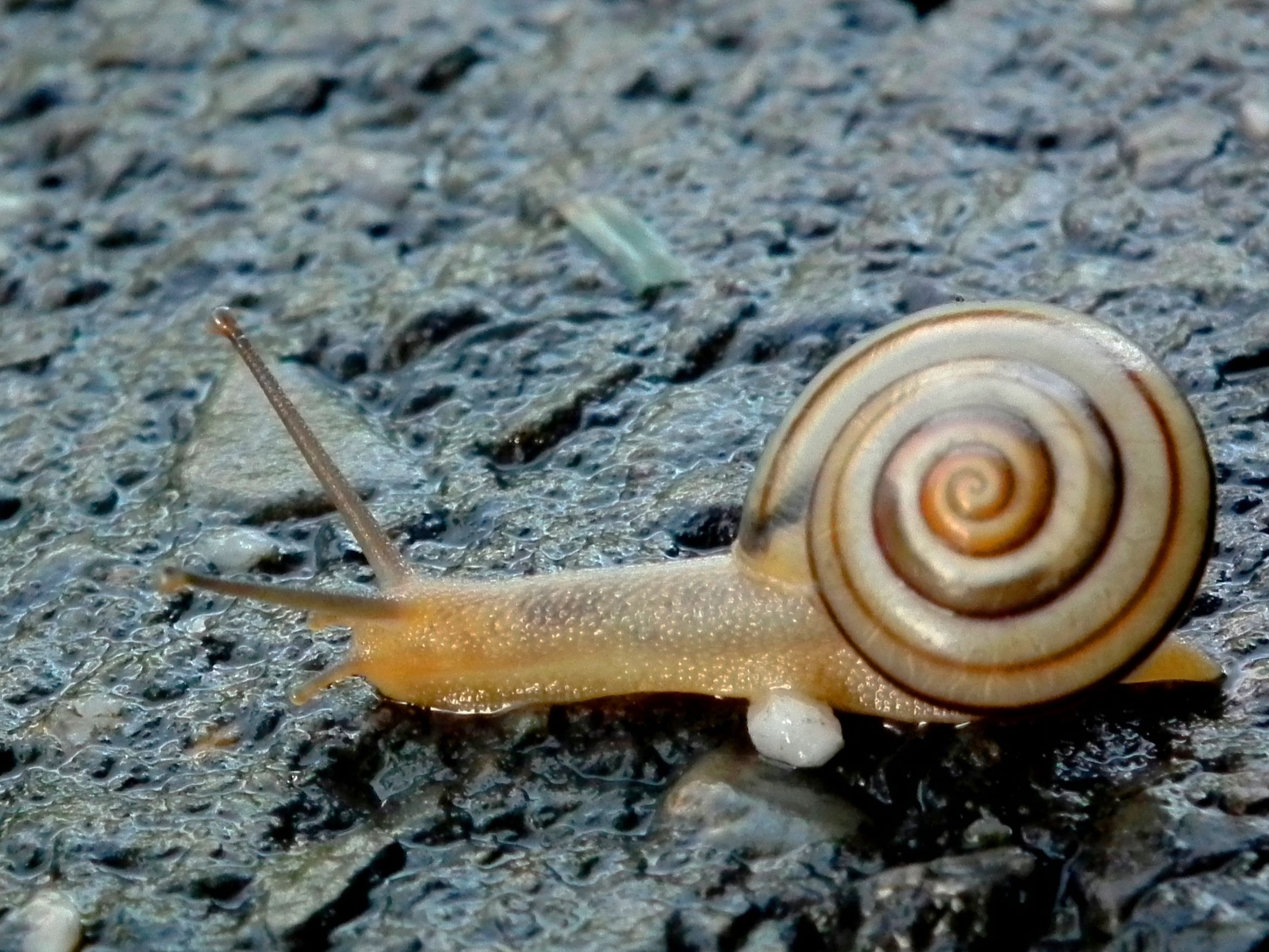
Mollusca
Gastropods
Developed an advanced
digestive and circulatory
system
digestuve ab

Subtopic
Echindordermada
Asteroidea
Have multiple nerves
that help extend the arms
Domains of Life
Bacteria
Archaea
Arthropoda
Myriapoda
Chilopoda
Cingulata
Diplopoda
Sierra
.jpg)
Symphyla
Immaculata

Pauropoda
Amicus

Crustacea
Branchilopoda
Salina
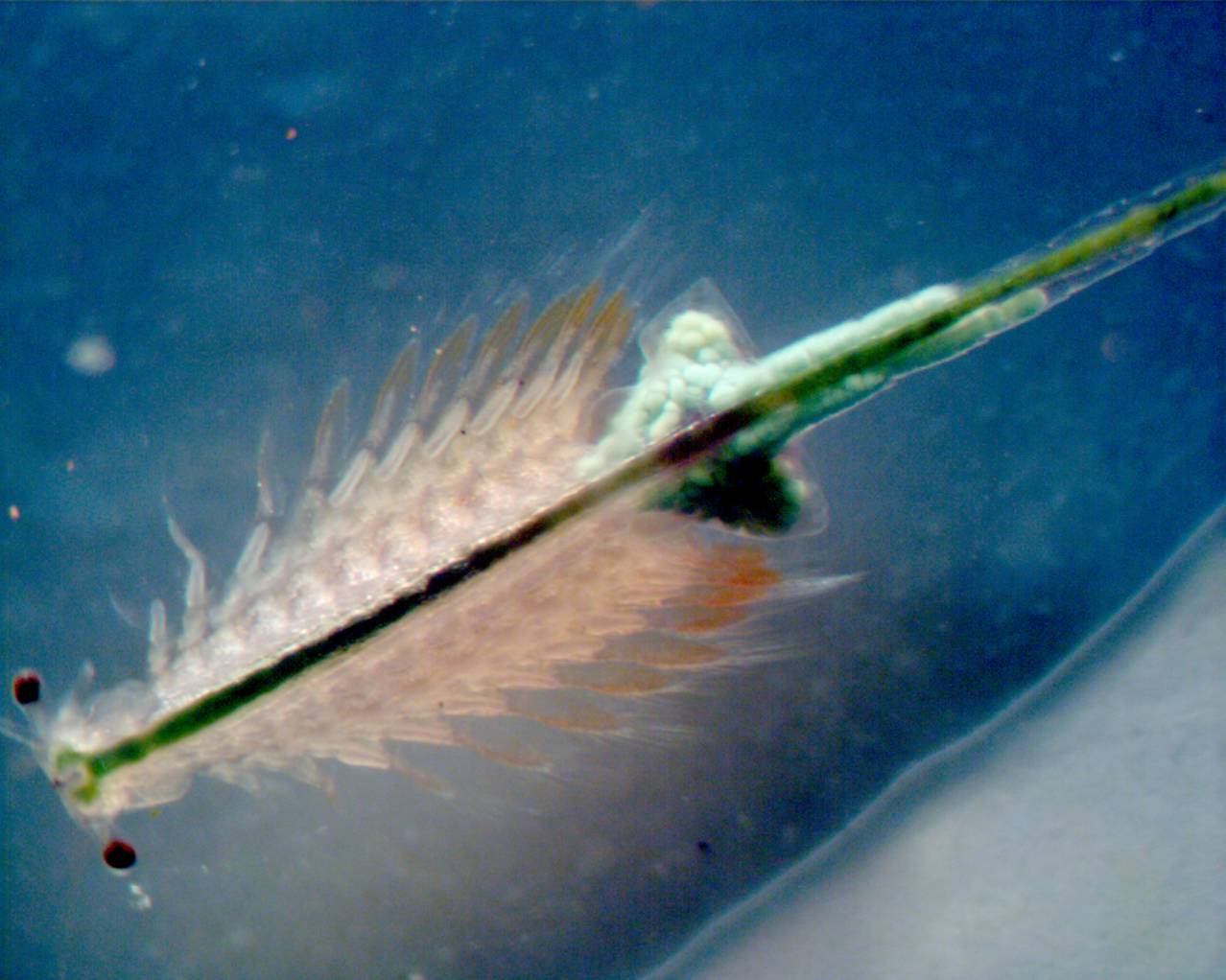

Malacostra
Grapsus

Maxillopoda
Pavo

Ostracoda
Mediterranea

Hexapoda
Insecta
Livida

Enthognatha
Sensillata

Chelicerates
Arachnida
Acariformes
Merostromata
Polyphermus
Subtopic
pycnogonida
Hydrozoans
Subtopic
Eubacteria
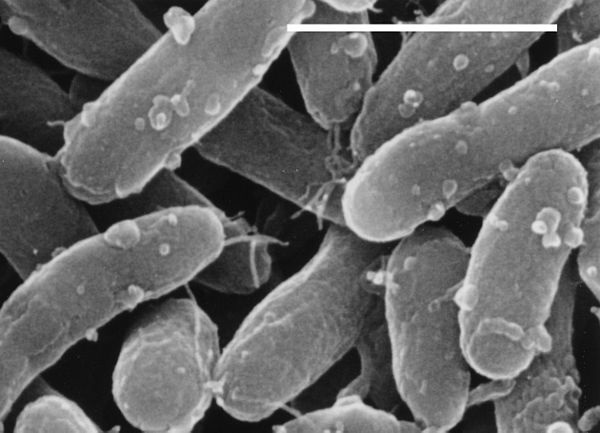
Bacillus
Bacillus Circulans

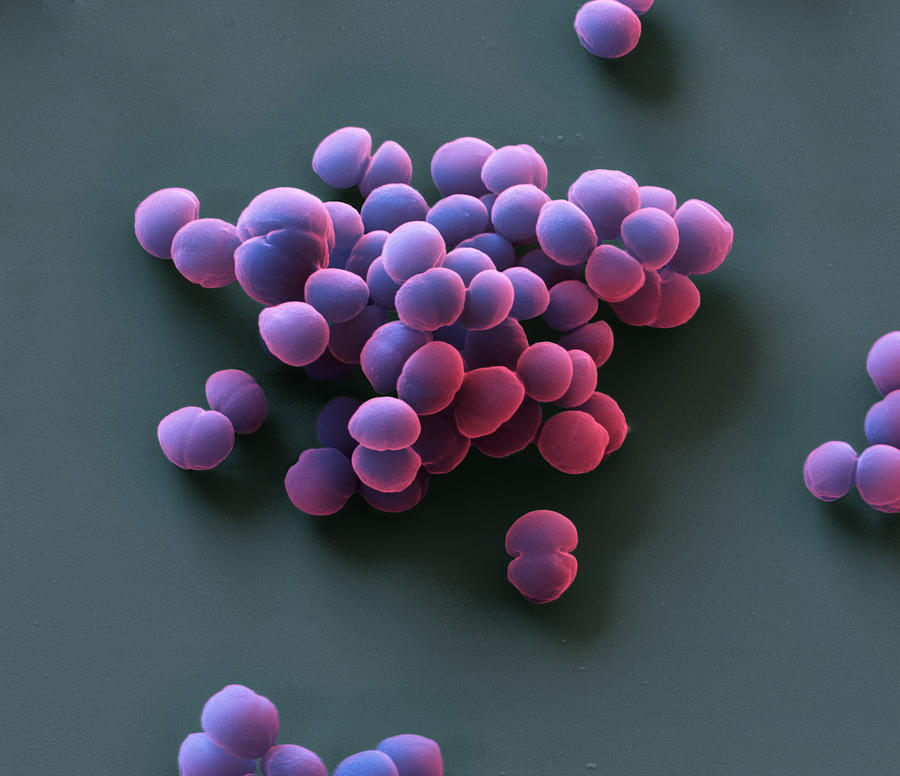
Coccus
Staphylococcus Epidermidis
sprillum
Campylobacter Jejuni

Archaeabacteria
Methanogens
Halophiles

Thermoacidphiles
Chordata
Tunicates
Vertebrate
Agnathans
Gnathostomata
Osteichthyes

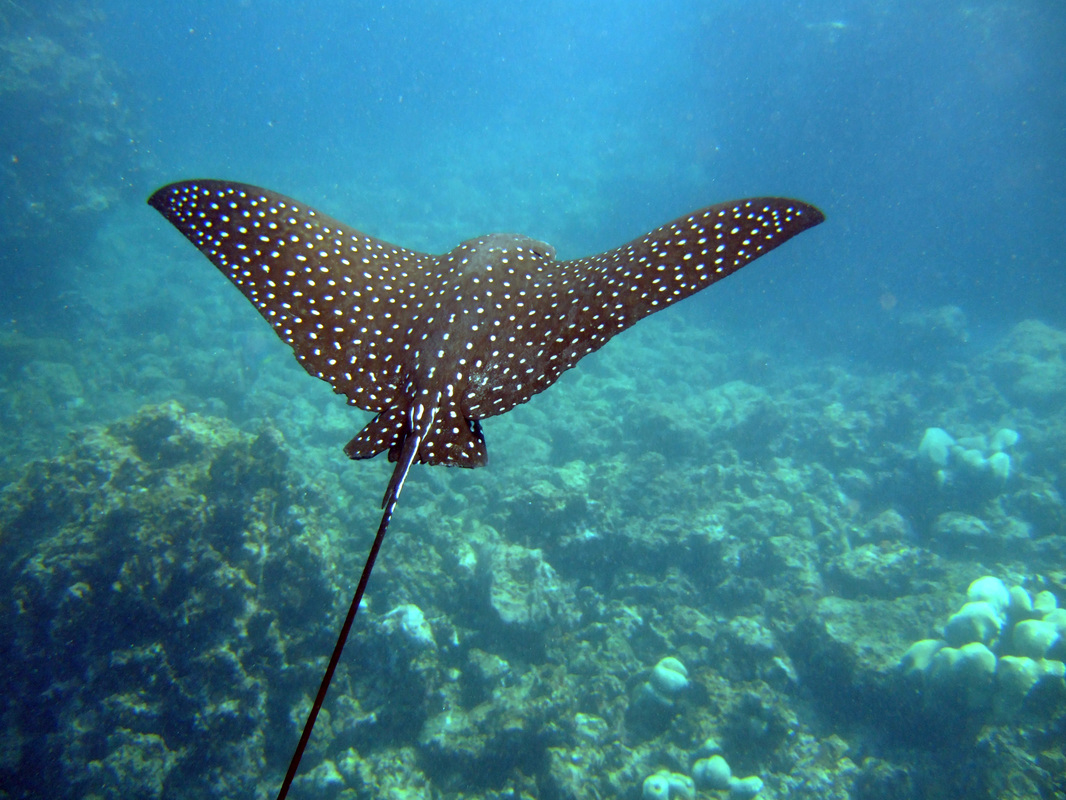
Chondrichthyes

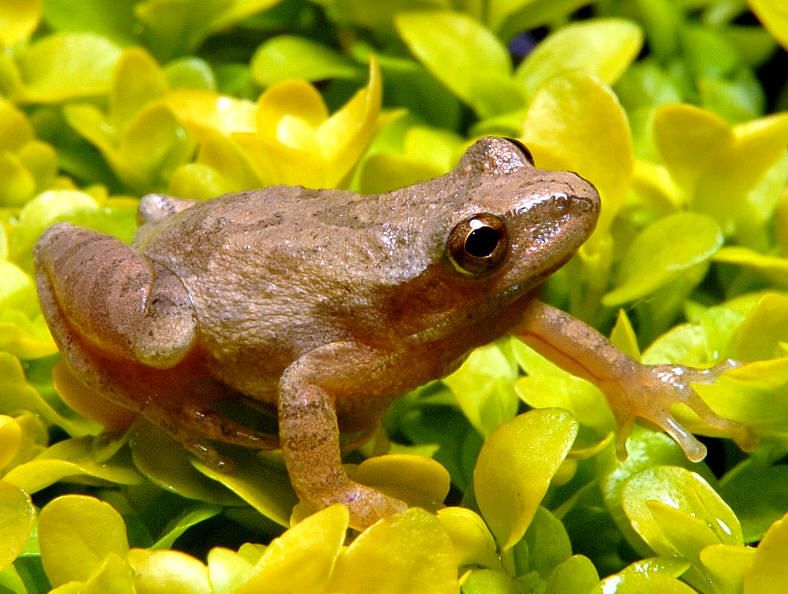
Amphibia

Reptillia

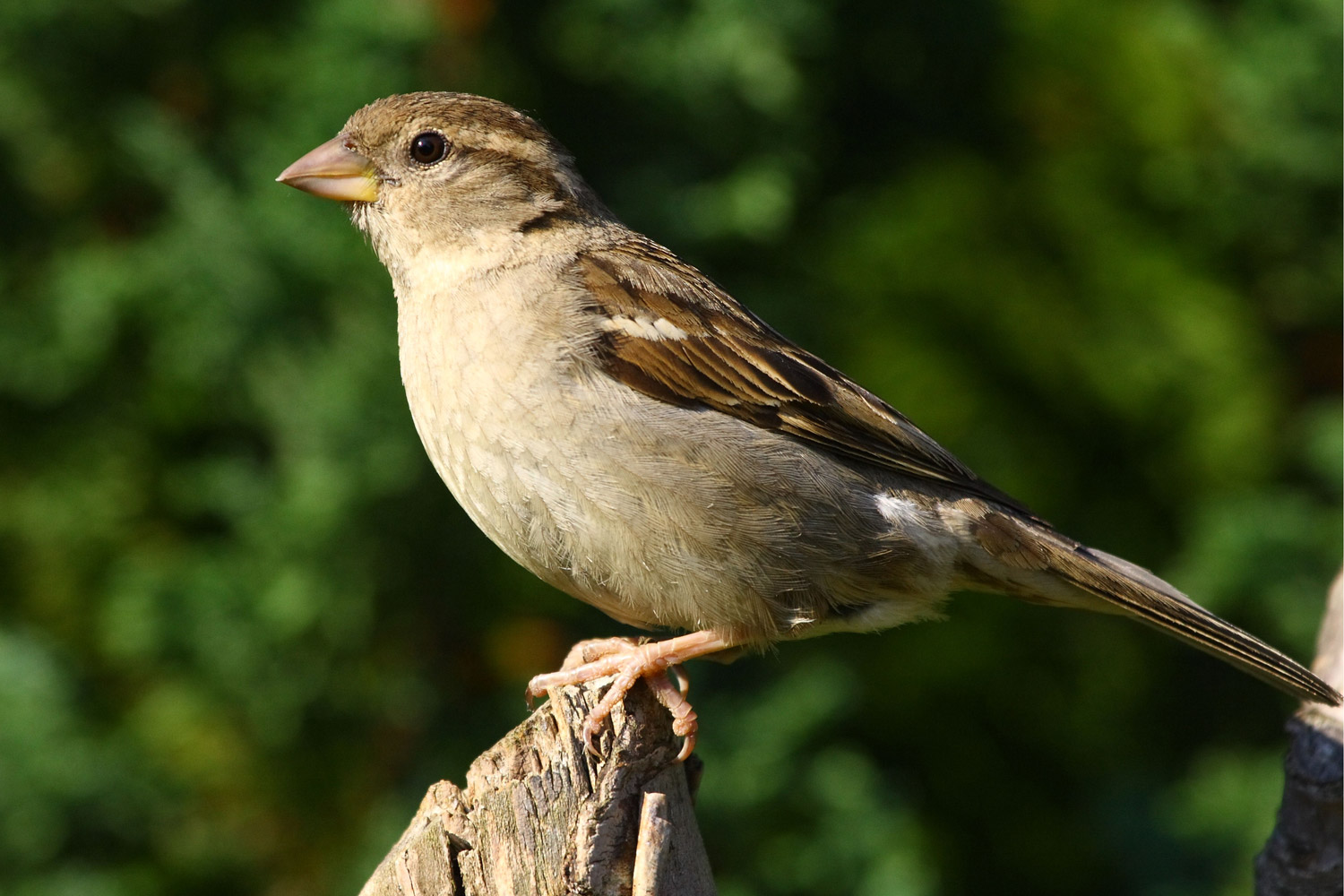
Aves

Mammalia
Placentals
Young nourished by
placenta
It is more superior because the offspring are able to develop
completely inside the mothers body, unlike Marsupial where they are born immature. Since they are born mature, they have have higher chance of survival
Monotremes
Egg layers
Marsupial
Small immature
fetus
It is more superior because monotreme offspring are less likely to survive, due to the fact that their eggs are harder to protect