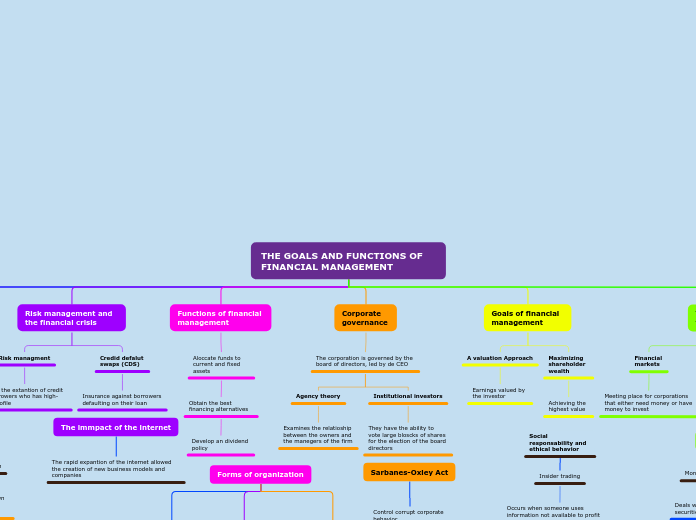
THE GOALS AND FUNCTIONS OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
The field of finance
Economics
Provides a structure for decision making
Accounting
Provides finance data through the statements
Evolution of the field of finance
Financial capital
Money, credit
Real capital
Long-term plan and equipment
Risk management and the financial crisis
Risk managment
Allows the extantion of credit to borrowers who has high-risk profile
Credid defalut swaps (CDS)
Insurance against borrowers defaulting on their loan
Functions of financial management
Aloccate funds to current and fixed assets
Obtain the best financing alternatives
Develop an dividend policy
Corporate governance
The corporation is governed by the board of directors, led by de CEO
Agency theory
Examines the relatioship between the owners and the manegers of the firm
Institutional investors
They have the ability to vote large bloscks of shares for the election of the board directors
Goals of financial management
A valuation Approach
Earnings valued by the investor
Maximizing shareholder wealth
Achieving the highest value
The role of the financial markets
Financial markets
Meeting place for corporations that either need money or have money to invest
Public financial markets
Borrowers of funds for education, welfare,etc
Corporate financial markets
Where corporations such as Nike and Ford raise funds
Format of the text
Introduction
Examines the goals and objectives of the financial management
Working capital management
Techniques for managing the dhort-term assets ans liabilities are examined
The capital budgeting process
The decision on capital outlays
Modern issues in finance
Capital structure theory
The study of the relative importance of debt and equity
Inflation
Increase of prices
Desinflation
A slowing down of prices increases
The immpact of the internet
The rapid expantion of the internet allowed the creation of new business models and companies
Forms of organization
Sole propertioship
Represents single-person ownership and offers simplicity at decision making
Partnership
Two or more owners
Corporation
Its a legal entity unto itself
Articles of incorporation
Subchapter S corporation
Sarbanes-Oxley Act
Control corrupt corporate behavior
Social responsability and ethical behavior
Insider trading
Occurs when someone uses information not available to profit
Structure and fuctions
Money Markets
Deals with short-term securities
Capital markets
Markets that have a life of more than a year