Common Ancestor for All Life -ester bonds
-DNA present
Bacteria
-simple RNA polymerase
-no histones
-no membrane bound organelles
-membrane bound nucleus
-cell wall contains peptidoglycan
Eukarya and Archaea Common Ancestor -presence of histones
-multiple RNA
-no peptidoglycan

Eukarya
-membrane bound organelles
-chromosomes in membrane bound nucleus
Archaeplastida
-primary plastids
Common ancestor of chlorophytes, charophytes, and land
plants
-Chlorophyll a & b and b-carotene (traits chart)
-Cellulose-rich cell walls (traits chart)
Common ancestor of charophytes and land plants
-ring-shaped cellulose-synthesizing proteins (traits chart)
-phramgoplast

Common ancestor of land plants
-sporic life cycle
-embryo
-dessication-resistant spores
-gametangia
-sporangia
Common ancestor of mosses, hornworts, lycophytes,
monilophytes, gymnosperms, angiosperms
Common ancestor of hornworts, lycophytes, monilophytes,
gymnosperms, angiosperms
Common ancestor of lycophytes, monilophytes,
gymnosperms, angiosperms
-Lignin
-xylem and phloem
-thick waxy cuticle
-stomata
-leaves
Common ancestor of monilophytes, gymnosperms, angiosperms
-megaphylls
Common ancestor of gymnosperms and angiosperms
-pollen
-seeds
-heterospory
-wood
-ovules
Gymnosperms
Bald Cypress

Scotts Pine
Angiosperms
-endosperm
-fruit
-flowers
-ovaries

Southern Magnolia

White Water Lily

Monilophytes
Eastern Marsh Fern

Lycophytes
Fan clubmoss

Hornworts
Field Hornwort

Mosses
Wooly Feather Moss

Liverworts
Common Liverwort

Charophytes
Braun's stonewort
-zygotic life cycle

Chlorophytes

Rhodophyta
-phycoerythrin photosynthetic agent
Unikonta
-heterotrophic

Opisthokonta
-single posterior flagellum on swimming cells
-absorptive heterotrophy
Common Ancestor of Choanoflagellatea and animals

Choanoflagellatea
Kingdom Animalia
-multicellularity
-mobility
-complex organ systems
-gametic life cycle

Porifera
-asymmetry
-no tissues
Eumetazoa
-tissues
Bilateria
-triploblasty
-bilateral symmetry
-cephalization
Deuterostomia
-radial and indeterminate cleavage

Chordata
-notochord
-dorsal nerve cord
-pharyngeal slits
-endostyle
Common Ancestor of vertebrates and urochordates
Vertebrata
-cranium
-vertebral column
Gnathostomes
-jaws
-bony skeleton

Chondrichthyes
-bony skeleton lost
-cartilaginous skeleton in extant species
Osteichthyes (bony fishes)
-lungs/ lung derivatives

Ray-finned fishes (actinopterygii)

Lobe-finned fishes (Sarcopterygii)
-skeleton extends into the fin
Common ancestor of lungfishes and tetrapods
Tetrapods
-4 limbs with digits

Amphibians
-non-amniotic egg
Amniotes
-amniotic egg
Mammals
-hair
-milk
Common ancestor of Marsupials and Eutherians
Eutherians
Marsupials
Monotremes
-egg-laying mammals

Reptiles
-ectothermic
Lepidosaurs (snakes, lizards, amphisbaenians)
Archosaurs

Turtles
Common ancestor of birds and crocodilians
Birds (Aves)
Crocodilians

Lungfishes

Coelocanths
Agnathans
(Cyclostoma)

Petromyzontida (lampreys)

Myxini (hagfish)
Urochordata

Cephalochordata

Echinodermata
-"spiny skin"
-water vascular system
-adults radially symmetrical, larvae are bilaterally symmetrical
-no brain
-complete digestive tract
Holothuroidea
-sea cucumbers
Ophiuroidea
-brittle stars
Echinoidea
-sea urchins and sand dollars
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/sea-star-underwater-1068024188-d6f4e834df784a24a0892b7e10051b03.jpg)
Asteroidea
-sea stars
Protostomia
-spiral and determinate cleavage
-blastopore becomes mouth
Lophotrochozoa
-lophophore and/or trocophore larvae

Platyhelminthes
-acoelomates
-incomplete digestive tract
-no respiratory or circulatory system

Free-living Rhabditophorans
Trematodes
-parasitic
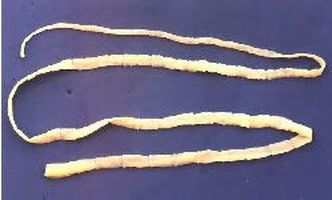
Tapeworms
-parasitic
-no digestive
Common ancestor of Mollusca and Annelids

Annelida
-segmented worms
-closed circulatory system
-complete digestive tract

Mollusca
-soft-bodied
-foot, visceral mass, mantle
-coelomates
-organ systems

Gastropoda

Cephalopoda
-reduced or absent shell (except nautilus)
-closed circulatory system
Bivalvia
-two-part shell
Ecdysozoa
-ecdysis
-metamorphosis (most)

Anthropoda
-"jointed foot"
-segmented
-exoskeleton made of chitin
-complete digestive tract
-open circulatory system

Pancrustaceans

Crustaceans
-cephalothorax

Hexapoda
-six legs
-insects
-many have wings (crucial to their success as a group)
-head, thorax, abdomen

Chelicerates
-cephalothorax and abdomen
-4 pairs of walking legs, pedipalps, chelicerae

Nematoda
-round worms
-free-living and parasitic
-cuticle
-pseudocoelom
-complete digestive tract
Cnidaria
-radial symmetry
-diploblasty
Medusozoa

Hydrozoa
-polyp and medusa

Scyphozoa
-usually only medusa

Anthozoa
-usually only polyp

Kingdom Fungi
-multicellularity
-chitin cell wall
-zygotic life cycle with dikaryotic stage

Amebozoa -pseudopiles
SAR Clade
Common ancestor of Stramenopila and Alveolata
Stramenopiles
-tripartite flagellar hair
-secondary plastida

Diatoms

Kelp

Alveolata
-membrane vesicles
-secondary plastids
-Dinoflagellates have secondary or tertiary plastids
Rhizaria
-filose pseudopodia

Radiolarians
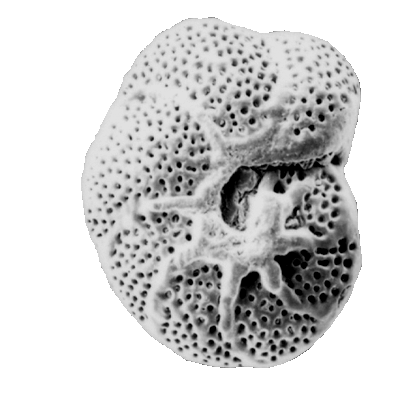
Foraminifera
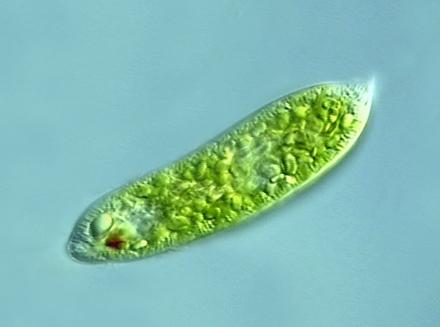
Excavata
-feeding groove
-secondary plastids
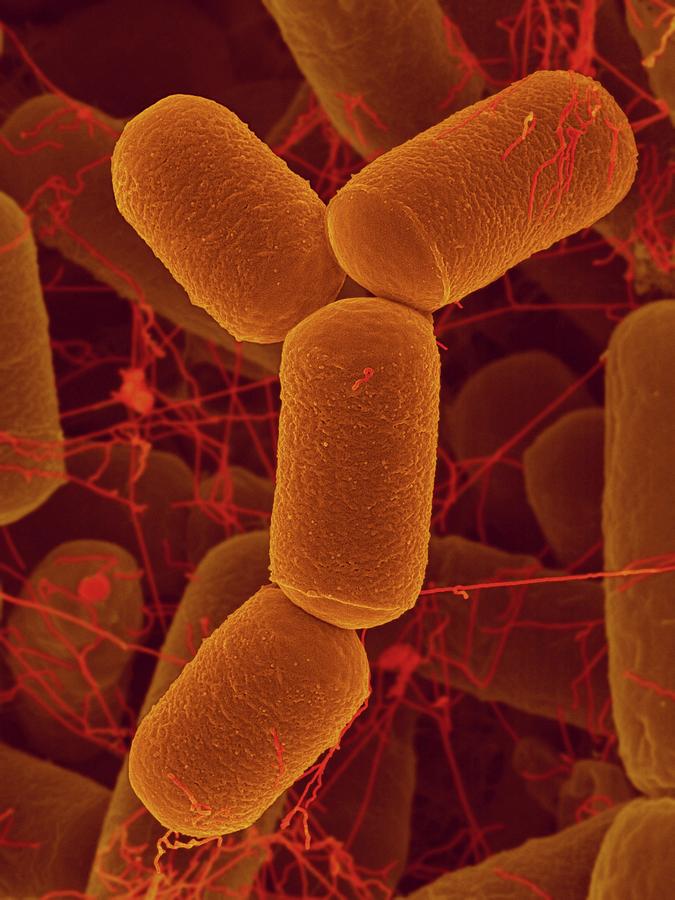
Archaea
No membrane bound organelles
No chromosomes in nucleus
Ether bonds