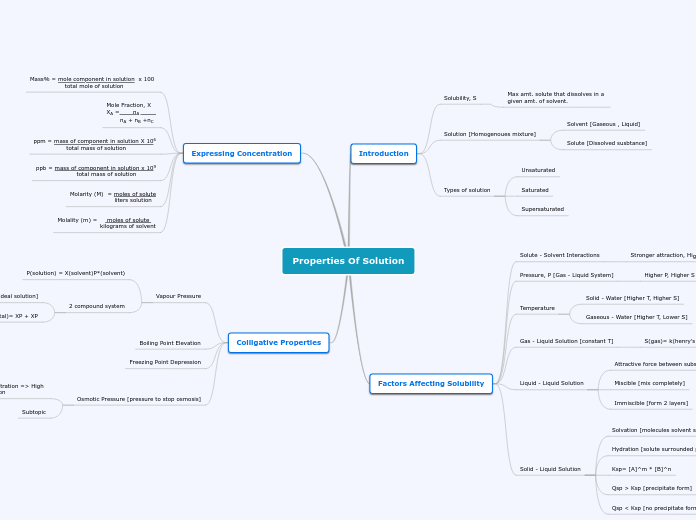
Properties Of Solution
Introduction
Solubility, S
Max amt. solute that dissolves in a
given amt. of solvent.
Solution [Homogenoues mixture]
Solvent [Gaseous , Liquid]
Solute [Dissolved susbtance]
Types of solution
Unsaturated
Saturated
Supersaturated
Factors Affecting Solubility
Solute - Solvent Interactions
Stronger attraction, Higher S
Pressure, P [Gas - Liquid System]
Higher P, Higher S
Temperature
Solid - Water [Higher T, Higher S]
Gaseous - Water [Higher T, Lower S]
Gas - Liquid Solution [constant T]
S(gas)= k(henry's law)* P(gas)
Liquid - Liquid Solution
Attractive force between substances
Miscible [mix completely]
Immiscible [form 2 layers]
Solid - Liquid Solution
Solvation [molecules solvent surround molecules solute]
Hydration [solute surrounded by water molecules]
Ksp= [A]^m * [B]^n
Qsp > Ksp [precipitate form]
Qsp < Ksp [no precipitate form]
Expressing Concentration
Mass% = mole component in solution x 100
total mole of solution
Mole Fraction, X
XA = nA
nA + nB +nC
ppm = mass of component in solution X 106
total mass of solution
ppb = mass of component in solution x 109
total mass of solutionundefined
Molarity (M) = moles of solute
liters solution
Molality (m) = moles of solute
kilograms of solvent
Colligative Properties
Vapour Pressure
P(solution) = X(solvent)P*(solvent)
2 compound system
Raoult's Law [ideal solution]
P(total)= XP + XP
Boiling Point Elevation
Freezing Point Depression
Osmotic Pressure [pressure to stop osmosis]
Low solute concentration => High
solute concentration
Subtopic