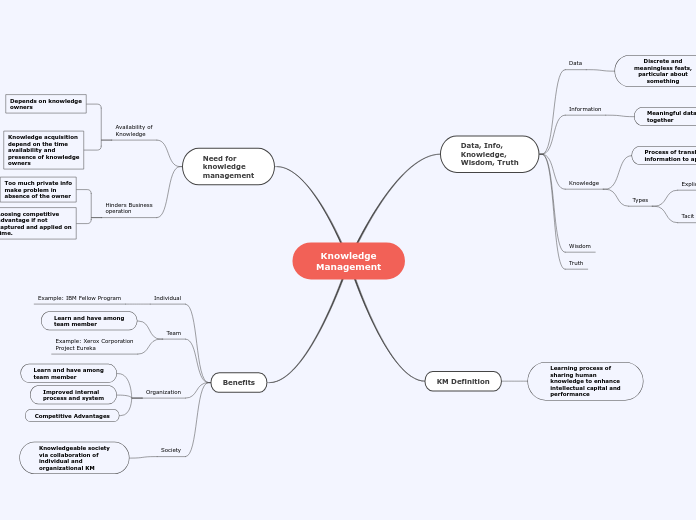
Knowledge
Management
Data, Info,
Knowledge,
Wisdom, Truth
Data
Discrete and
meaningless feats,
particular about
something
Information
Meaningful data put
together
Knowledge
Process of translating
information to apply
Types
Explicit 5%
Documented
Tacit 95%
Subjective knowledge
Wisdom
Truth
KM Definition
Learning process of
sharing human
knowledge to enhance
intellectual capital and
performance
Need for
knowledge
management
Availability of
Knowledge
Depends on knowledge
owners
Knowledge acquisition
depend on the time
availability and
presence of knowledge
owners
Hinders Business
operation
Too much private info
make problem in
absence of the owner
Loosing competitive
advantage if not
captured and applied on
time.
Benefits
Individual
Example: IBM Fellow Program
Team
Learn and have among
team member
Example: Xerox Corporation
Project Eureka
Organization
Learn and have among
team member
Improved internal
process and system
Competitive Advantages
Society
Knowledgeable society
via collaboration of
individual and
organizational KM