Common Ancestor: DNA is present as genetic storage
Prokaryotic
Bacteria: ester bonds, peptidoglycan in cell walls, no membrane bound nucleus or organelles, no histones
Escherichia coli
Common Ancestor of Archaea and Erukarya: Presence of Histones, No Peptidoglycan in Cell Membrane
Archaea: ether bonds, no membrane bound nucleus or organelles
Methanobrevibacter smithii
Eukarya: ester bonds, presence of membrane bound nucleus and organelles
Archaeplastida: Primary Plastids in photosynthetic species, no feeding groove, no tripartite flagellar hair, no membranous vesicles on cell membrane, no filose pseudopodia or pseudopodia that extend like tubes or flat lobes, and no single posterior flagellum on swimming cells
autotrophic ancestor produces pollen, has seeds, wooded, heterospory, contains ovules
angiosperms: produce flowers and fruit, presence of endosperm, presence of ovaries

Southern Magnolia
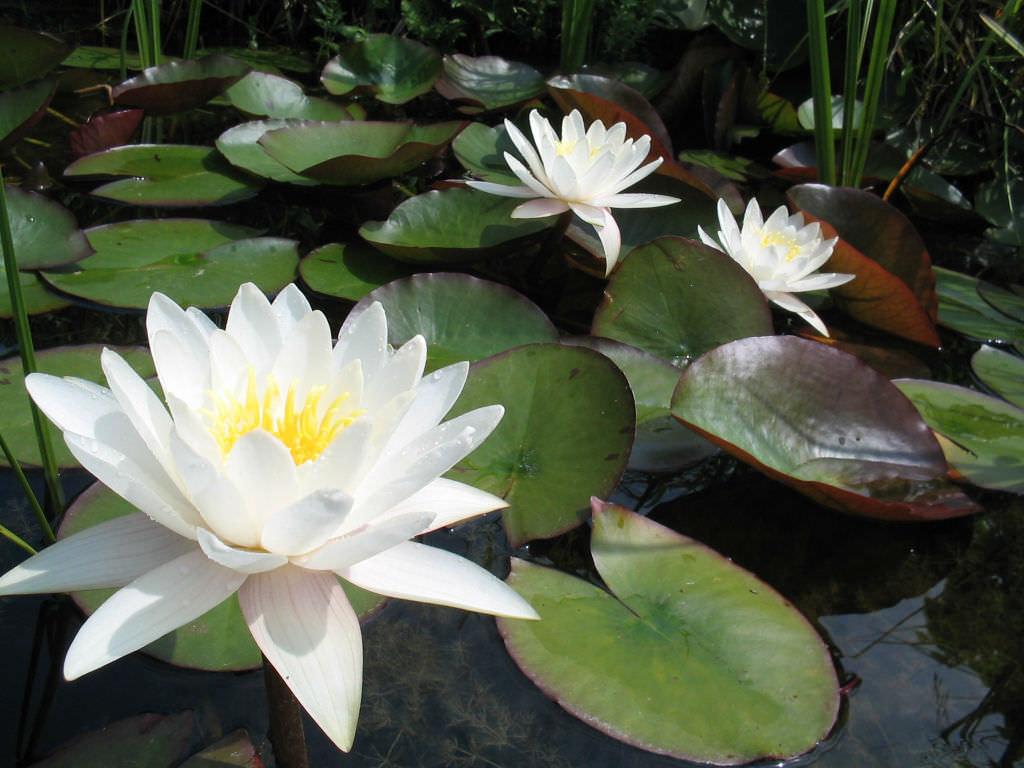

White Water Lily (Nymphaea alba)
gymnosperms: no flowers or fruit production, no endosperm, no ovaries

Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris)
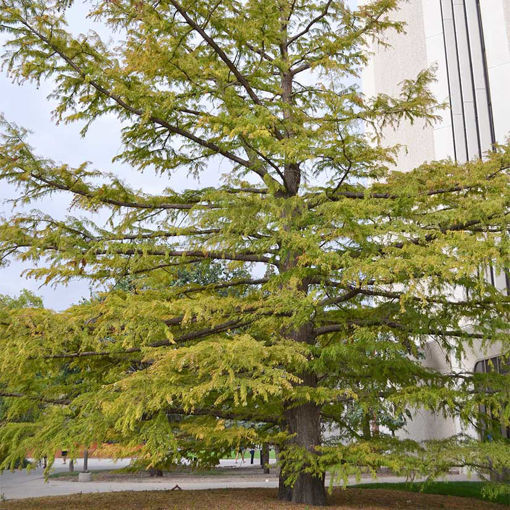

Bald Cypress (Taxodium distichum)
autotrophic ancestor with sporic life cycle, presence of embryo and desiccation resistant spores, tissue growth on apical meristems only, presence of gametangia and sporangia
common ancestor: presence of lignin, xylem/phloem circulation of waters and sugars, dominant sporophyte generation, presence of stomata and thick waxy cuticle
Lycophytes: lycophylls aka microphylls leaves (one single unbranched leaf vein)

Fan Clubmoss
Monilophytes: megaphylls leaves (multiple veins)

Eastern Marsh Fern
common ancestor: no lignin present, diffusion/osmosis circulation of waters and sugars, dominant gametophyte generation, no thick waxy cuticle, no stomata
Liverworts: can be foliose or thallus, lobate structures

Common Liverwort
Hornworts: thallus, narrow pipe-like structures

Field Hornwort
Mosses: foliose

Wooly Feather Moss
autotroph with zygotic life cycle, no presence of embryo or desiccation-resistant spores, tissue growth throughout body, no gametangia or sporangia
Common Ancestor: no lignin, diffusion/osmosis circulation of waters and sugars, no true leaves, dominant gametophyte generation, no thick waxy cuticle, no stomata

(Charophytes) Braun's Stonewort

Chlorophytes

Rhodophytes
SAR Clade
Secondary Plastids in photosynthetic species (also no filose pseudopodia or pseudopodia that extend like tubes or flat lobes, no single posterior flagellum on swimming cells)
Stramenopila: no feeding groove, presence of tripartite flagellar hair, no membranous vesicles on cell membrane

Diatoms

Giant Kelp
Alveolata: no feeding groove, no tripartite flagellar hair, presence of membranous vesicles on cell wall, possible to have tertiary plastids as well

Dinoflagellates
No plastids, filose pseudopodia, uses pseudopodia for motility (no single posterior flagellum on swimming cells)
Rhizaria: no feeding groove, no tripartite flagelar hair, no membranous vesicles on cell membrane
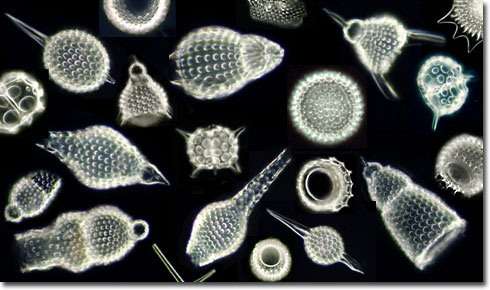
Radiolarians

Foraminiferas
Excavata
Common Ancestor: presence of feeding groove, no tripartite flagellar hair, no membranous vesicles on cell membrane, Secondary Plastids in photosynthetic species (also no filose pseudopodia or pseudopodia that extend like tubes or flat lobes, no single posterior flagellum on swimming cells)
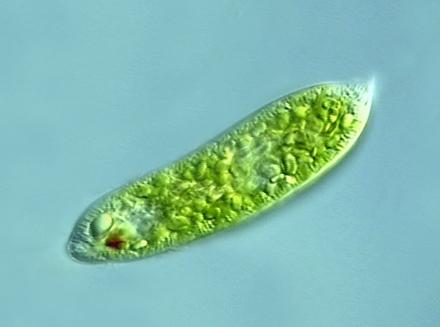
Euglenoids

Slime Molds
Unikonta
Amoebozoa: no single posterior flagellum on swimming cells, no plastids (also no feeding groove, no tripartite flagelar hair, no membranous vesicles on cell membrane), pseudopodia that extend like tubes or flat lobes, uses pseudopodia for motility
Opisthokonta: single posterior flagellum on swimming cells, no plastids (also no feeding groove, no tripartite flagelar hair, no membranous vesicles on cell membrane)
Common Ancestor: multicellular, absorptive heterotroph
Fungi: presence of cell wall, lack of mobility and complex organ systems, zygotic life cycle

Fly Agaric

Black Bread Mold/Rhizopus stolonifer
Animalia (Metazoa): lack of cell wall, mobile, presence of complex organ systems, gametic life cycle
Eumetazoa
Bilateria: Bilateral Symmetry
Protostomia: tissues present in three
embryonic tissue layers (triploblasty), spiral and indeterminate embryonic cleavage, blastopore into mouth, no trochophore larvae or lophophore
Ecdysozoa: tissues present in two
embryonic tissue layers (diploblasty), spiral and
determinate embryonic cleavage, blastopore into mouth, no trochophore larvae or lophophore, only group with ecdysis
Arthropoda: spiracles and
tracheal system, book lungs, gills, cephalization
Hexapoda: aka Insecta; presence of a consolidated thorax with three pairs of legs (six legs)

Monarch butterfly (Danaus plexippus)
Crustacea: presence of a hard exoskeleton made of calcium, two compound eyes, two pairs of antennae, a pair of green glands excrete wastes near the base of antennae, and the abdominal segments have swimmerets (swimming legs)

Chesapeake Blue Crab (Callinectes sapidus)
Chelicerata: presence of two main body segments, four pairs of legs, have pedipalps (i.e. pinchers or secondary legs), lack antennae, majority of them are terrestrial

Southern Black Widow (Latrodectus mactans)
Nematoda: no cephalization
Roundworm (Caenorhabditis elegans)
Lophotrochozoa: tissues present in three
embryonic tissue layers (triploblasty), spiral and
determinate embryonic cleavage, blastopore into mouth, presence of trochophore larvae or lophophore
Mollusca: presence of gills, Cephalization
Gastropoda: have a muscular foot which is used for "creeping" locomotion sometimes modified for swimming or burrowing; most have 1-2 tentacles and a well developed head with eyes

Golden Apple Snail (Pomacea canaliculata)
Bivalva: have two shells called valves which act like protective armor
Soft Shell Clam (Mya arenaria)
Cephalopoda: the foot has developed into a set of arms or tentacles; ability to squirt ink when threatened; symmetrical

Humboldt squid (Dosidicus gigas)
Platyhelminthes: no cephalization
Rhabditophora: presence of specialized, rod-like secretory granules on their body surface (rhabdites) responsible for the production of a layer of viscous slime
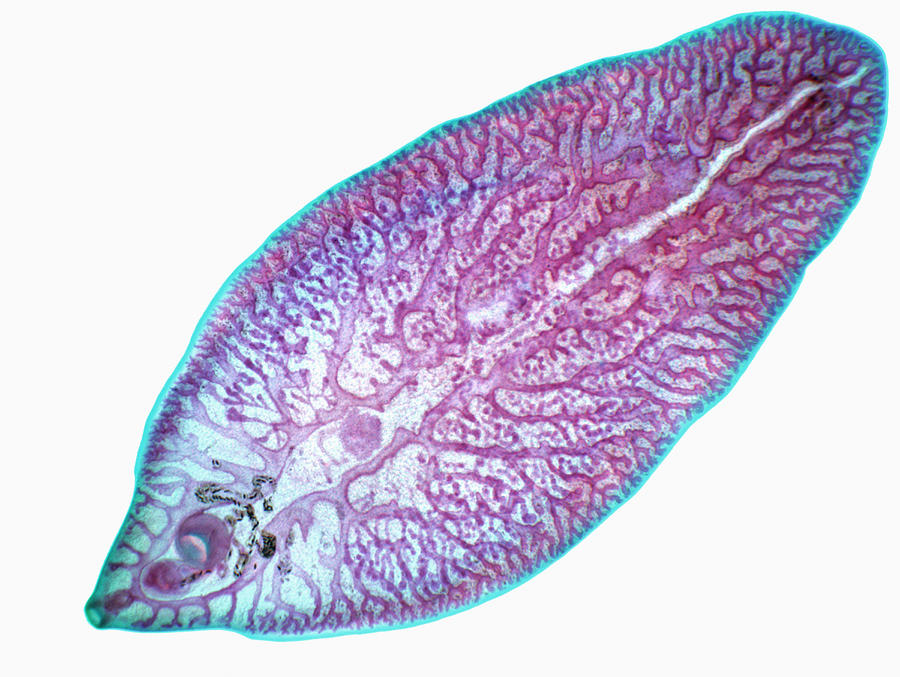
Sheep Liver Fluke (Fasciola hepatica)

Macrostomum lignano
Trematoda: flattened oval or worm-like animals, usually no more than a few centimeters in length; presence of two suckers, one close to the mouth, and the other on the underside
Cestoda: type of parasitic worm that can be found in the gastrointestinal tract of their hosts; characterized by a long, flat body (ribbon-like) that can grow to over 20 meters in length

Pork Tapeworm (Taenia solium)
Annelida: Cephalization

Common Earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris)
Deuterostomia: tissues present in three
embryonic tissue layers (triploblasty), radial and
indeterminate embryonic cleavage, blastopore into anus, no trochophore larvae or lophophore
Echinodermata: presence of water vascular system, no cephalization
Asteroidea
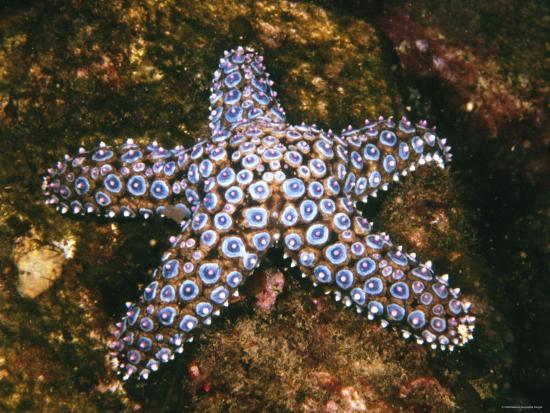

Giant Sea Star (Pisaster giganteus)
Ophiuroidea: "brittle stars"; five part symmetry and an internal calcium carbonate skeleton in the mineral form of calcite
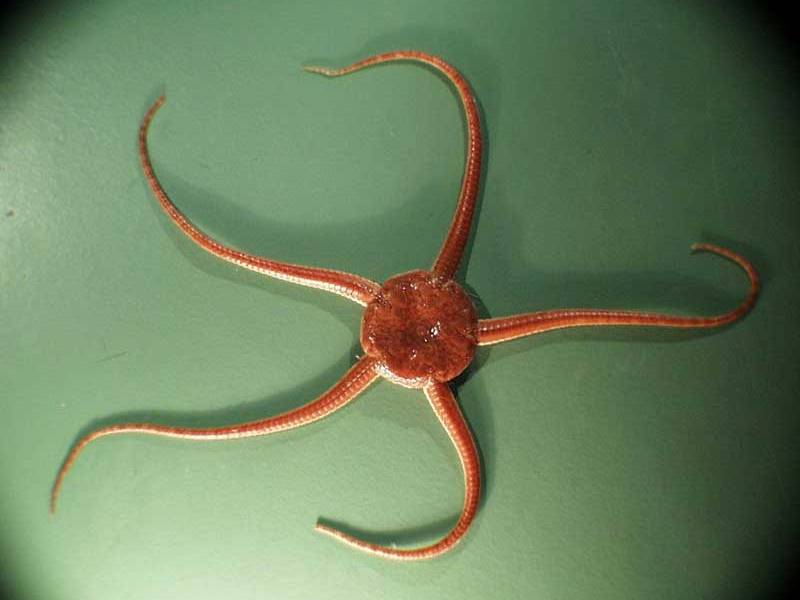
Serpent Star (Ophiura ophiura)
Echinoidea: have a globoid shape without any arms are features the sea urchins share with the sea cucumbers; have fivefold symmetry and move around on a large number of hydraulically powered tube feet
Purple Sea Urchin (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus)
Holothuroidea: lack arms, bilateral symmetry, body wall soft rather than calcareous, sedimentary feeders, body surrounded by tube feet
California sea cucumber (Apostichopus californicus)
Chordata
Urochordata: possess a notochord, a hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a post anal tail; body has more than two cell layers and includes tissues and organs, has a U shaped gut, and body has no coelomic body cavity, no cranium, no vertebral column, no cartilage or bony skeleton, no jaws, no limbs, no lungs or lung derivatives, no heart chambers, no internal temperature maintenance, no amniotic egg, no hair, and no milk production; single circulation
tunicates
Sea Peaches (Halocynthia aurantium)
Cephalochordata: segmented marine animals that possess elongated bodies with a notochord that extends the length of the body, extending from head to tail, persisting throughout the animal's life; possesses a hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a post anal tail; body has more than two cell layers and includes tissues and organs, has a U shaped gut, and body has no coelomic body cavity, no cranium, no vertebral column, no cartilage or bony skeleton, no jaws, no limbs, no lungs or lung derivatives, no heart chambers, no internal temperature maintenance, no amniotic egg, no hair, and no milk production; single circulation
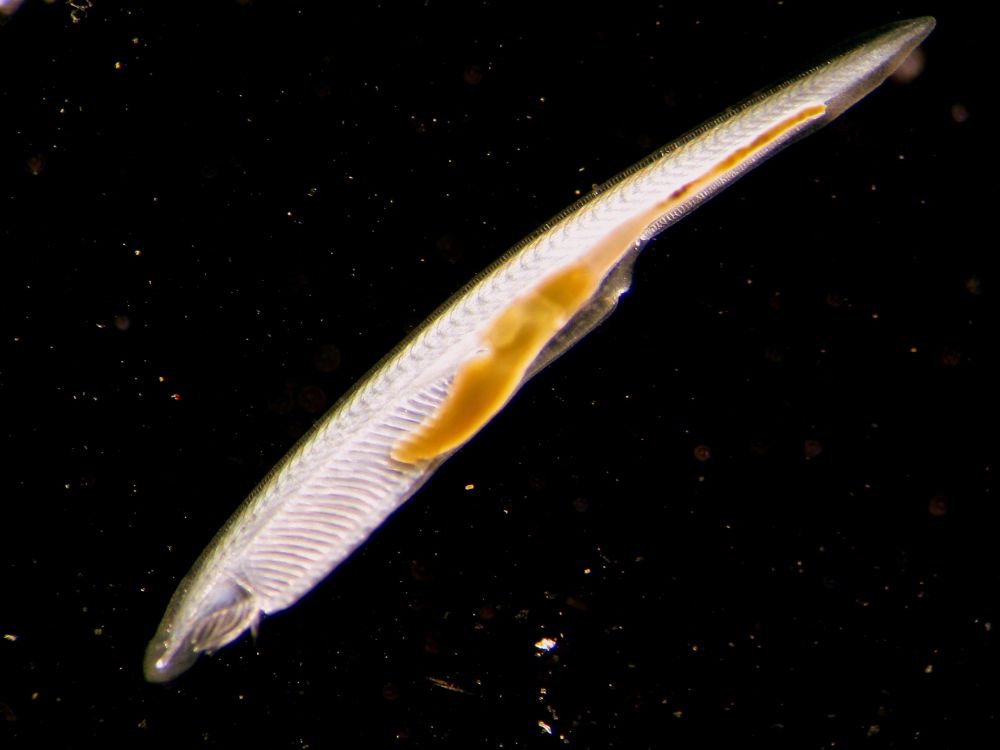

Branchiostoma lanceolatum
Vertebra: possess a notochord, a dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail; vertebrates are further differentiated from chordates by their vertebral column, which forms when their notochord develops into the column of bony vertebrae separated by discs
Agnathans aka Cyclostomes: possess a cranium; no jaws, no limbs, no lungs or lung derivatives, no amniotic egg, no hair or milk production; cartilage skeleton, 2-chambered heart, ectothermic, single circulation

Pacific hagfish (Eptatretus stoutii)
Chondrichthyes: possess a cranium and jaws; cartilage skeleton, no lungs or lung derivatives, no limbs, 2 chambered heart, ectothermic, no amniotic egg, no hair or milk; single circulation

Great White Shark (Carcharodon carcharias)
Osteichthyes (bony fish)
Actinopterygii: ray-finned fishes which possess a cranium, jaws, and lungs or lung derivatives; bony skeleton, no limbs, 2 chambered heart, ectothermic, no amniotic egg, no hair or milk; single circulation
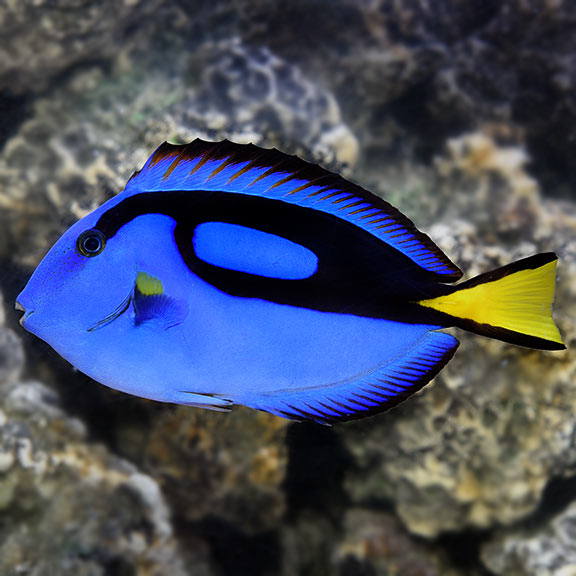

Blue Tang (Paracanthurus hepatus)
Sarcopterygii: lobe-finned fishes which possess a cranium, jaws, and lungs or lung derivatives; bony skeleton, no limbs, 2 chambered heart, ectothermic, no amniotic egg, no hair or milk; single circulation

Coelacanth (Latimeria chalumnae)
Amphibia: possess a cranium, jaws, and lungs or lung derivatives; bony skeleton, limbs, 3 chambered heart, ectothermic, no amniotic egg, no hair or milk; double circulation

Red Eyed Tree Frog (Agalychnis callidryas)
Reptilia: possess a cranium, jaws, and lungs or lung derivatives; bony skeleton, limbs, 3 or 4 chambered heart, ectothermic (non-bird reptiles) endothermic (birds), amniotic egg, no hair or milk; double circulation

Green Sea Turtle (Chelonia mydas)
Mammalia: possess a cranium, jaws, and lungs or lung derivatives; bony skeleton, limbs, 4 chambered heart, endothermic, amniotic egg, hair and milk; double circulation

American Black Bear (Ursus americanus)
Radiata: radial symmetry
/
Anthozoa: have dominant polyp i.e. sea anemones and coral

Elkhorn coral (Acropora palmata)
Hydrozoa: alternate between polyp and medusa i.e. Portuguese Man O War

Pennaria disticha
Scyphozoa: have dominant medusa

Moon Jelly (Aurelia aurita)
Parazoa: Asymmetry
Porifera (Sponges): no tissues, no trochophore larvae or
lophophore, no cephalization
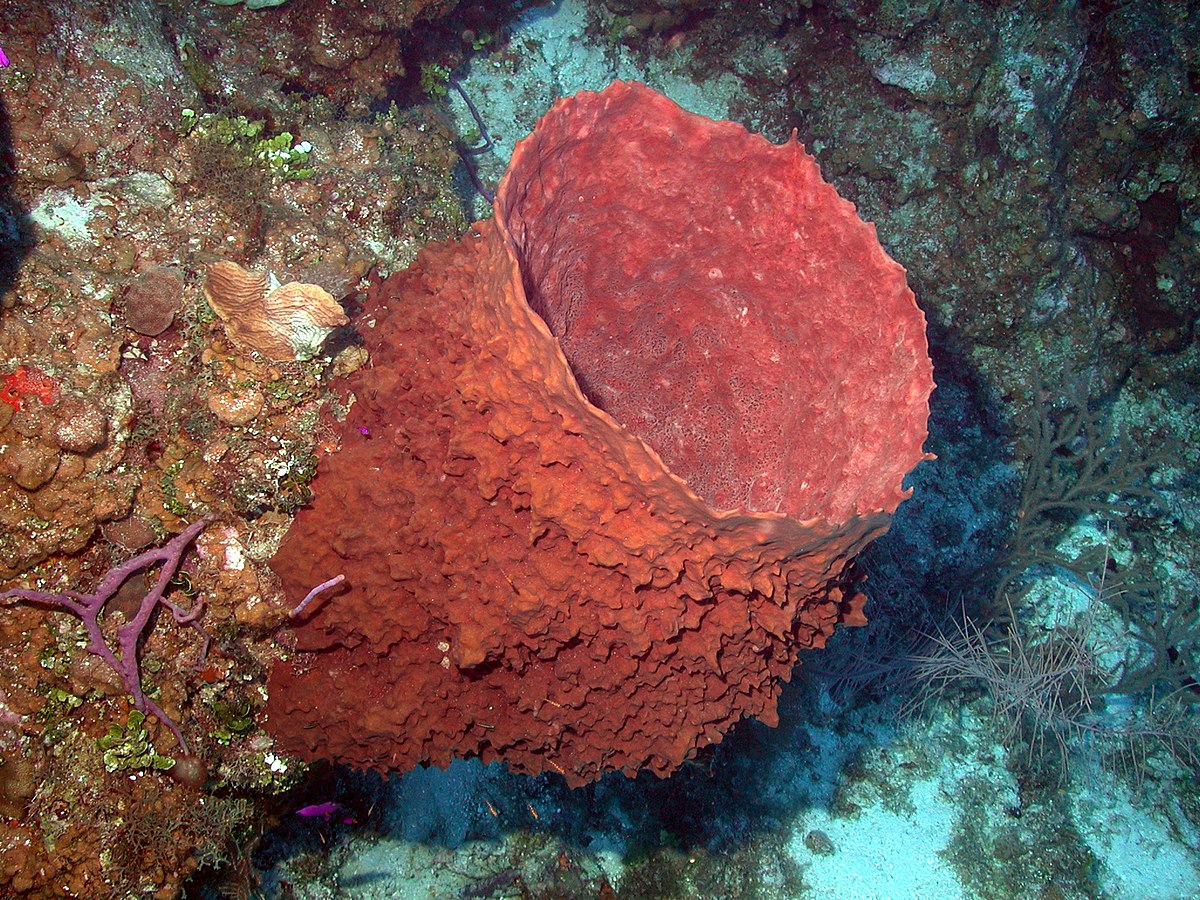

Giant Barrel Sponge (Xestospongia muta)