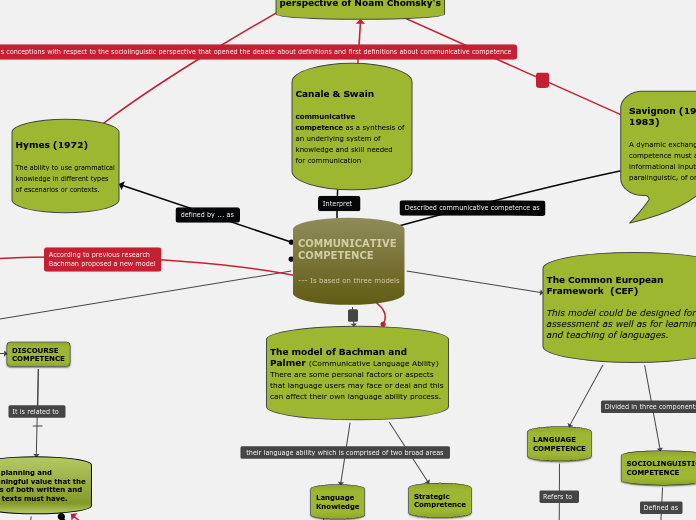
COMMUNICATIVE
COMPETENCE
--- Is based on three models
The model of Canale
and Swain
GRAMMATICAL
COMPETENCE
" enables the speaker to use knowledge and skills needed for understanding and expressing the literal meaning of utterances"
GRAMMATICAL KNOWLEDGE
- Vocbulary knowledge
- morphological knowledge
- syntactic knowledge
- semantic knowledge
- phonetic and orthographic
rules.
STRATEGIC
COMPETENCE
" Knowledge of verbal and non-verbal communication strategies that are recalled to compensate for breakdowns in communication"
Subtopic
- paraphrase
- circumlocution,
- Repetition
- Reluctance
- Avoidance of words, structures or themes, etc.
SOCIOLINGUISTIC
COMPETENCE
The idea of this competence is to promote knowledge of the language through the use of utterances in different contexts.
DISCOURSE
COMPETENCE
The planning and meaningful value that the units of both written and oral texts must have.
Coherence
The use of cohesion devices (e.g. pronouns, conjunctions, synonyms, parallel structures etc.)
The model of Bachman and Palmer (Communicative Language Ability)
There are some personal factors or aspects that language users may face or deal and this can affect their own language ability process.
Language
Knowledge
PRAGMATICAL
KNOWLEDGE
Abilities for creating and interpreting discourse.
SOCIOLINGUISTIC
KNOWLEDGE
ORGANISATIONAL
KNOWLEDGE
Different skills that support the control of formal structures (GRAMMATICAL AND TEXTUAL KNOWLEDGE)
Strategic
Compretence
"Defined as a set of metacognitive
components which enable language user involvement in goal setting, assessment
of communicative sources, and planning. "
The Common European Framework (CEF)
This model could be designed for assessment as well as for learning and teaching of languages.
LANGUAGE
COMPETENCE
Knowledge of and ability to use language resources to form well structured messages.
- Lexical competences
- Grammatical competences
- Semantic competences
- Phonological competences
- Orrthographic and orthoepic competences
PRAGMATICAL
COMPETENCE
DISCOURSE
COMPETENCE
SOCIOLINGUISTIC
COMPETENCE
Mastery of skills and knowledge for the appropriate use of the language in a given context.