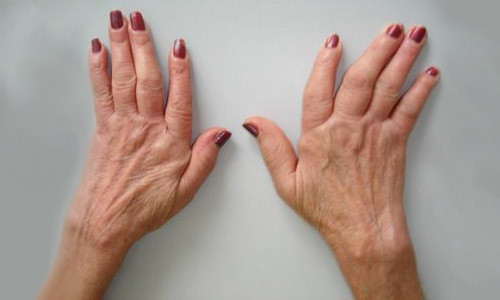
ARTRITIS

TRATAMIENTO

OBJETIVOS
Disminuir dolor
Disminuir inflamación
Conservación de la funcionalidad
Rsolución de complicaciones extrarticulares
Educación del paciente y la familia
Medicamentos
AINES
Glucocorticoides
Antirreumáticos
Inflitraciones
Cirugía
Artroscopía
FISIOTERAPÉUTICO

Reposo
Modalidades terapéuticas

Termoterapia
Crioterapia
TENS
Modalidades Cinéticas

Cineciterapia activa

Fuerza muscular

Flexibilidad

Mecanoterapia

Ejercicios isométricos

Ejercicio dinámico

Ejercicio aeróbico
¿ QUE ES?

INFLAMACIÓN DE UNA ARTICULACIÓN
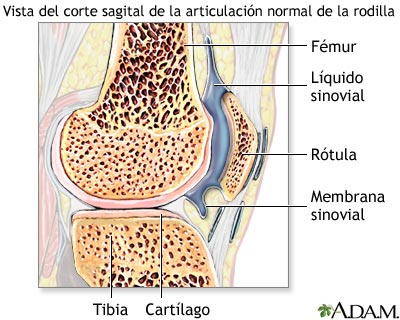
SE DA EN LA MEMBRANA SINOVIAL
DE TIPO DESCONOCIDO
CRÓNICA
SUELE DARSE ENTRE LOS 30-40 AÑOS
PREVALENCIA
1% de la población
las mujeres tienen mayor riesgo de padecer la enfermedad
entre los 60-64 años
factores ambientales
el clima y la urbanización
aumenta la insidencia

TIPOS
TRAUMÁTICA
microtraumatismos mantenidos en niños deportistas
TEMPORAL
inflamación de vasos angíneos
OSTEOARTRITIS
afecta el cartilago
dolor
rigidez

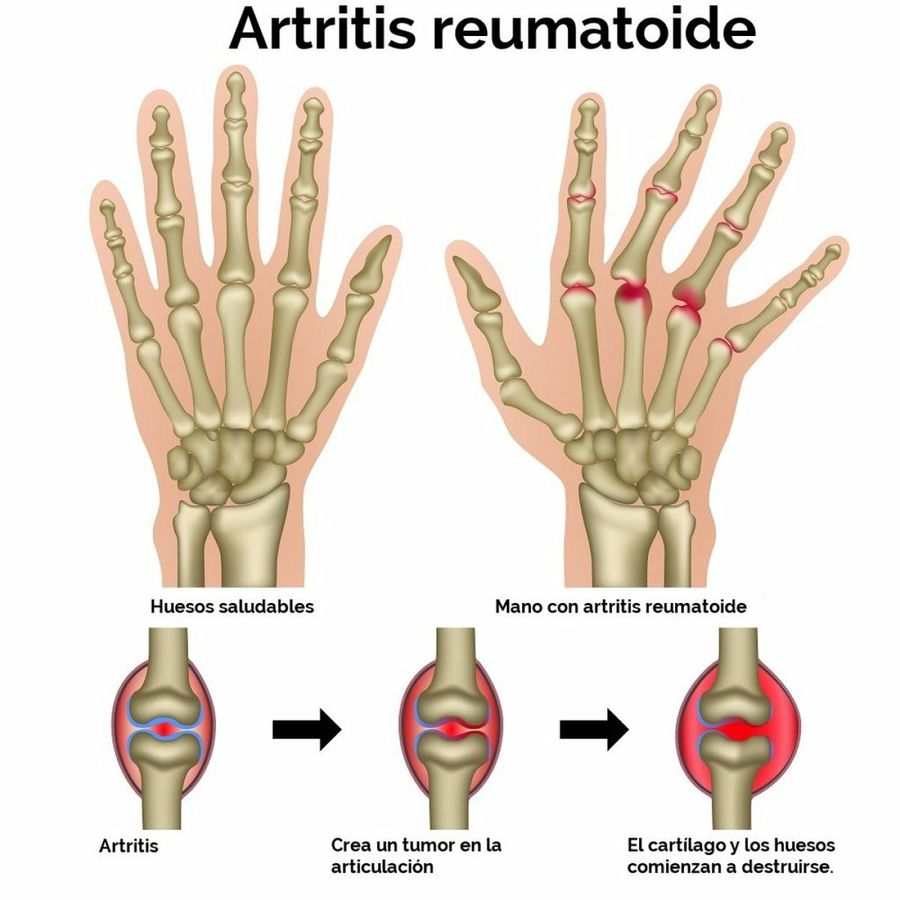
REUMATOIDE
inflamación crónica
afecta varias articulaciones
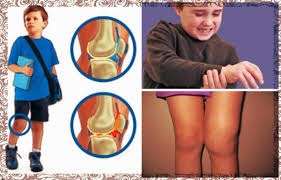
JUVENIL
se da antes de los 16 años
incapacidad
poliartritis crónica
se detectan 7 tipos según
patrón de aparición
sistémica poliarticular
presencia o ausencia de factor reumatoide
psoriasis

MONOARTRITIS
tumefación o limitación articular por dolor de una solo articulación
HEMOFILIA
defiicit factores de coagulación
TUMORAL

CAUSAS

INFECCIÓNES
FIEBRE MALTA

enfermedad infecciosa transmitida por un animal portador

TUBERCULOSIS
enfermedad bacteriana que afecta los pulmones
TRASTORNOS DE BASE GENÉTICA

predisposición genética
ENFERMEDADES AUTOINMUNES

CANCER

ENFERMEDADES ENDOCRINAS
post-parto
hormona femenina
menopaucia
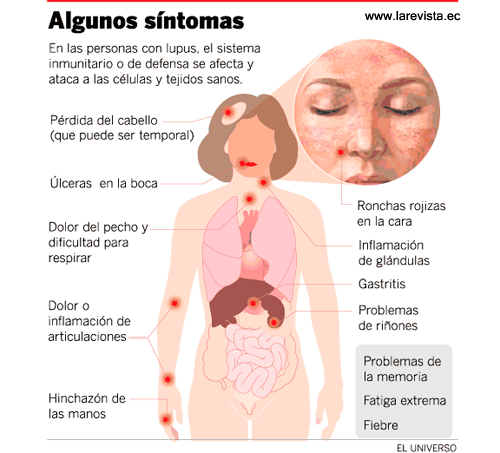
LUPUS
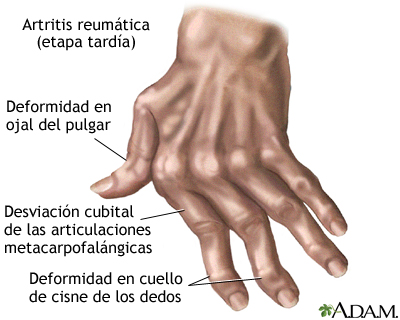
DEFORMIDADES
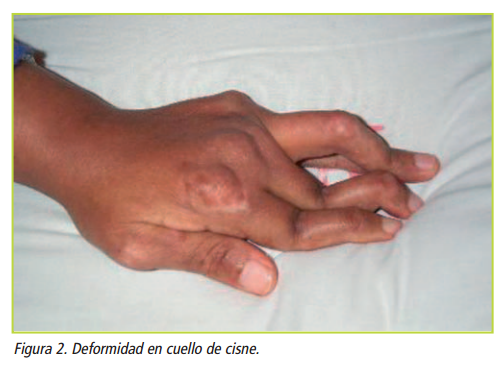
CUELLO DE CISNE
Hiperextensión de IFP
Flexión falange distal
DEFORMACIÓN EN "Z"

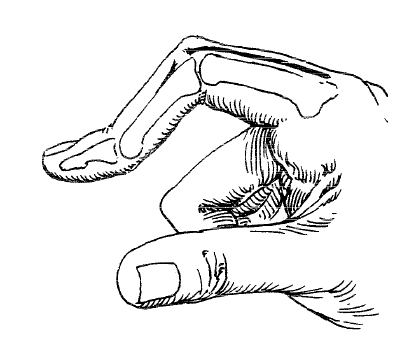
DEDO EN OJAL
flexión IFP
Hiperextensión FD

DEDOS EN RAFAGA
Desviación cubital

PIE TRIANGULO
Subtema

PATOGÉNESIS
LOCALIZACIÓN DE LEUCOCITOS EN LIQUIDO SINOVIAL
PRODUCIENDO DOLOR E INFLAMACIÓN
PRODUCEN ACTIVACIÓN DE CITOQUINAS
INICIA INFLAMACIÓN
AUMENTO LIQUIDO SINOVIAL

LAS CÉLULAS T
entran hacia el liquido sinovial
produce citoquinas
encargadas de la respuesta inmune y hematopoyesis
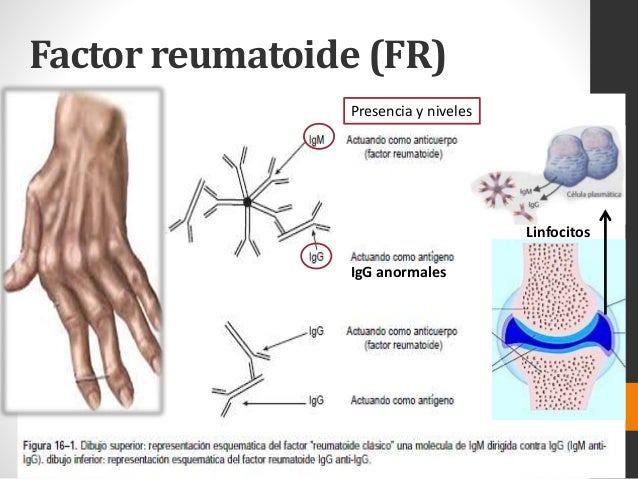
AUMENTO DEL FACTOR REUMATOIDEO
globulina anormal

ACTIVACIÓN DE MACRÓFAGOS,LINFOCITOS Y FIBROBLÁSTOS
genera aumento de la vascularidad

CLASIFICACIÓN

SEGÚN CAPACIDAD FUNCIONAL
CLASE I
NINGUNA LIMITACIÓN FUNCIONAL
CLASE II
RESTRICCIÓN MODERADA
CLASE III
RESTRICCIÓN CONSIDERABLE
CLASE IV
INCAPACIDAD
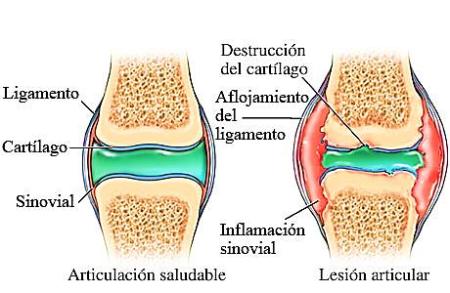
EL SISTEMA INMUNE CAUSA DESTRUCCIÓN DEL CARTÍLAGO
atacando por tanto tejidos sanos y no microorganismos
Topic principal

MEDIOS DIAGNOSTICOS

RADIOGRAFÍA
disminución espacio articular
quistes subcorticales
bordes imprecisos

ANÁLISIS DE SANGRE
VELOCIDAD DE SEDIMENTACIÓN
DETERMINA LA INFLAMACIÓN

ANTICUERPOS
FACTOR REUMATOIDEO
anticuerpo elevado

ECOGRAFÍA
sinovitis avanzada
inflamación de la membrana sinovial
derrame articular
Hiperhemia

RESONANCIA MAGNETICA

SIGNOS Y SINTOMAS
ARTICULAR

DOLOR
AUMENTA CON EL MOVIMIENTO

TUMEFACCIÓN

RIGIDEZ
SE DA EN LAS MAÑANAS
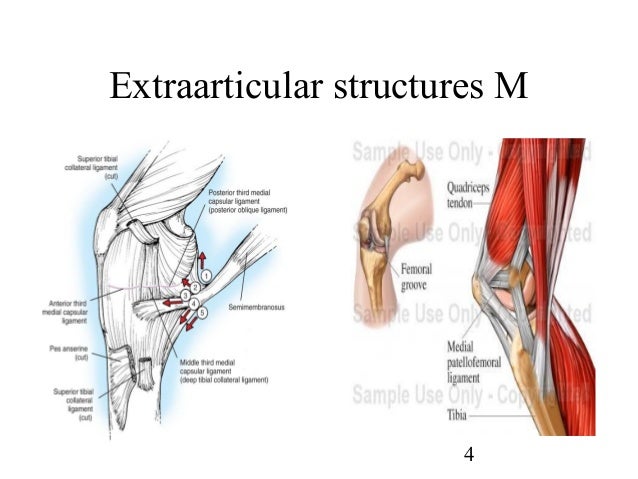
EXTRAARTICULAR

NODULOS
APARECE EN ESTRUCTURAS PERIARTICULARES

INFLAMACIÓN

FATIGA
PROBLEMAS DEL SUEÑO
AFECCIONES PULMONARES

FIEBRE
HIPERSENSIBILIDAD
CALOR EN LA ZONA
BIBLIOGRAFÍA
J.Banilla.(2015).Artritis reumatoidea. Guía de la enfermedad. Sociedad Española de Reumatología. Recuperado de: https://inforeuma.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/Guia_Artritis.pdf
Sociedad española de reumatología.(2015).¿Que es la artritis?.cap.41 .Recuperado de: https://inforeuma.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/41.pdf
Dra. Vallejo.(2013).Artritis Reumatoide.Recuperado de: https://es.slideshare.net/R0SIA/radiologia-artritis-reumatoide
Gobierno federal.(S.F).Guía de referencia rápida.Diagnostico y tratamiento de artritis reumatoide del adulto.Guía de practica clínica. Recuperado de: http://www.cenetec.salud.gob.mx/descargas/gpc/CatalogoMaestro/195_ARTRITIS_REUMATOIDE/artritis_reumatoide_RR_CENETEC.pdf
M.García.S. Quesada.(2004).Artritis reumatoide fisiopatología y tratamiento. Centro de información de medicamentos.Recuperado de: http://www.discapacidadonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/12/artritis-reumatoide-fisiopatologia-tratamiento.pdf