Fluids
Chapter 8
Viscosity
Viscosity is the resistance of a fluid to flow. Fluids with high viscosity do not flow as easily as fluids with a low viscosity.
Friction is a force that works to slow down motion as a result of surfaces rubbing against each other. The greater the friction or rubbing, the higher the viscosity. A fluid with a high viscosity has a large amount of internal friction.
When heat is added to a liquid, the particles move faster and spread farther apart. Since the distance between particles has increased, there is less attraction between the particles. As the temperature of a liquid increases, its viscosity decreases. As a result, the fluid flows more easily. As the temperature of a liquid decreases, the particles slow down. The result is that the viscosity increases.
Density & Buoyancy
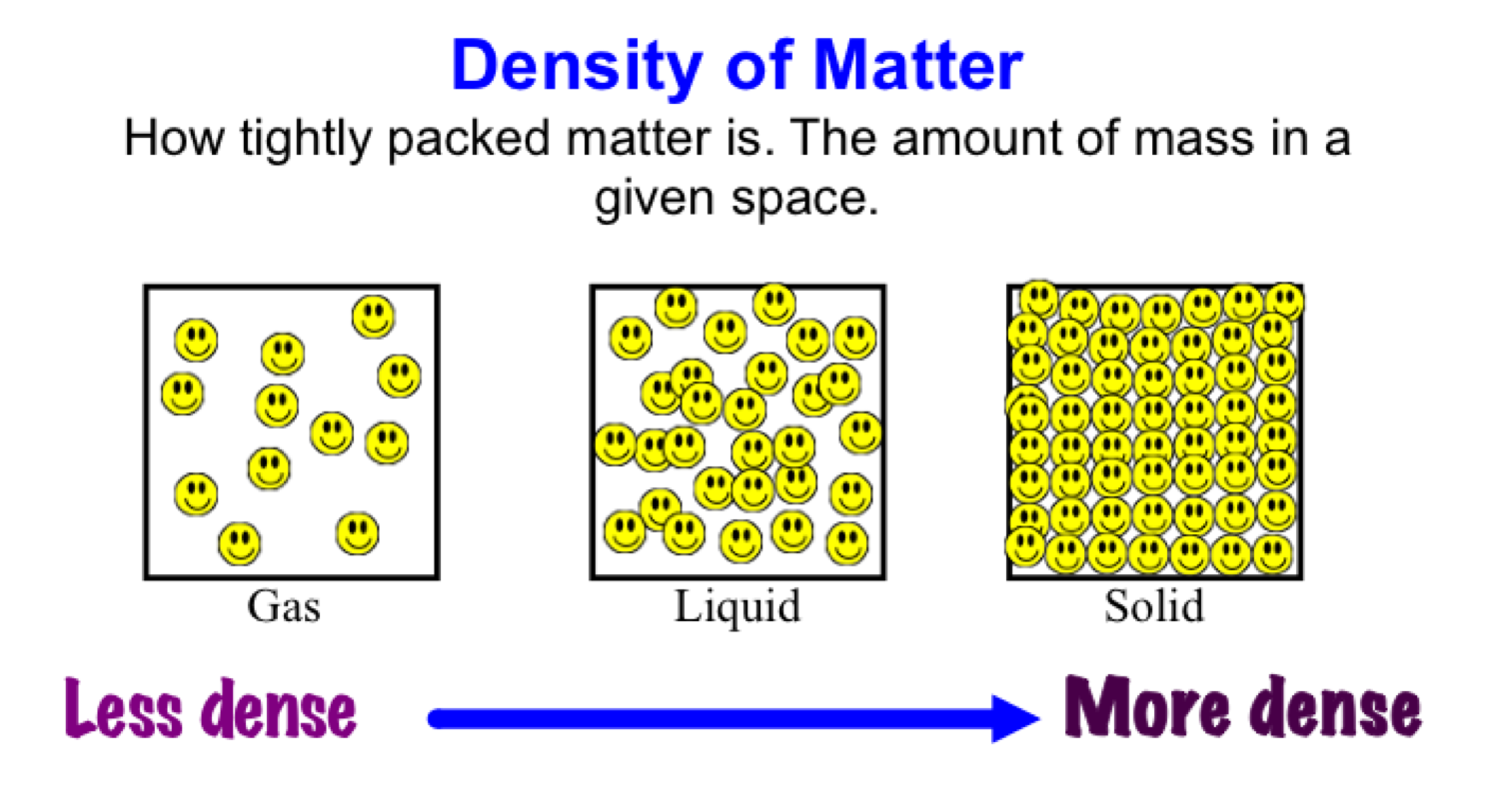
Density describes how closely packed together the particles are in a substance.
A substance is most dense when it is a solid and less dense when it is a gas. A solid is denser than a gas because the particles in a solid are much closer together
Buoyancy is the tendency of an object in a fluid to rise or sink due to density differences with its surroundings.
Buoyant Force is the upward force exerted by a fluid.

Pressure in Fluids
Pressure is the amount of force applied to a given area. There is less air pressure if we travel to higher altitudes because there are fewer layers of air above us and the air there is less dense.
Pressure increases with the depth of a fluid. A fluid flows from an area of higher pressure to an area of lower pressure.undefined
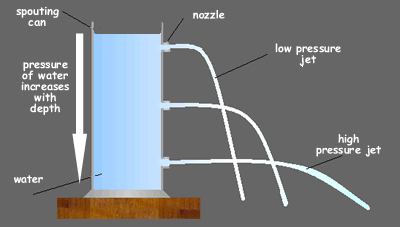
If a force compresses the particles of a fluid, the volume of the fluid is reduced. When the volume is reduced and the temperature stays the same, the pressure inside the fluid increases.
Chapter 7
The Many uses of Fluids
A fluid is any substance that flows.
Fluids have many uses, including holding and transporting other materials.
Substances in their fluid form can be shaped and then cooled to become solids.
Fluids for life, so that we can stay alive.
Oxygen:
Helps the body get energy from food
Blood:
Moves materials into cells and moves waste out of cells
Sweat:
Cools the body
Urine:
Takes waste out of the body
Stomach acids:
Helps the body digest food
We find fluids everywhere in our lives. Fluids can be a gas or a liquid. Some fluids that are gases that we can use everyday are leaf blowers, and some liquids that we use everyday are gas for our cars.

Leaf blower

Gas for our cars
The liquids you drink, the blood that pumps through your body, and the air you breathe are all fluids that you use on a daily. Some other examples are shampoo and toothpaste.

Shampoo is a fluid that you use everyday

Toothpaste is another fluid that you use every day
Fluids can transport solids
A slurry is a mixture of solids and water and is used to transport solids.undefined
Ex #1 the paper you write on was once a slurry - was once wood pulp and water
Ex #2 Hydroseeding- spraying seeds, fertilizer and sawdust for farming
Fluids and the Particle Theory
Matter is anything that has both mass and volume. Matter can be a gas, a solid, or a liquid.
Water is an example of matter that can exist in all three states, or forms.
Water is part of the air we breathe, the ice we skate on, and the pools we swim in.
Air, ice, and water are examples of the three states of matter.
The particle theory of matter
is a set of ideas that can help you understand matter. It can help you predict how different materials and substances will behave.
1. All matter is made of tiny particles.
2. Particles are constantly in motion.
3. All of the particles of one substance are exactly the same.
4. Temperature affects how quickly or slowly particles move.
5. In liquids and solids, the particles are close together. They are very attracted to each other.
6. In a gas, the particles are farther apart. They are slightly attracted to each other.
Thermal Expansion and Contraction
When a substance becomes warmer, its particles move faster and farther apart, causing the substance to expand, or increase in volume. This response to an increase in temperature is called thermal expansion.
When a substance cools, its particles move more slowly and closer together, causing the substance to contract, or decrease in volume.
The decrease in volume is due to a decrease in the temperature of the substance.
Cracks in the road when the road expands on heating is an example of thermal expansion.
Chapter 9
Fluid System
Is a group of parts, including at least one fluid, that interact with each other and function together as a whole.
An example in nature is the movement of sea stars.undefined

Hydraulic systems
Are systems that use a liquid under pressure to transmit a force and do work.
An example is the Jaws of Life©

Liquids cannot be compressed: meaning that when pressure is applied to a liquid in a pipe or tube, the force can be transmitted over a distance.
Hydraulic systems have the ability to multiply the force exerted by a liquid.
Hoists use two pistons of different sizes to create pressure to lift a vehicle.
Pistons are a disk that move inside a cylinder.

Pneumatic systems
Is a system that uses a gas, usually air, under pressure to transmit a force.
Two advantages of pneumatic systems are safety and reasonable costs.
Compressed air is safe to use, as the devices do not create sparks.
Larger temperature range than are hydraulic systems.
An example is a dentist drill.

Pumps
Is a device that moves a fluid through or into something.
An example is our heart. It pumps blood to your lungs for oxygen and then pumps the blood through your body.undefined
Some pumps can raise water from a lower elevation to a higher elevation. Other pumps can force air into a bicycle tire or oil through a car’s engine.undefined
Another example of a pump is the Archimedes screw pump.

Valves
Are devices that control the flow of fluids.
An example could be our heart and blood vessels. Many veins in your body contain one-way valves that ensure that your blood flows in the correct direction.undefined

Controls the amount of water flowing through a faucet. Turning a tap one way allows water to flow out. Turning a tap the other way closes off the flow of water.undefined

Pascal's Law
States that when force is applied to an enclosed fluid, the increase in pressure is transmitted equally to all parts of the fluid.
An example is when you have squeeze the end of a toothpaste tube and watch the fluid push out of the opening.

If you have press on one end of an air mattress to push the air out of the opening at the other end.

Oil Spills
Clean-up Methods
The fact that oil floats on water makes the clean-up easier. Even though the oil floats, if the surface of the water is moving quickly, the oil can “mix” with the water.undefined
On a large body of water, such as an ocean or lake, waves can cause the oil to mix temporarily with the water.undefined
Damage depends on factors like the type of oil, the location of the spill, and the size of the spill.undefined
Waves and wind also have an effect on the amount of environmental damage. Oil spills affect the marine environment
Clean-up methods
Booms
Booms are large, floating barriers that act like a fence to contain the oil. (Oil is easier to clean up if it is contained in one area)

DISADVANTAGES
- water is not calm; the oil will eventually mix with the water
- Isn’t effective with violent waters
- Only contains; doesn’t remove
Skimmers
Skimmers are machines like vacuum cleaners that pull up the oil from the surface of the water

DISADVANTAGES
- If the water is not calm, you can’t suck up the oil and it will just mixed up with the water
- Mixing with the water affects our drinking water sources
- Can become clogged
- Only works on the surface
Sorbents
Sorbents are large, sponge-like materials that absorb the oil.

DISADVANTAGES - If the oil sinks to the bottom of the water then it will be harder to remove oil
- Spreads oil through water
- Kills plants and animals
Dispersants
Dispersants are chemicals that act like detergents and break the layer of oil into smaller pieces.undefined

DISADVANTAGES - Marine animals can eat the tiny pieces filled with chemicals and oil
- Could kill plants and animals out of water
- This poisons them; eventually - if not immediately killing them
Burning
Burning the oil can remove over 90% of the spill.

DISADVANTAGES - If it is windy, the fire won’t stay put and will not work effectively
- It has to be a certain amount of thickness for the burning process to work
- Can cause air pollution; contaminating air for people, plant, and animals
Bioremediation
Bioremediation involves using bacteria and fungi to break down oil.

DISADVANTAGES - Plants growing near the water the fertilizers will grow excessively
- Slow process
- Bacteria and fungi will harm the environment
Oil spills on water
Oil spills are the most common pollutant of water.
51% is from down drainage systems
2% offshore drilling