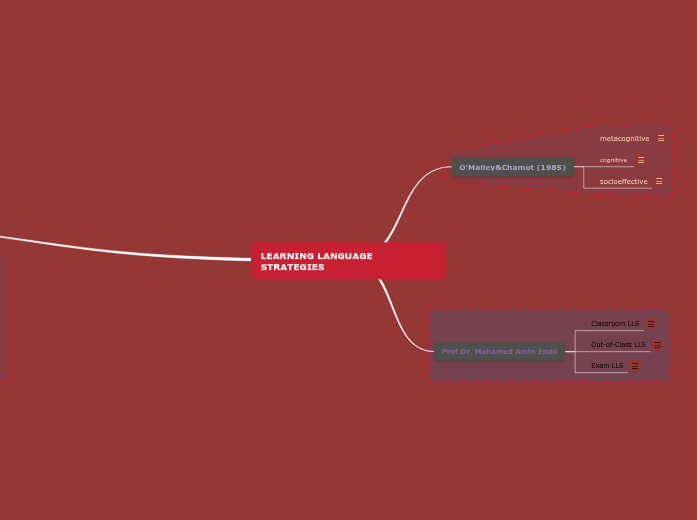
LEARNING LANGUAGE STRATEGIES
O'Malley&Chamot (1985)
metacognitive
cognitive
socioeffective
Prof.Dr. Mohamed Amin Embi
Classroom LLS
Out-of-Class LLS
Exam LLS
Oxford (1990)
TWO major classes:
1).DIRECT STRATEGIES
a).MEMORY STRATEGIES
b).COGNITIVE STRATEGIES
c).COMPENSATION STRATEGIES
2).INDIRECT STRATEGIES
a).METACOGNITIVE STRATEGIES
b). AFFECTIVE STRATEGIES
SOCIAL STRATEGIES