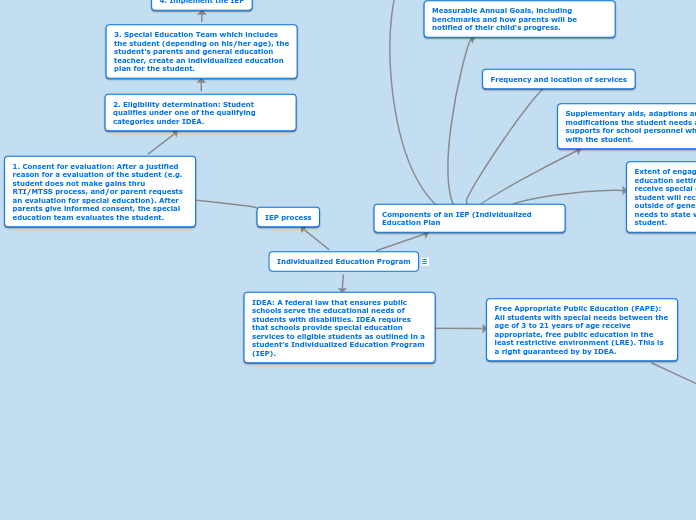
Individualized Education Program
IDEA: A federal law that ensures public schools serve the educational needs of students with disabilities. IDEA requires that schools provide special education services to eligible students as outlined in a student’s Individualized Education Program (IEP).
Free Appropriate Public Education (FAPE): All students with special needs between the age of 3 to 21 years of age receive appropriate, free public education in the least restrictive environment (LRE). This is a right guaranteed by by IDEA.
Least Restrictive Environment (LRE): Students with disabilities should be educated to the maximum extent possible in the general education setting, with students who do not receive special education services; given supplementary aids/modifications as determined by the student's individualized education plan (IEP).
Inclusion
IEP process
1. Consent for evaluation: After a justified reason for a evaluation of the student (e.g. student does not make gains thru RTI/MTSS process, and/or parent requests an evaluation for special education). After parents give informed consent, the special education team evaluates the student.
2. Eligibility determination: Student qualifies under one of the qualifying categories under IDEA.
3. Special Education Team which includes the student (depending on his/her age), the student's parents and general education teacher, create an individualized education plan for the student.
4. Implement the IEP
Components of an IEP (Individualized Education Plan
Present Levels of Academic Achievement and Functional Performance (PLAAP)
Supplementary aids, adaptions and/or modifications the student needs and/or supports for school personnel who work with the student.
Measurable Annual Goals, including benchmarks and how parents will be notified of their child's progress.
Frequency and location of services
Extent of engagement within the general education setting with students who do not receive special education services. If student will receive seperate schooling (or outside of general education), the team needs to state why this is necessary for the student.