Climate Mind Map
Weather and Climate
Weather is the atmospheric conditions over a short period of time.
Weather can be described by temperature, precipitation, wind, humidity, and atmospheric pressure.
Climate is the average of the weather over a long period of time. The climate determines the types of plant and animal species that live in a certain region.
Latitude, presence of a body of water, altitude, presence of ocean and air currents, and land formations are factors that affect the climate.
Sun and Earth's Climate System
The climate system is a complex set of components that interact with each other to produce Earth's climate.
The components include the atmosphere (gases), hydrosphere (water, ice, vapour), lithosphere (land surfaces, Earth's rock crust), and the biosphere (plants, animals, etc).
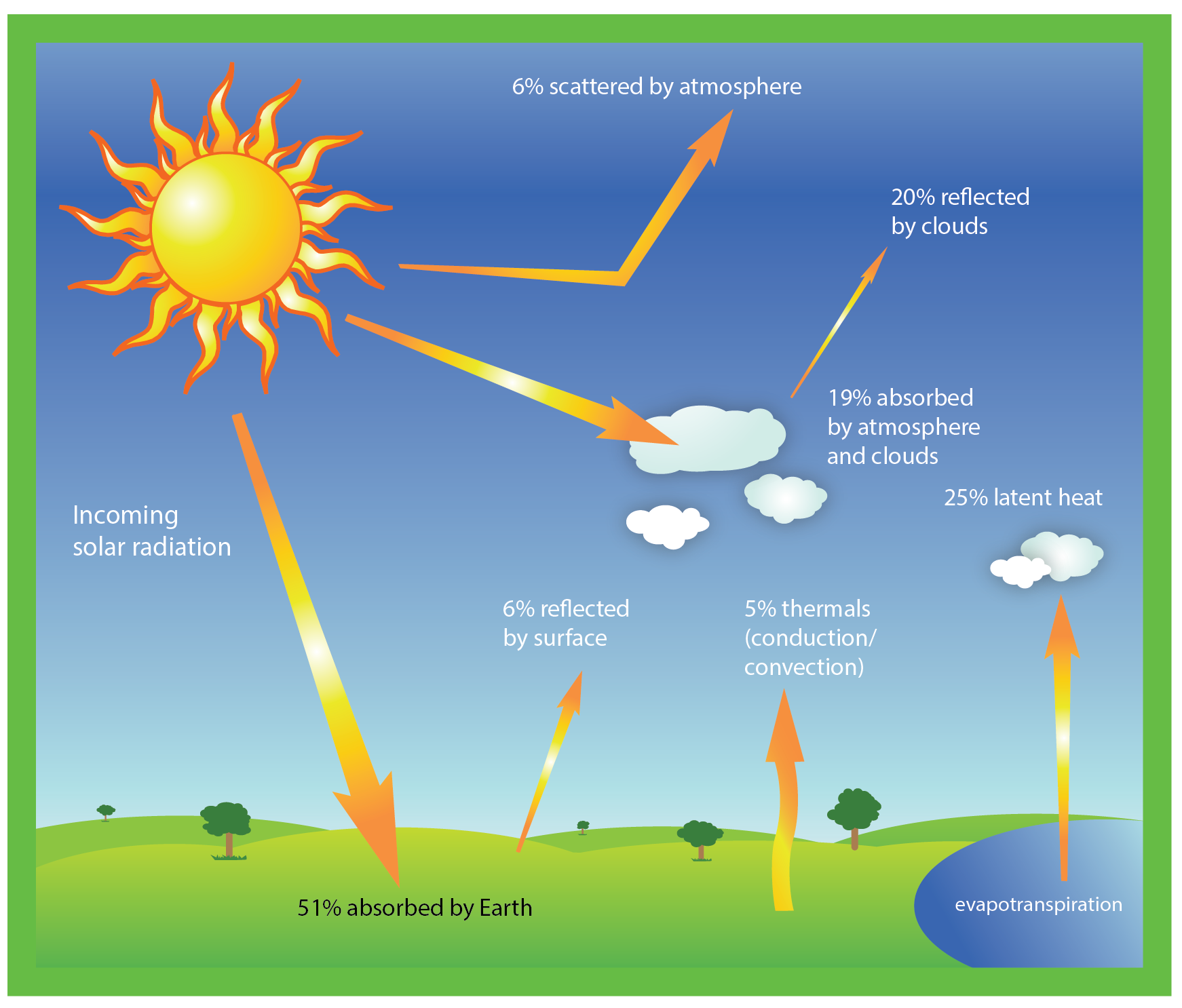
Earth's Energy Absorption from the Sun
Earth's surface gains thermal energy from the sun, and converts it into low-energy infrared radiation.
Subtopic
The amount of energy radiated by Earth is equal to the amount of energy that is absorbed by the Earth from the sun.
This balance between the amount of energy absorbed and emitted by Earth is what keeps the global temperature fairly constant.
Climate Zones
Earth's equator receives more intense energy from the sun, because it receives direct sunlight.
Earth's poles receive less intense energy, because they get indirect sunlight from the sun.
The Greenhouse Effect
Is a natural process that moderates Earth's temperature by trapping and storing energy from the sun and distributes it around the world.

Greenhouse Gases
Gases in the atmosphere that trap heat and keep the Earth warm - they absorb lower energy infrared radiation emitted from the Earth's surface and radiate it.
Carbon dioxide, water vapour, methane, ozone, and nitrous oxide.
Feedback loops
Positive feedback loops are when the product of a reaction leads to an increase in that reaction, which leads to an ongoing cycle.
Negative feedback loops are a self regulating system that maintains sustainability.
Anthropogenic Greenhouse Effect
Is the increase of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere due to human activities. It is causing the Earth's average global temperature to rise.
Sources
Burning fossil fuels, and deforestation causes an increase in carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Agricultural activities, landfills, sewage treatment, coal mining, and natural gas extractions is increasing the amount of methane in the atmosphere.
Use of nitrogen fertilizers, fossil fuel combustion, and livestock manure causes an increase of nitrous oxide in the atmosphere.
CFCs leak out of refrigerators and air conditioners into the atmosphere.
Beef and cattle production increases methane emission, deforestation, and causes degradation of soil.
Indicators of Climate Change
Heat Waves
Warming temperatures are causing the soil, lakes, and rivers to warm up.
Extreme heat can worsen or cause drought. Hot and dry conditions can cause other disasters such as wildfires.
Permafrost is defrosting much more, causing the soil to loosen and destabilize the trees.
Drought
Hotter weather can cause more water to evaporate from the soil.
Dry regions with low precipitation are most severely affected.
This can also change the atmospheric rivers, which affects the precipitation alters of other regions.
Causes a positive feedback loop because there isn’t enough rain, so plants die off, which limits how much water vapor is added to the air. This further suppresses rainfall.
Wildfires
The risk of wildfires increases as the weather becomes more dry and hot.
Heat, wind, and humidity are all factors of wildfires.
Climate change caused by anthropogenic sources has worsened wildfires by 30%.
Storms
Global warming can change and influence the frequency and severity of storms.
Warmer ocean temperatures can intensify tropic storm wind speeds, which would cause more damage if they make landfall.
Areas affected by hurricanes are shifting towards the south and north pole due to expanding tropics from higher global temperatures.
Melting Ice
As the temperature becomes warmer, both sea and glacier ice is melting.
Melting ice can change the coastlines and the shapes of continental coasts. This would also affect the habitats of shoreline species.
Could further cause flooding above sea level land, loss of properties, and create less accessible fresh water.
Floods
As melting ice can cause coastal floods, more prominent floods are caused seasonally.
When the weather warms to quickly in spring, the snow or ice can melt too quickly fro the rivers and streams to handle.
Seasonal floods can cause damage to homes/properties and cropland.
Changing Ocean Currents
Warmer temperatures can cause differences in the density of the water, which affects its current.
Ocean currents can change due to melting icebergs and glaciers that add fresh water to the oceans, which also causes differences in the waters density as it dilutes the salinity.
Warming Oceans
Warmer water causes the oceans to expand and increase sea levels. This affects the coastal land.
The hotter the water, the less carbon dioxide is retained.
Threatened Wildlife & Species
Climate change affects the habitats and lifestyles of many species.
Polar bears are unable to hunt their prey without sea ice, making them starve.
Earth is losing its coral reefs, which threatens many other marine species.
Wildfires can destroy the biodiversity in certain regions.
Discovering Past Climates
Proxy Records
They record weather data for a few hundred years to learn about Earth's past climate, and the changes that have happened.
People who study past climates are called paleoclimatologists.
Tree rings, ice cores, and fossils give clues to what the climate was like in the past.
Tree Rings
The amount that a tree grows each season (depending on the temperature and rainfall) is indicated by the size and colour of the annual rings in the tree trunk.
Tree trunks from archaeological sites show what the climate was like thousands of years ago.
Wide tree rings are produced in cool and wt weather, allowing the tree to grow fast.
Thin tree rings are produced in in hot and dry weather, causing the tree to grow slowly.
Dark rings indicate growth in later summer months, while light rings indicate growth during spring.
Ice Cores
Scientists study the thickness and composition of each ice layer in ice cores to better understand past climates.
They use a special drill that goes deep into they ice layers to extract long cylinder shapes pieces of ice to examine.
They can obtain information about past climates from hundred of thousands of years ago.
Dissolved and matter in the ice gives clues about past events and conditions.
You can get clues about volcanic eruptions, forest fires, meteorite impacts, etc by finding dust, ash, salts, etc from the samples.
The physical characteristics of the ice cores give an idea about the temperature and humidity of past climates.
The physical characteristics are the size and overall shape.
Trapped air bubbles indicate the amount of greenhouse gases in past climates.
Small air bubbles can get trapped in the ice as the water freeze over time.
The composition of the ice can indicate the temperature at the time the ice formed.
Water contains differing proportions of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes.
Water that contains oxygen-18 freezes at a higher temperature than water that has oxygen-16 (it evaporates more quickly).
The concentration of different isotopes in different ice layers allow scientists to observe temperature changes over many years.
Sedimentary Rocks
Annually, billions of tons of sediment get washed from the land into the ocean where the accumulate at the bottom.
The hard parts of small sea species and pollen from flowers get preserved in the sediments.
Over time, the sediments get compressed, and then harden in sedimentary rocks.
Scientists examine these rocks because they get evidence of past climates from up to a million years ago.
Sediment cores can give clues about the global temperature during a specific time, and the temperature of the water in which organisms lived.
Fossils
Are the remains or traces of living things that provide valuable clues about past climates.
Gives scientists clues about what environments were like thousands of millions of years ago
The types and abundance of fossilized remains in each rock layer help scientists reconstruct the environment at the time the layer and climate formed.