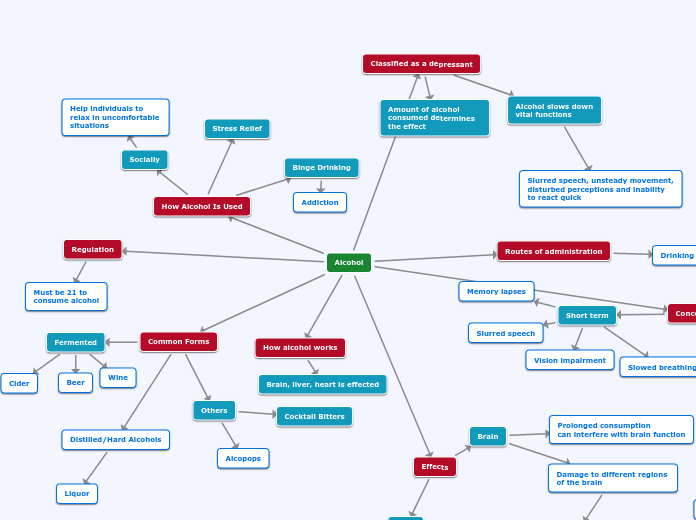
Others
Cocktail Bitters
Alcopops
Fermented
Cider
Beer
Wine
Distilled/Hard Alcohols
Liquor
Socially
Help individuals to relax in uncomfortable situations
Stress Relief
Binge Drinking
Addiction
Amount of alcohol consumed determines the effect
Alcohol slows down vital functions
Slurred speech, unsteady movement,
disturbed perceptions and inability to react quick
Must be 21 to
consume alcohol
Body
Memory loss and
coordination
Weaken the heart
Cause heart disease
and diabetes
Liver damage
Pancreatic health
problems
Brain
Prolonged consumption
can interfere with brain function
Damage to different regions
of the brain
Cerebellum, limbi system
and cerebral cortex
Short term
Slurred speech
Vision impairment
Memory lapses
Slowed breathing
Long term
Cardiovascular diseases
Liver disease
Cancer
Nerve damage
Ulcers
Respiratory infections
Drinking
Brain, liver, heart is effected
Short term
Nausea
confusion
Blurred vision
Light headed
Short-term memory loss
Dizziness
Slowed breathing
Long term
Addiction
Dependence
Affects brain development
Body
Subtopic
Heighten senses
Affect motor skills
Mind
Anxiety
Afraid
Panicked/paranoid
Legalized recreational and medical
10 states
Legalized medical use
more than 15 states
Dried plant
Liquid
Smoked
Blunt
Bong/pipes
Joints
Vaporized
Dab pens
Eaten
Food
Brownies
Candies
Drinks
Depressant
Calm nerves
Relax muscles
Help with sleep
Helps slow down brain
functions
Stimulant
Increased body temp.
Paranoia
Anxiety
Irregular heart beat
Elevatd moods
Hallucinogen
Nausea
Dry mouth
Increased heart rate
Altered sense of
time or space
loss control of
motor skills
THC the main chemical that
allows an individual to be effected
THC pass from the lungs
and into the bloodstream
Rapidily carries throughout the
body and into the brain
Smoking
Edibles/eating
Vaporizing
Beverages
Stimulant
Central nervous
system stimulant
Drinking
Eating
Taken medically
Prescription
Pills
Coffee
Americano
Latte
Expresso
Mocha
Iced coffee
Frappe
Macchiato
Cold brew
Teas
Black tea
Green Tea
Sodas
Mountain dew
Coke
Coca Cola
Energy drinks
Bang
Red bull
C4
Celsius
Monster
Rockstar
Foods
Medicine
Dietary supplements
Fiorinal capsules
Aspirin
Cafeeine suppositories
Short term
Headaches
Vomiting
Diarrhea
Anxiety
Nausea
Irritability
Alergic reactions
Rash
Hives
Itching
Lack of concentration
Higher body temp
Long term
Trouble sleeping
Addiction
Seizures
Tremors
Irritability anf headaches
Rapid heart rate
Irregular heart rate
Low blood pressure
Weakness and fatigue
Mental alertness
Increased metabolic rate
Decreased fatigue
Feeling more active
Restlessness
Faster breathing and
heart rate
Stimulates the central
nervous system, heart, muscles
and centers that control
blood pressure
No age restriction
on caffeine
Those who are very young
should consume little to no
caffeine
Food
Chocolate
Ice creams
Frozen yogurts
Pills/supplements
Drinks
Cigarettes
Cigars
Smokeless tobacco
Waterpipes
Hooka
Shisha
Electronic Cigarettes
Vape pens
E-hookahs
Short term
Bad breath
Bad taste in mouth
Smelly hair and clothes
Yellow colored teeth
Damage to the
respiratory system
Long term
Addiction
Acute bronchitis
Heart attack
Kidney cancer
High blood pressure
Mouth cancer
Cataracts
Asthma
Blood vessel disease
Low bone density
Throat cancer
Stomach cancer
Body
Mood stimulation
Smelly hair
Unhealthy teeth
Poor vision
Persistent coughing
Brain
Cognitive decline
Increased risk
of dementia
Loss of brain
volume
Chewed
Stuff tobacco between
inner cheeks and gums
Smoked
Cigarettes
Once inhaled and into
the bloodstream it acts as a receptors
in the brain
Stimulates the brain to make
you feel better
21 years and
older to buy tobacco
States: Arkansas, California
Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii
Illinos, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts
New Jersey, New Yorl, Ohio, Texas, Utah, Vermont, Viriginia, Washington
18 years or older to
buy tobacco in some
states
Stimulant
Provides stimulant
to your adrenal glands
which releases adrenaline
Depressant
Smoked
Inhaled into the lungs
and into the bloodstream
Chewed
Sniff
Smoking
Injected
Smoking
Snorted
Swallowed as
a pill
injected
Short term
Anxiety
Confusion
Hallucinations
Paranoia
Lost appetite
Increased heart
rate
Nausea
Disturbed sleep
patternspatterns
Convulsions
Long term
Weight loss
Agressiveness
Hyperactivity
Delusions of power
cardiovascular
collapse or death
Liver damage
Kidney and lung
damage
Damaged blood vessels
Brain damaged
Subtopic
depression
Severe tooth decay
Hyperactivity
Twitching, jerky movements
Paranoia
Skin sores
Dilated pupils
Rapid eye movement
Respiratory problems
Malnutrition
Destruction of tissues
Confused exhaustion
Brain cells transmit and
recevie chemical messages
Increases heart rate
and blood pressure
Dilates pupils
Those in possession
will be treated with a felony charge
5 years for possession
for anything less than a gram
Max sentence of 40 years
for anyhting over a gram
Stimulant
Depressant
Smoking
Injected
Snorted
Pills
Tablet orally
Concentrated solution
Liquids
Short term
Headaches
Irritability
Talkativeness
Diffculty concentrating
Dry mouth
Memory problems
Nausea
Joint pain
Weight changes
Difficulty urinating
Long term
Anxiety
Difficulty sleeping
Tingling sensations
Blurred vision
Muscles cramps/twitching
Diminished appetite
Seizures
Coordination problems
Body
Reduction in nervous tension
Calming affect
Mind
Slows down movement
of brain chemicals
Pills
Depressant
Must be provided from a doctor
Dosage based on medical condition
Age
Response to treatments
Approved by the FDA in
October 1981
Acts on the brain and
central nervous system
Produces a calming effect
Decreases abnormal excitement
in the brain
Attach to protein receptors
in the brain, spinal cord etc.
The opioids block pain
messages sent from the body and
through the spinal cord to the brain
Depressant
Stimulant
Pain relief
Illegal opioids
Heroin etc.
Legal opioids
Prescribed for pain
relief
Hydrocodone
Vicodin
Brain
Block pain signals sent from the brain
to the body
Release large amounts
of dopamine throughout
the body
Short term
Drowsiness
Confusion
Constipation
Euphoria
Slowed breathing
Long term
Muscle and
bone pain
Sleep problems
Severe cravings
Diarrhea and vomting
Uncontrollable leg
movements
Pill form
Lozenges or lollipops
Injection through
Iv
Natural
Morphine
Codeine
thebaine
Semi-synthetic
Hydromorphone
Hydrocodone
OxyContin
Fully synthetic
Fentanyl
Pethidine
Levorphanol
Methadone
Tramadol
Dextropropoxyphene
Hallucinogen
Chemical substances
Stimulant
Recreational use
Use to deal with
stress
Relieve boredom
Spiritual
Induce detachment
from reality
Artistic inspiration
Gives artist, or writers
creative inspiration
Illegal and not approved
for medical or recreational use
Change and enhance
Sensory perceptions, energy
levels
Bad trips
Frightening or
disturbing hallucinations
Lead to panic
and unpredictable
behavior
Flashbacks
Re-experience of the drug
Can occur days,
weeks or months
LSD
Plants
Peyote
Ayahuasca
NBOMes
Psilocybin
Short term
Relaxation
and wellbeing
Vomiting
Sweating and chills
Numbness
Dizzines
Clumsiness
Confusion and
trouble concentrating
Breathing quickly
Long term
Disorganized thinking
hallucinations
Mood disturbances
Paranoia
Swallowed
Mushrooms are eaten fresh
cooked, or brewed into a "Tea"
Smoked
Inhaled