Macromolecules
Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides

Hydrolysis
Glucose
Galactose
Found In Milk
Found In Fruit
Energy For Humans
Alpha Glucose
OH in opposite
Direction of Carbon 6
Beta Glucose
OH in same
direction as carbon 6
Glycolysis
add nadt atp nadph pyruvate
Krob circle

many monosaccharides
are linked by Glyosidic bond or linkage
Isomers
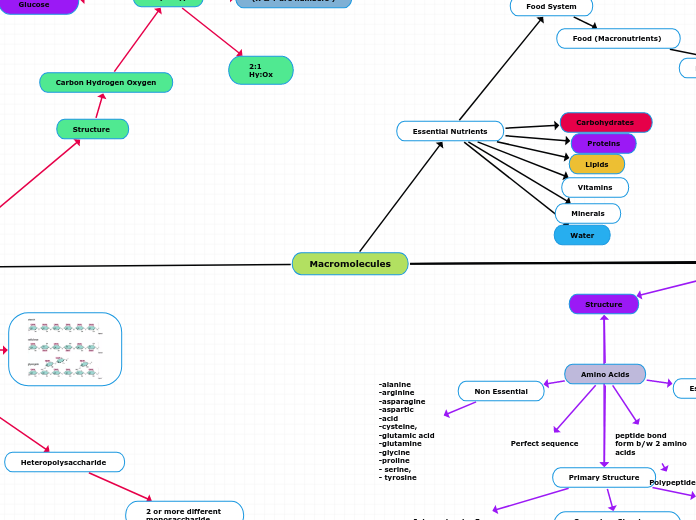
Oligosaccharides
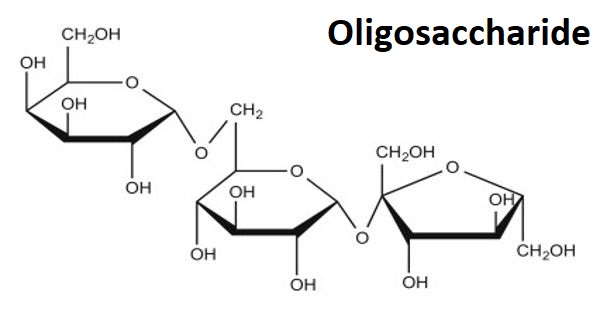
Disaccharides
Condensation
Maltose
Sucrose
Lactose
Glucose + Galactose
Glucose + Fructose
Glucose + Glucose
Polysaccharides
Heteropolysaccharide
2 or more different
monosaccharide
Homopolysaccharide
Starch
Amylase
+
amlodipine
Found
In
Plants
Single type of
Monosaccharides
Glycogen
Animal Starch
Found In animals
Cellulose
structural
component
plant cell walls
most abundant
polysaccharide
Dextran
Found In Corn starch
and other cereal starches

Polymer
Structure
Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen
Cx(H20)y
2:1
Hy:Ox
C_(H_O)_
Glucose
(X & Y are numbers )
Arranged In Sugar Units
Disaccahrides
2 Sugar Units
-O-O-
E,g Maltose
Monosaccarides
1 Sugar Unit
-O-
Eg Glucose
Poly Saccarides
Many Sugar Units
-O-O-O-O-
-O-O-O-O-
E.g Starch
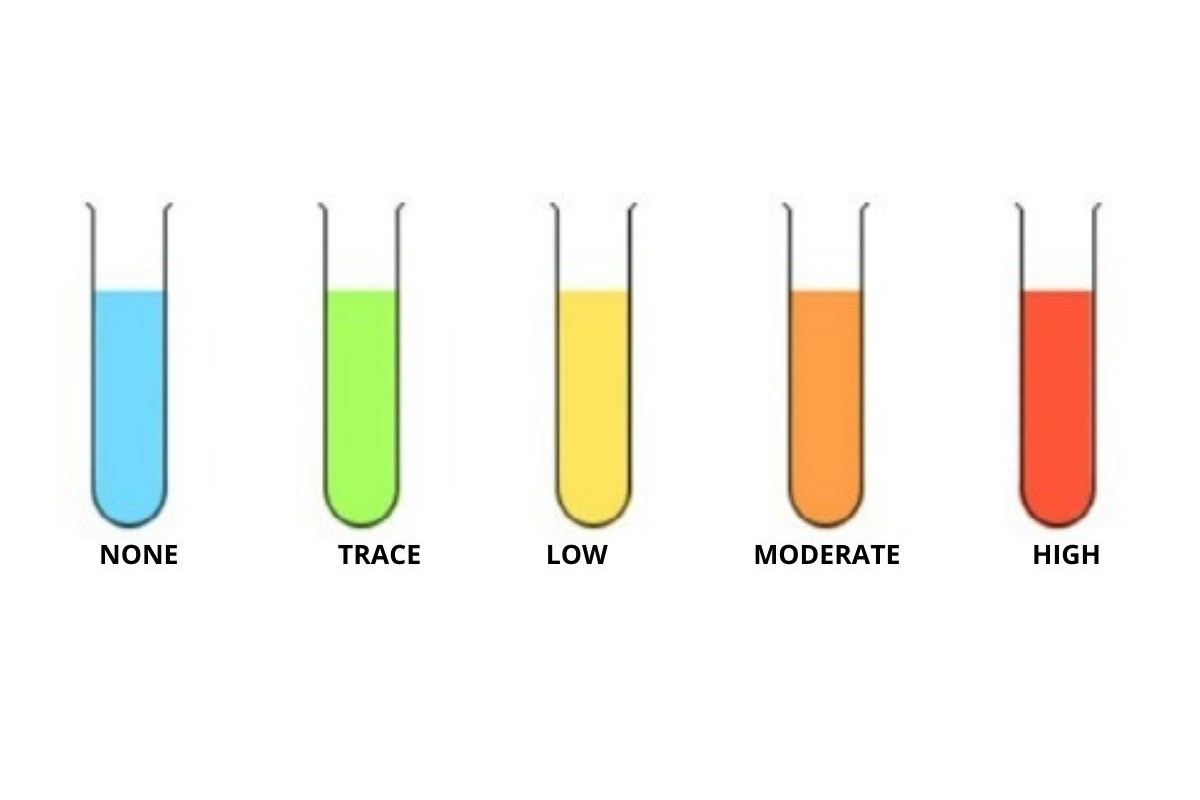
Tests
Reducing
Sugar Test.
Add 2ml testing
Solution + 2mll Benedicts Solution
Test
Brick
Red
precipitate
Absent
reducing
sugar
Absent
Brick Red
Precipitate
Present
reducing
Sugar
Present

Subtopic
Non reducing sugar test
test
2ml testing solution +
1ml dilute HCI +
2ml benedict solution
Brick Red precipitate
Absent
Non reducing
Sugar
Absent
Brick red
precipitate present
(non reducing
sugar present)
proteins
Structure
Primary Structure
Secondary Structure
polypeptide
Motifs
Intermolecular Interactions
Tertiary Structure
3-Dimensional
Structure
Ex.
Aquaporin
Transmembrane
Protein
Transport
water
Across Cell
Membrane
Receptor
protein
ligands
attach on it
Send Signal
aquaporin protein channel
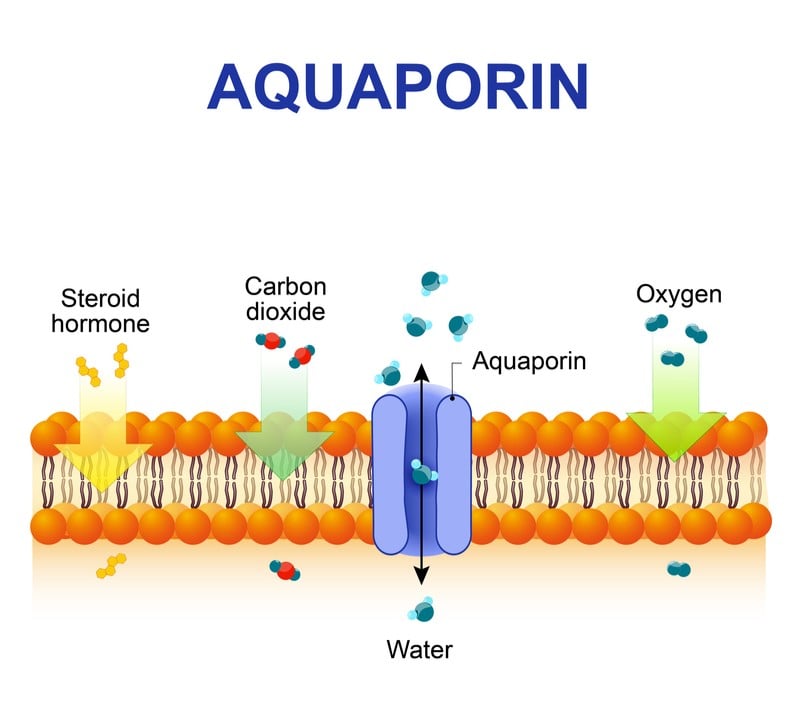
Example
Myoglobin
Found in muscle cell
Quaternary Structure
Haemoglobin
Found in RBCs
Transport O2
folding in of and interact 2 or more polypeptide
2d+2B Polypeptides
chain fold to form
among amino acids of a polypeptide
B-pleated
Sheet
D - Helix
Intramolecular Forces
Hydrogen
Bonding
intermolecular forces
Diet: Daily Needs
Source
Digestion Of peptide
Releases from meat, etc.
maize
(lack of tryptophan)
Additional needs
Replacing tissue
Injury
Cancer
Burns
Building tissue
Exercise/ training
Breast feeding
Pregnancy
Deficiencies
protein energy malnutrition
Pellagra (maize diet)
tryptophan deficiency
diarrhea
Skin lesions
Kwashiorkor
(Children)
Protein poor diet
(Banana/cassava)
Vitamin defciency
Poor growth
oedema
Marasmus
(Long term famine)
Organs/muscle
mobilized
Gut inefficiency
Muscle wasting
Function
Fibrous
Skeletal/support
e.g Collagen
Globular
Enyzmes
oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases.
Antibodies
Multiple Sclerosis.
Eicosanoid Receptor.
Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein.
Green Fluorescent Protein.
Antigen.
Peptide.
Proteome.
Epitope.
Membrane proteins
transmembrane α-helix protein, transmembrane α-helical protein and transmembrane β-sheet protein.
Mobile Carriers
Hemoglobin (Hgb or Hb)
is the primary carrier of oxygen in humans
Nucleic Acids

Monomers

Nucleotides
Phosphodiester Bonds (Bond Between Phosphate Group and Hydroxyl Group of the Next Nucleotide)
Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate (cAMP)
A Second Messenger for Internal Signalling In The Cells
Phosphate Group + Ribose + Adenine + Hydroxyl

Dinucleotides
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+)
Two Phosphate Groups + Two Ribose Sugar + Adenine + Nicotinamide
Nicotinamide Adenine
Dinucleotide Phosphate (NADP+)
Two Phosphate Groups + Two Ribose Sugar + Adenine + NADH Group
Used In Different Sets of Reactions That Remove Hydrogen (Ex. Cellular Respiration, Photosynthesis)
Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide
Two Phosphate Groups + Two Ribose Sugars + Adenine + Riboflavin)
Coenzyme A (CoA)
Two Phosphate Groups + Ribose + Adenine + Phosphoadenosine Diphosphate + Pantothenic Acid + Beta Mercaptoethylamine
Used to Move a Molecule to An Enzyme
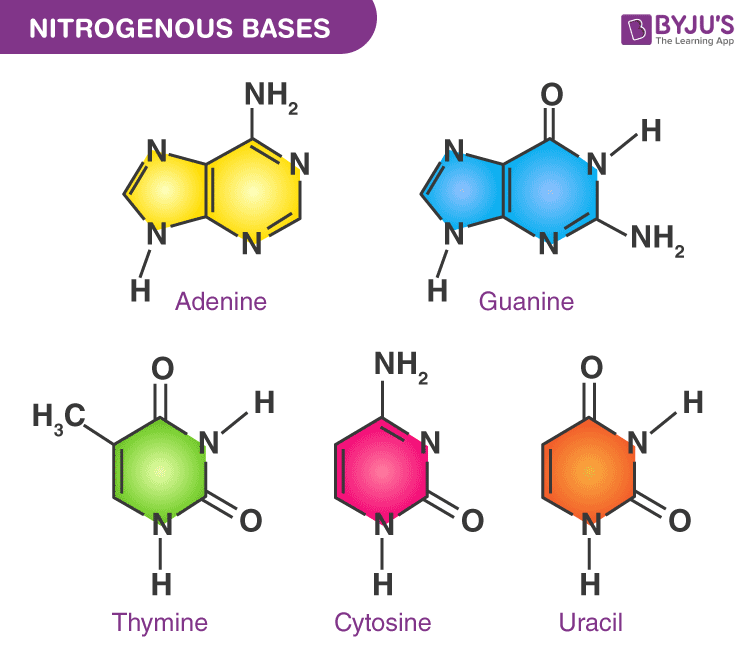
Nitrogenous Bases
Purines = Adenine, Guanine (Double Ring Structure)
Pyrimidines + Thymine, Cytosine, Uracil (Single Ring Structure)
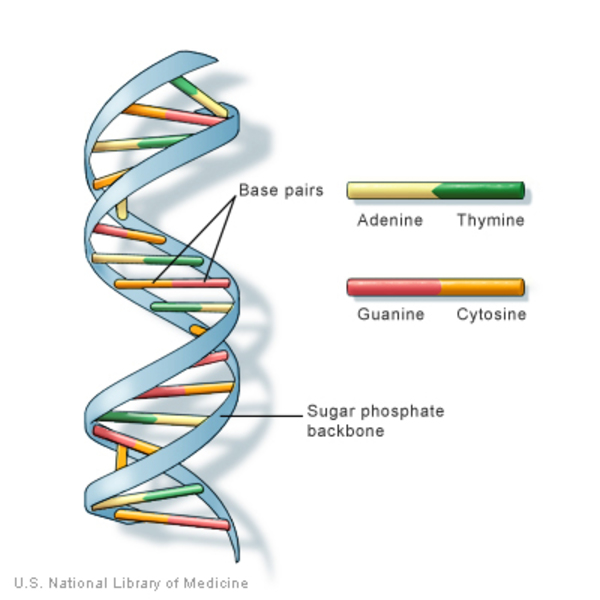
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
Phosphate + Deoxyribose Backbone and Nitrogenous Base (Double Stranded Helix)
Adenine Bonds with Thymine (Two Hydrogen Bonds), Guanine Bonds with Cytosine (Three Hydrogen Bonds)
Long Term Storage of Genetic Information
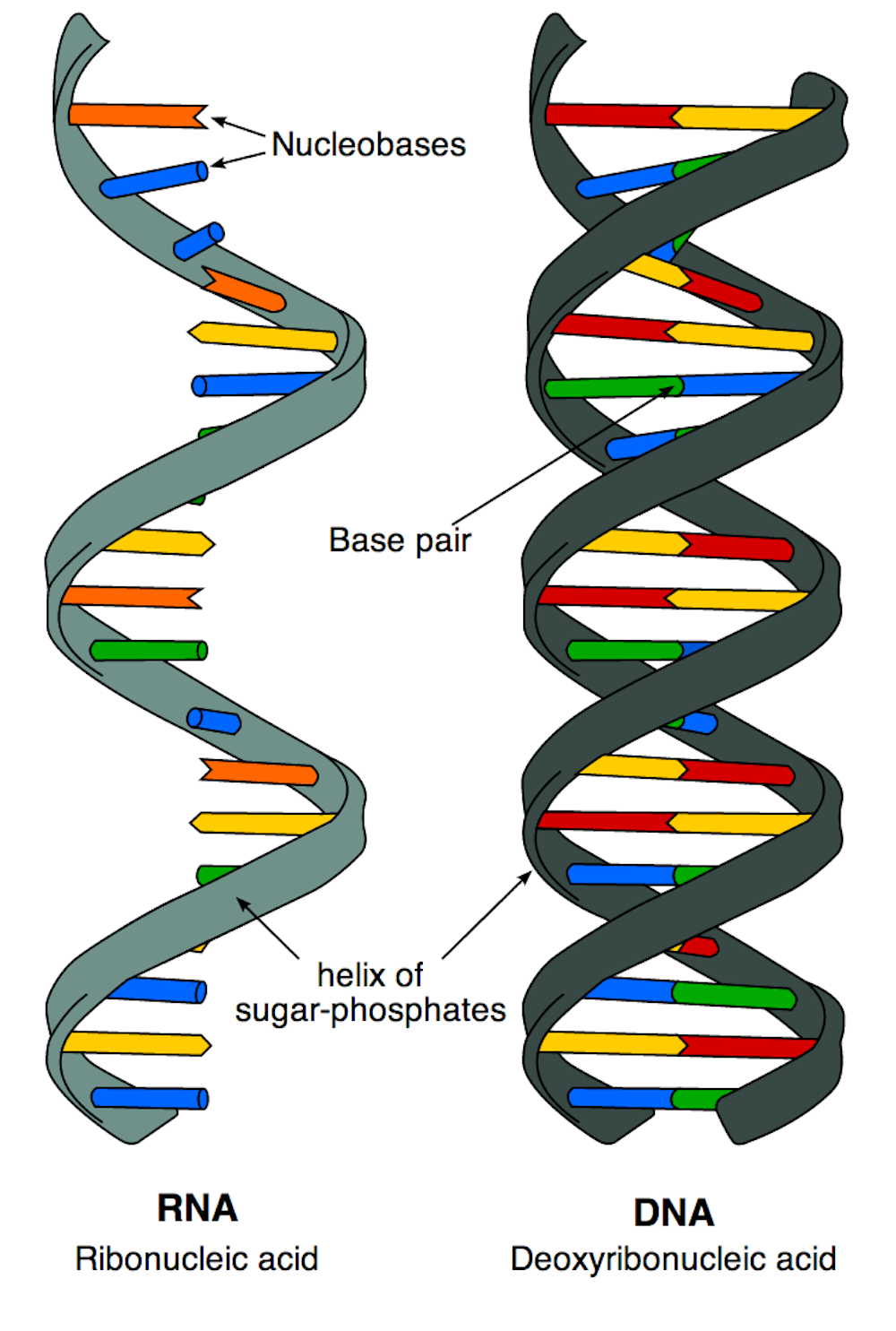
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
Phosphate + Ribose Backbone and Nitrogenous Base (Single Stranded)
Adenine Bonds with Uracil
(Two Hydrogen Bonds. Uracil Replaces Thymine in RNA), Guanine Bonds with Cytosine (Three Hydrogen Bonds)
Functions
Participates In Protein Synthesis
Transcribes and Translates DNA
Nucleic Acids Play a Large Role In The Food Chain and Transfer of Potential Energy
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is The Raw Form Of Energy
3 Phosphate Groups + Ribose Sugar + Adenine
Heterotrophs (Organisms That Need To Consume Their Energy Like Humans) Consume Their Energy, But Can Only get 5-20% of The Original Energy
Autotrophs (Organisms That Produce Their Own Energy Like Plants). Make Their Own ATP Using Sunlight
Lipids
Properties
Fatty Acids
Insoluble
Functions
Proection
Structure
Insulation
Hormonal Roles
Storage/Energy
Structure
Waxes

Steroids
Cholesterol
Plasma Membrane
Glycoprotein
Glyolipids
Transmembrane Protein

Phospholipid Bilayer

Phospholipids

Micelle

Triglycerides
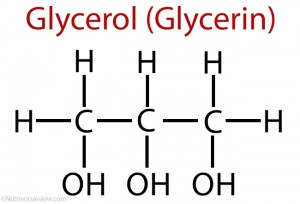
Glycerol
Fatty Acids

Hydrocarbon Chains

Methyl Group
Saturation
Saturated
Vegetable Oils
Animals Fats
Unsaturated
Trans Fatty Acids
Cls Fatty Acids
Acid Group
Water
States
Liquid
Lake
Ontario Lake
Gas
Clouds
Solid
Snow
Living Things
Animals
Penguins
Plants
Joshua Tree
Properties
High Specific
Heat capacity
Polarity
Universal
Solvent
Hydrogen
Bonding

High latent
Heat of
Vaporization
Cohesion
Water Sticks to itself
Adhesion
Water Sticks to other things

Functional Group
The chemical composition of water is H2O it does not contain any functional groups
Essential Nutrients
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Lipids
Vitamins
Minerals
Water
Food System
Food (Macronutrients)
E,g Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids
Autotroph
Synthesize Food
using sunlight
Photosynthesis
nadp + nadph
Plants
ADP ATP
ADP
camp
Used as secondary messanger
Heterotroph
Get food by eating
other living being or
organic matter
Amino Acids
Essential
- Histidine
- isoleucine
-Leucine
-Lysine
-Methionine
-Phenylalanine
-Theanine
- Tryptophan + valine
Non Essential
-alanine
-arginine
-asparagine
-aspartic
-acid
-cysteine,
-glutamic acid
-glutamine
-glycine
-proline
- serine,
- tyrosine
Perfect sequence
peptide bond
form b/w 2 amino
acids
Polypeptide