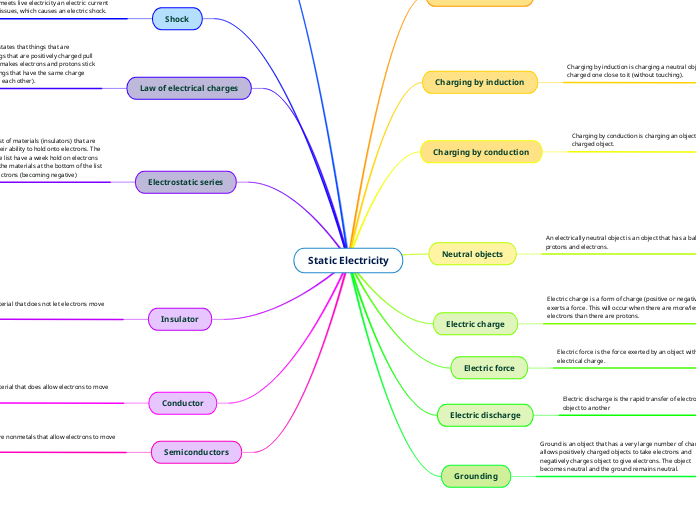
Static Electricity
Charging by friction
Charging by friction is the transfer of electrons between 2 neutral objects (different materials). It occurs when the surface are rubbed together.
For example when a plastic rod is rubbed with a piece of cloth, electrons are transferred from the rod to the cloth.

Charging by induction
Charging by induction is charging a neutral object by bringing a charged one close to it (without touching).
For example charging your phone.

Charging by conduction
Charging by conduction is charging an object with a previously charged object.
For example a positively charged aluminum plate is touched to a neutral metal sphere. The neutral metal sphere becomes charged as the result of being contacted by the charged aluminum plate.

Neutral objects
An electrically neutral object is an object that has a balance of protons and electrons.
The pieces of straw attracted to polished amber are neutral
Electric charge
Electric charge is a form of charge (positive or negative) that exerts a force. This will occur when there are more/less electrons than there are protons.
If you rub a balloon on your hair, the balloon becomes negatively charged and your hair becomes positively charged.

Electric force
Electric force is the force exerted by an object with an electrical charge.
An example of electric force is the charge in a bulb
Electric discharge
Electric discharge is the rapid transfer of electrons from one object to another
Ex. Shocks/lightning. Electrons "move/jump" from negatively charged objects
Grounding
Ground is an object that has a very large number of charges. It allows positively charged objects to take electrons and negatively charges object to give electrons. The object becomes neutral and the ground remains neutral.
For example lightning striking the earth
Static electricity
Static electricity is an imbalance of charge at the surface of an object.
Ex. Balloon + hair. A balloon becomes negatively charged (gained electrons) hair becomes positively charged (lost electrons)
Shock
If any part of your meets live electricity an electric current flows through the tissues, which causes an electric shock.
For example a singer getting shocked from their microphone
Law of electrical charges
The law of electric charges states that things that are negatively charged and things that are positively charged pull on (attract) each other. This makes electrons and protons stick together to form atoms. Things that have the same charge push each other (they repel each other).
For example magnets push away from each other which is a repulsive force.
Electrostatic series
Electrostatic series is a list of materials (insulators) that are arranged according to their ability to hold onto electrons. The materials at the top of the list have a week hold on electrons (becoming positive) and the materials at the bottom of the list have a strong hold on electrons (becoming negative)
For example human skin does not hold onto electrons and is at the top of the list

Subtopic
Insulator
An insulator is a material that does not let electrons move through it
Ex. Plastic/rubber. They are used to cover wires and connectors to prevent electric shocks.
Conductor
A conductor is a material that does allow electrons to move from atom to atom.
Ex. metal (copper). Used for wires (Cu and Al)
Semiconductors
Semi-conductors are nonmetals that allow electrons to move fairly well
Ex. Silicon.