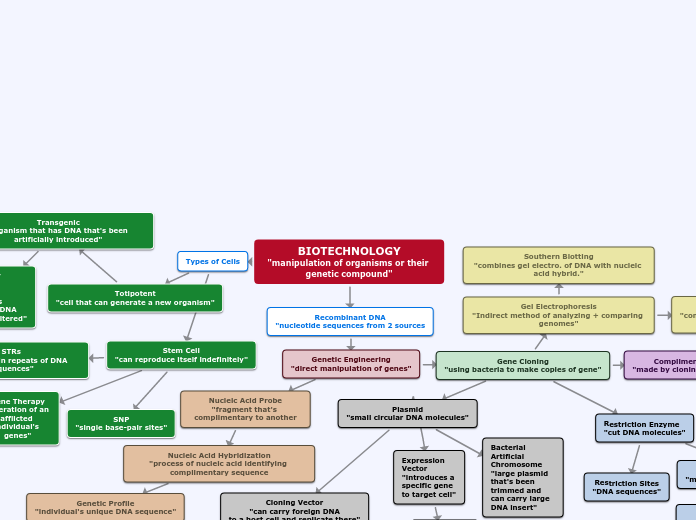
BIOTECHNOLOGY
"manipulation of organisms or their genetic compound"
Recombinant DNA
"nucleotide sequences from 2 sources
Genetic Engineering
"direct manipulation of genes"
Gene Cloning
"using bacteria to make copies of gene"
Plasmid
"small circular DNA molecules"
Cloning Vector
"can carry foreign DNA
to a host cell and replicate there"
Cloning
"creating copies of cells/DNA"
DNA Microarray Assays
"compare patterns of gene expression"
Bacterial Artificial Chromosome
"large plasmid that's been trimmed and can carry large DNA insert"
Yeast Artificial Enzyme
"chromosomes derived from the DNA of yeast"
Expression Vector
"introduces a specific gene to target cell"
Electroporation
"introducing DNA to bacteria using electricity"
Polymerase Chain Reaction
"can produce many copies of a target segment of DNA"
Restriction Enzyme
"cut DNA molecules"
Restriction Sites
"DNA sequences"
Restriction Fragments
"many cuts made by restriction enzymes"
Sticky Ends
"fragments that bond with other fragments
DNA Ligase
"enzyme that seals bonds"
Complimentary DNA
"made by cloning DNA in vitro"
cDNA
"represents the subset of genes transcribed into mRNA"
Gel Electrophoresis
"Indirect method of analyzing + comparing genomes"
Southern Blotting
"combines gel electro. of DNA with nucleic acid hybrid."
Northern Blotting
"combines gel electro. of mRNA followed by hybrid. with a probe on membrane"
Nucleic Acid Probe
"fragment that's complimentary to another
Nucleic Acid Hybridization
"process of nucleic acid identifying complimentary sequence
Genetic Profile
"individual's unique DNA sequence"
Types of Cells
Stem Cell
"can reproduce itself indefinitely"
SNP
"single base-pair sites"
Gene Therapy
"alteration of an afflicted individual's genes"
STRs
"variations in repeats of DNA sequences"
Totipotent
"cell that can generate a new organism"
Transgenic
"organism that has DNA that's been artificially introduced"
Genetically Modified Organisms
"organisms where the DNA has been altered"