MOVIMIENTO CIRCULAR UNIFORME
Wade
Chandler's wobble is a small variation on the Earth's axis of rotation, discovered by American astronomer Seth Carlo Chandler in 1891. This is a variation of 0.7 arcseconds over a period of 433 days.
PRECES ION
Precession or precession motion nutation is the motion associated with the change of direction in space, which experiences the instantaneous axis of rotation of a body.

Period and frequency
Frequency
The frequency F measures the number of revolutions or turns completed by the mobile in the unit of time and is given by:

Therefore, the frequency is the inverse of the period:

Subtopic
Period
The period T represents the time needed for the mobile to complete a turn and is given by:

velocity
ANGULAR VELOCITY
Angular velocity is a measure of rotational velocity. It is defined as the angle rotated by a unit of time and is designated by the Greek letter ω. Its unit in the International System is the radian per second (rad/s).
The velocity is obtained from the position vector by tangecial derivation
LINEAR SPEED
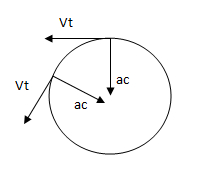
Linear velocity. It is one whose direction is always tangent to the trajectory of the rotating particle. This velocity has direction perpendicular to the axis of rotation (i.e. the vector ω) to the centripetal acceleration and the vector radius.

Subtopic
Centripetal acceleration
Centripetal acceleration (also called normal acceleration), is the acceleration that determines the change of direction of velocity in bodies rotating or moving along curved trajectories. This acceleration is called centripetal because it is always directed towards the center of rotation.
LINEAR SPEED
TANGENTIAL VELOCITY
The tangential velocity is equal to the angular velocity by radius. It is called tangential because it is tangent to the trajectory. The tangential velocity is a vector, which results from the vector product of the angular velocity vector (ω) by the position vector (r) referred to the point P.
Topic principal
NUTACION
Nutation is a slight irregular movement on the axis of rotation of symmetrical objects that rotate on their axis.