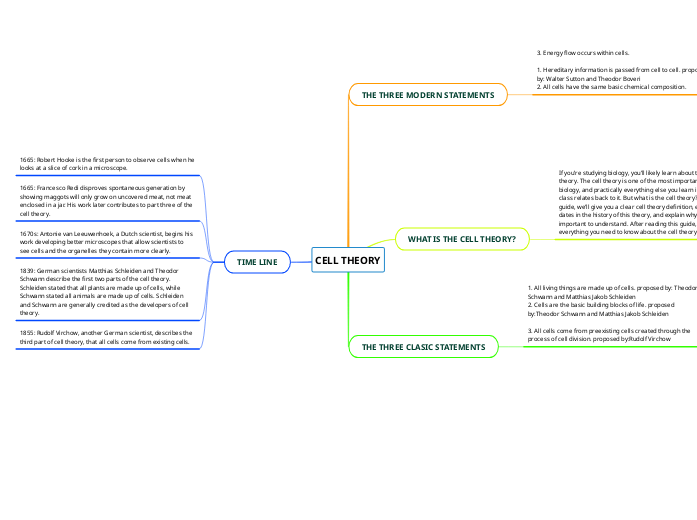
CELL THEORY
THE THREE MODERN STATEMENTS
3. Energy flow occurs within cells.
1. Hereditary information is passed from cell to cell. proposed by: Walter Sutton and Theodor Boveri
2. All cells have the same basic chemical composition.
WHAT IS THE CELL THEORY?
If you’re studying biology, you’ll likely learn about the cell theory. The cell theory is one of the most important tenets of biology, and practically everything else you learn in science class relates back to it. But what is the cell theory? In this guide, we’ll give you a clear cell theory definition, explain key dates in the history of this theory, and explain why it’s so important to understand. After reading this guide, you’ll know everything you need to know about the cell theory!
THE THREE CLASIC STATEMENTS
1. All living things are made up of cells. proposed by: Theodor Schwann and Matthias Jakob Schleiden
2. Cells are the basic building blocks of life. proposed by:Theodor Schwann and Matthias Jakob Schleiden
3. All cells come from preexisting cells created through the process of cell division. proposed by:Rudolf Virchow
TIME LINE
1665: Robert Hooke is the first person to observe cells when he looks at a slice of cork in a microscope.
1665: Francesco Redi disproves spontaneous generation by showing maggots will only grow on uncovered meat, not meat enclosed in a jar. His work later contributes to part three of the cell theory.
1670s: Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, a Dutch scientist, begins his work developing better microscopes that allow scientists to see cells and the organelles they contain more clearly.
1839: German scientists Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann describe the first two parts of the cell theory. Schleiden stated that all plants are made up of cells, while Schwann stated all animals are made up of cells. Schleiden and Schwann are generally credited as the developers of cell theory.
1855: Rudolf Virchow, another German scientist, describes the third part of cell theory, that all cells come from existing cells.