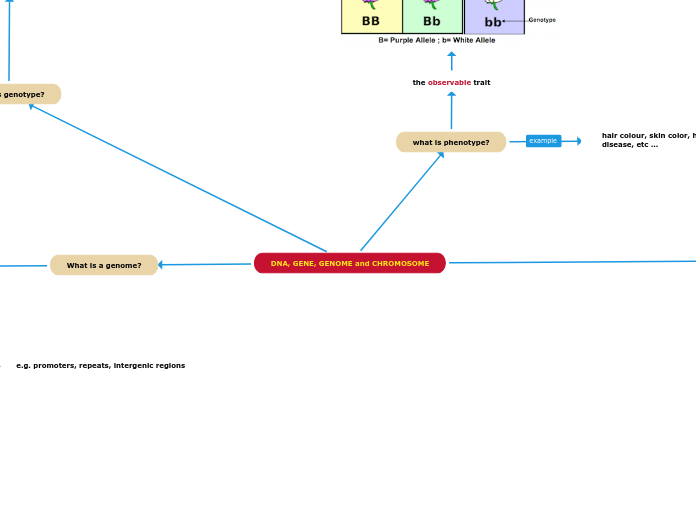
DNA, GENE, GENOME and CHROMOSOME
What is a genome?
the complete set of genetic material (DNA) in a cell
What is genetic material (DNA)?
genetic information that gets passed from one generation to the next
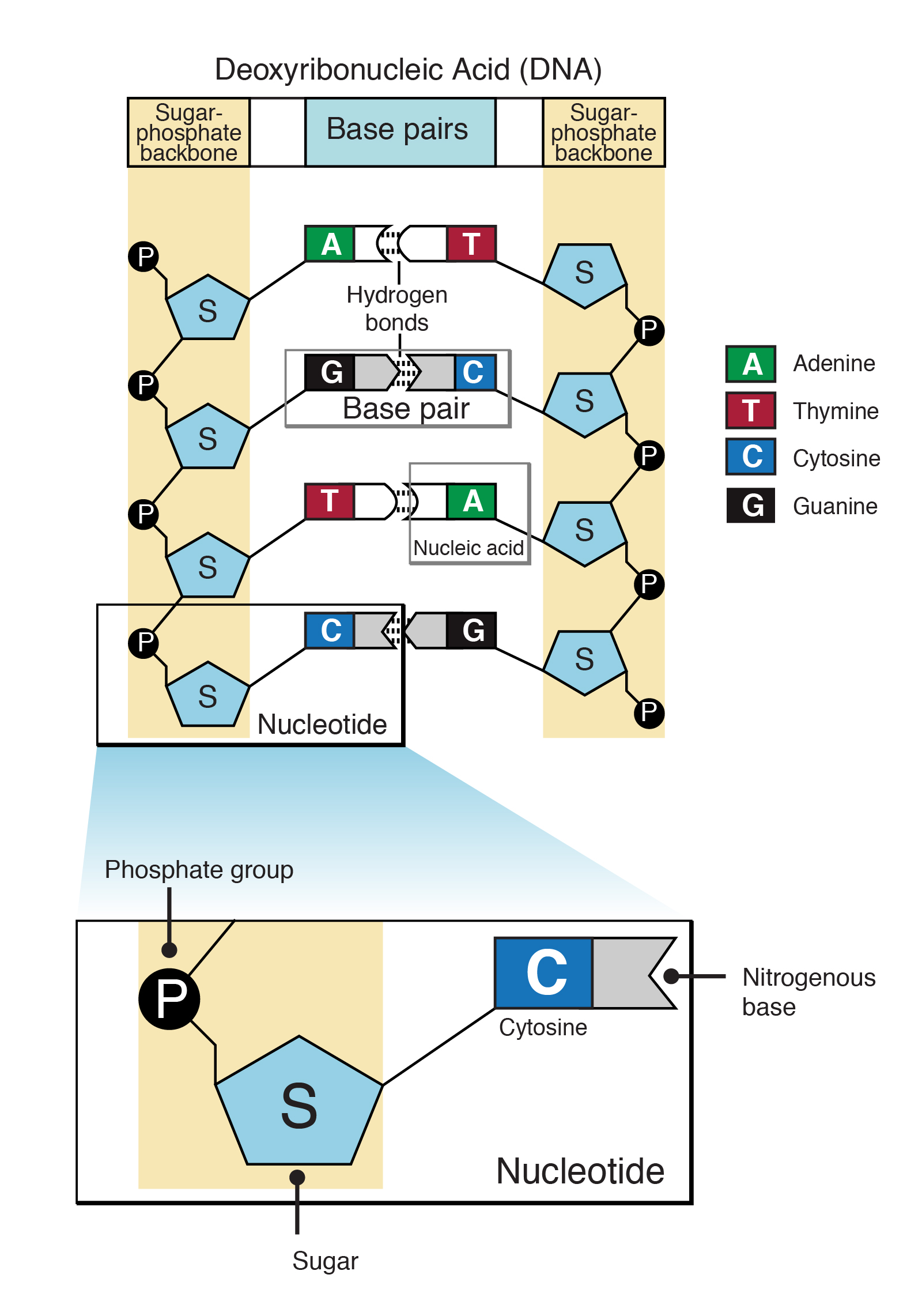
DNA = Deoxyribonucleic acid
consist of chemical blocks called nucleotides
What is nucleotide?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)
consists of a sugar molecule attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen base
4 common nitrogen bases for DNA
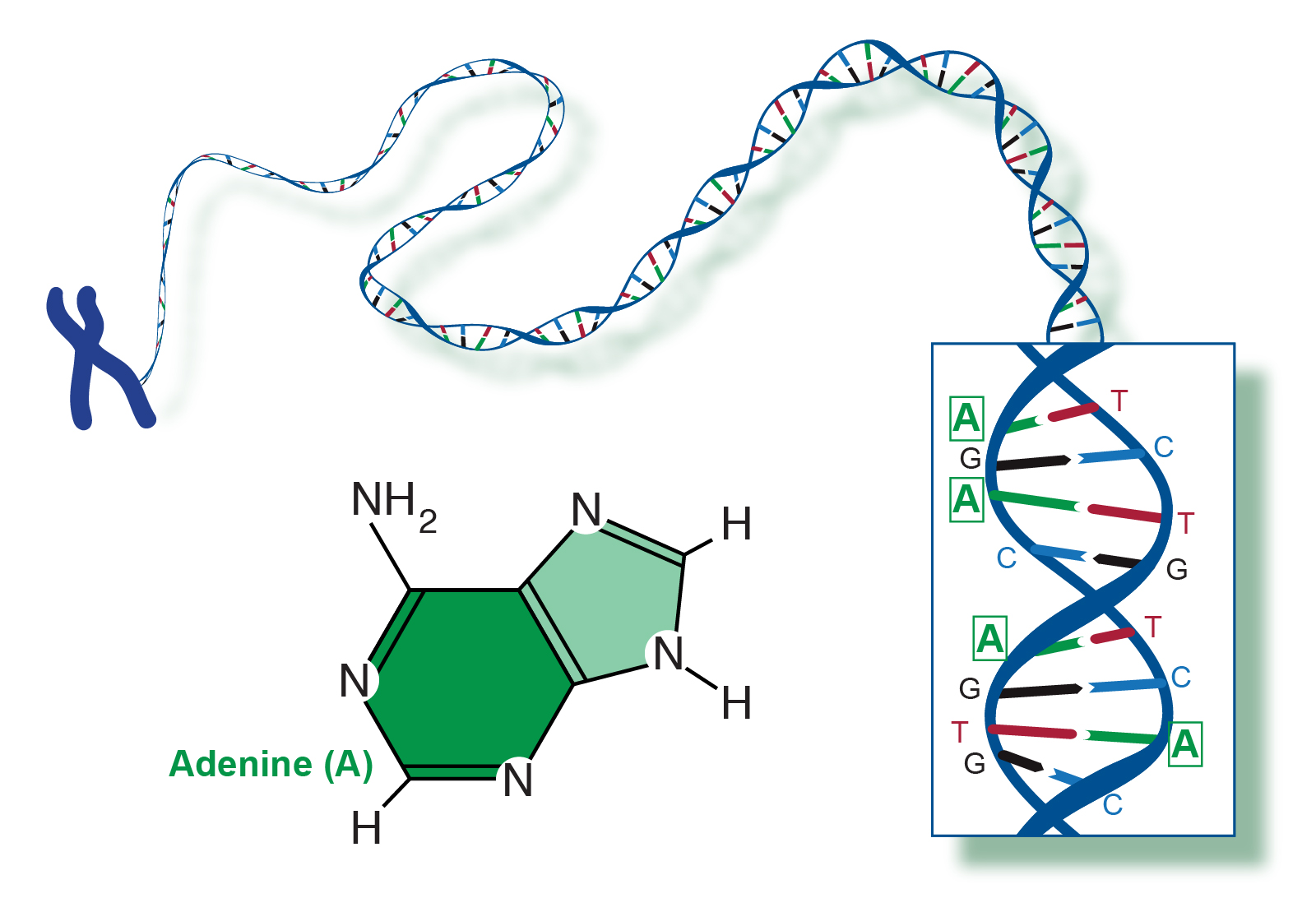
Adenine (A)
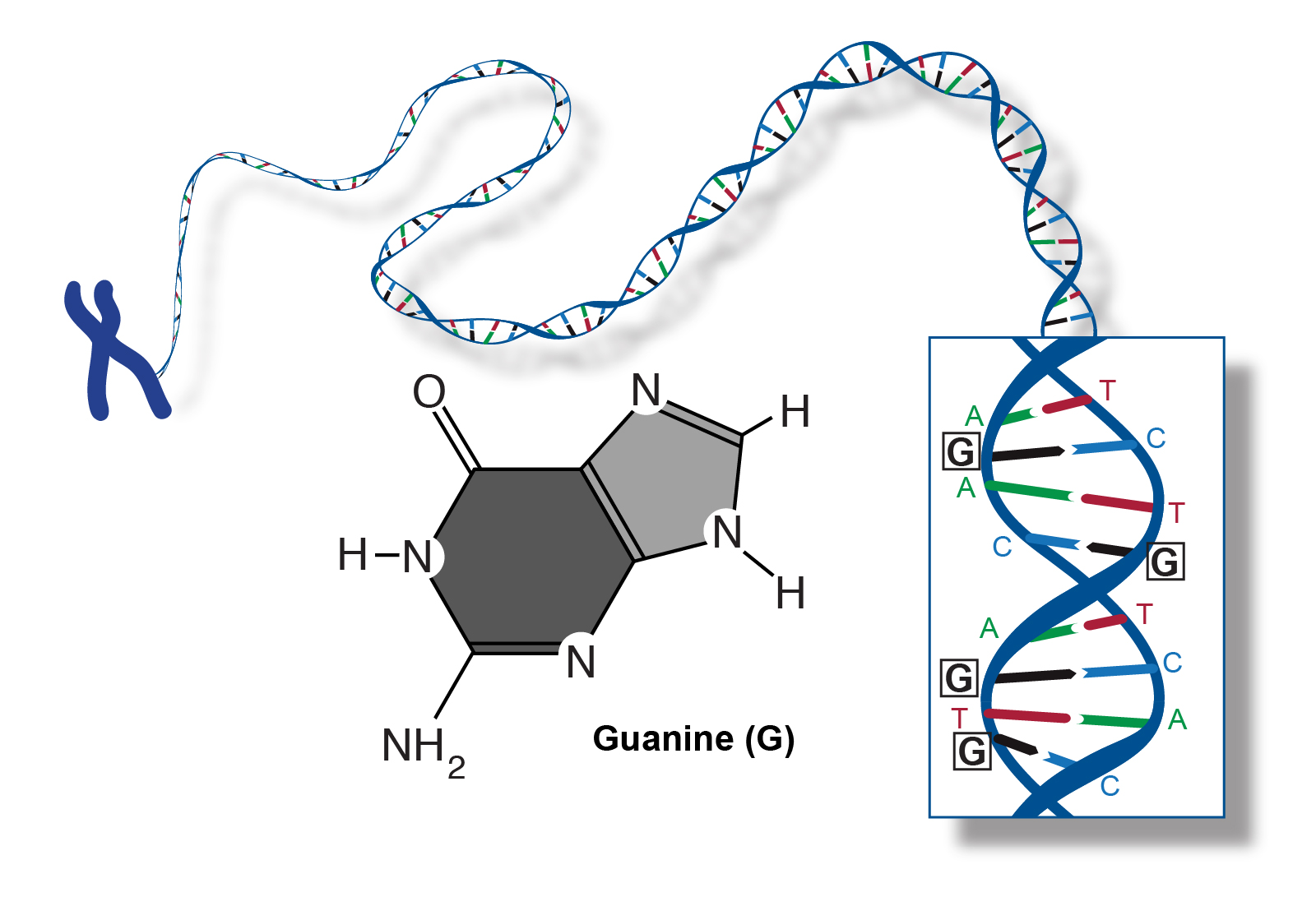
Guanine (G)
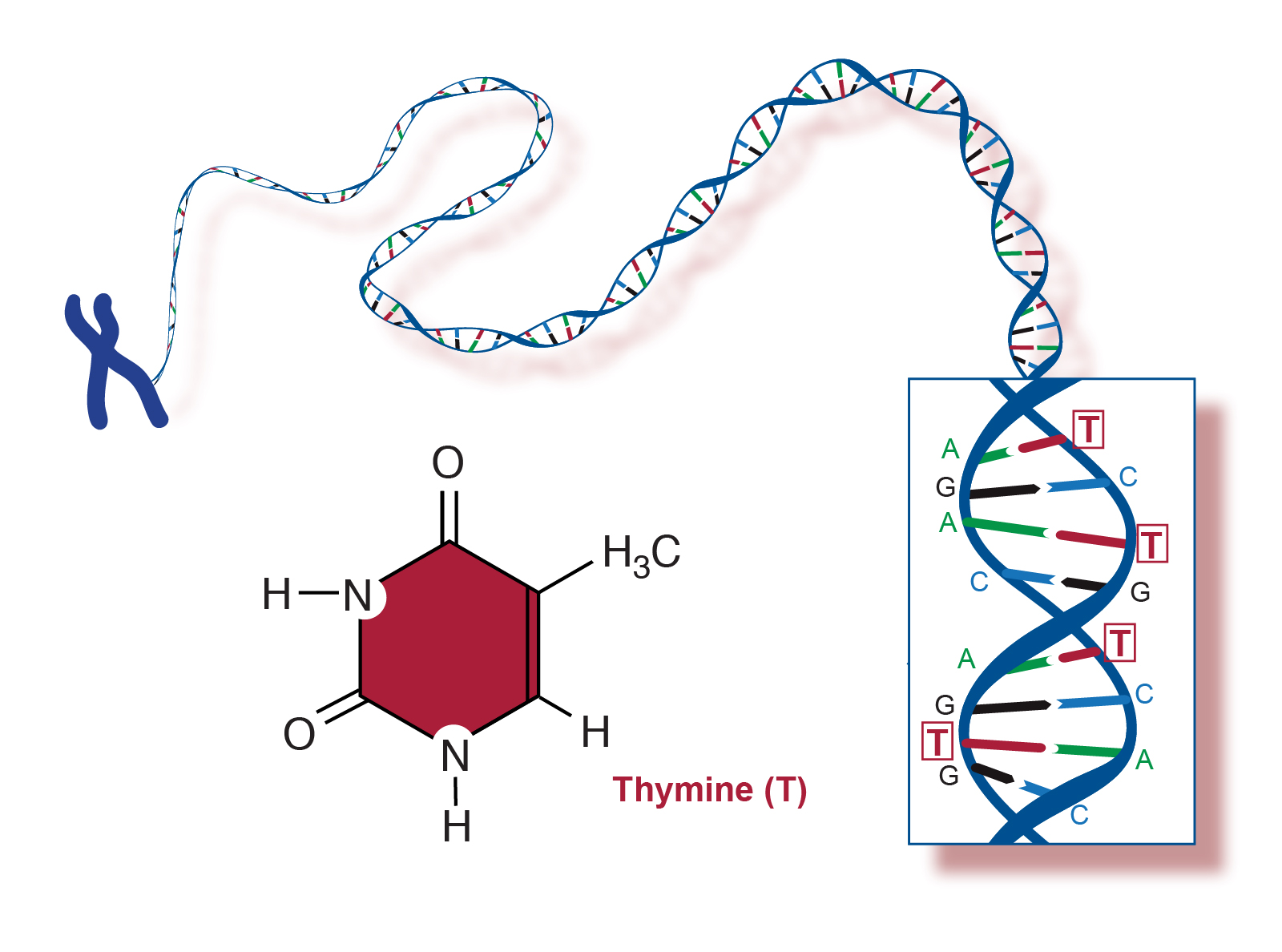
Thymine (T)
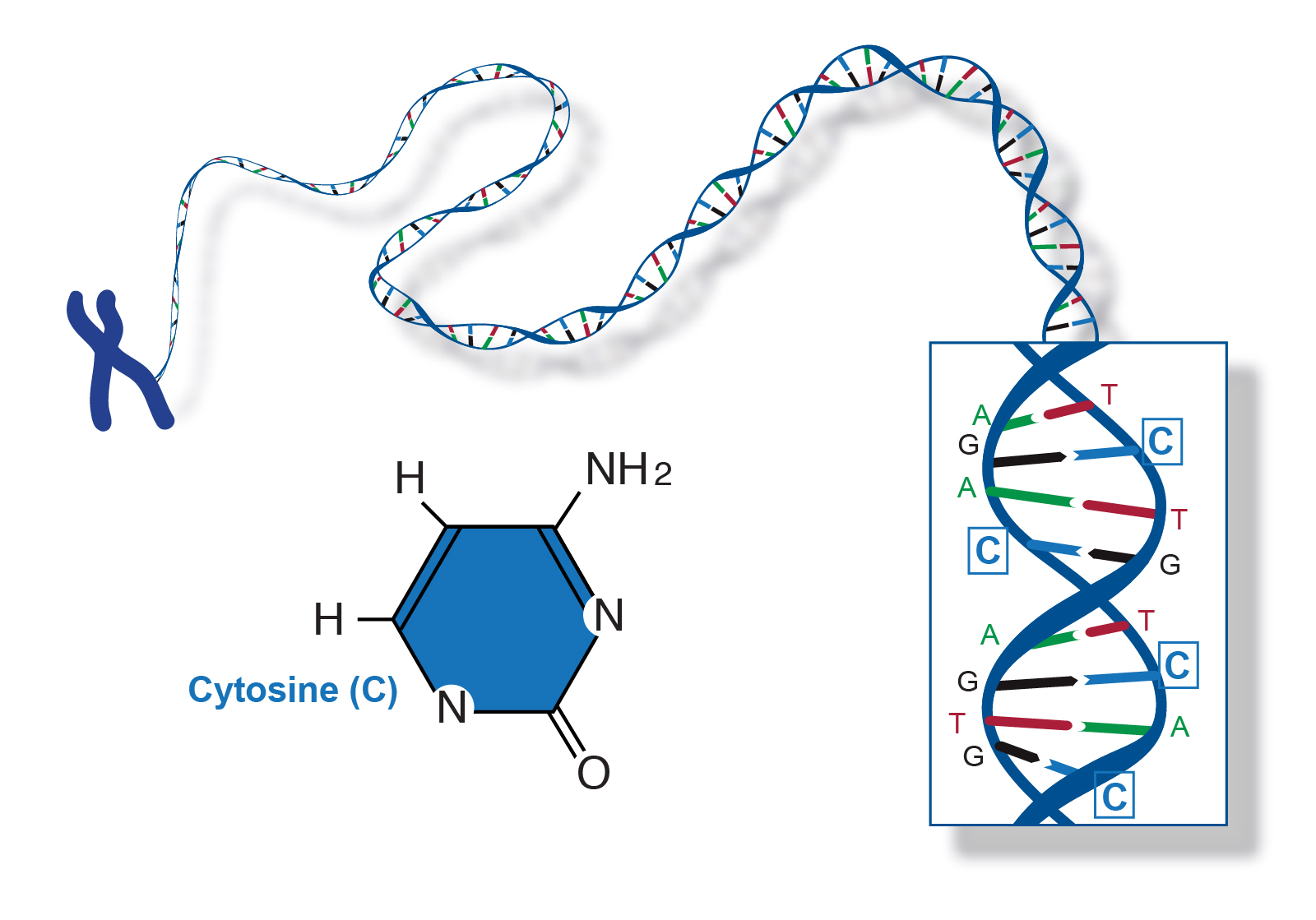
Cytosine (C)
“bases” vs “nucleotides”
refers to the entire chemical block, which includes the nitrogen base
refer to the 4 nitrogenous bases
approximately 3.2 billion base pairs (human)
double-stranded helix
example of common DNA

Nuclear DNA
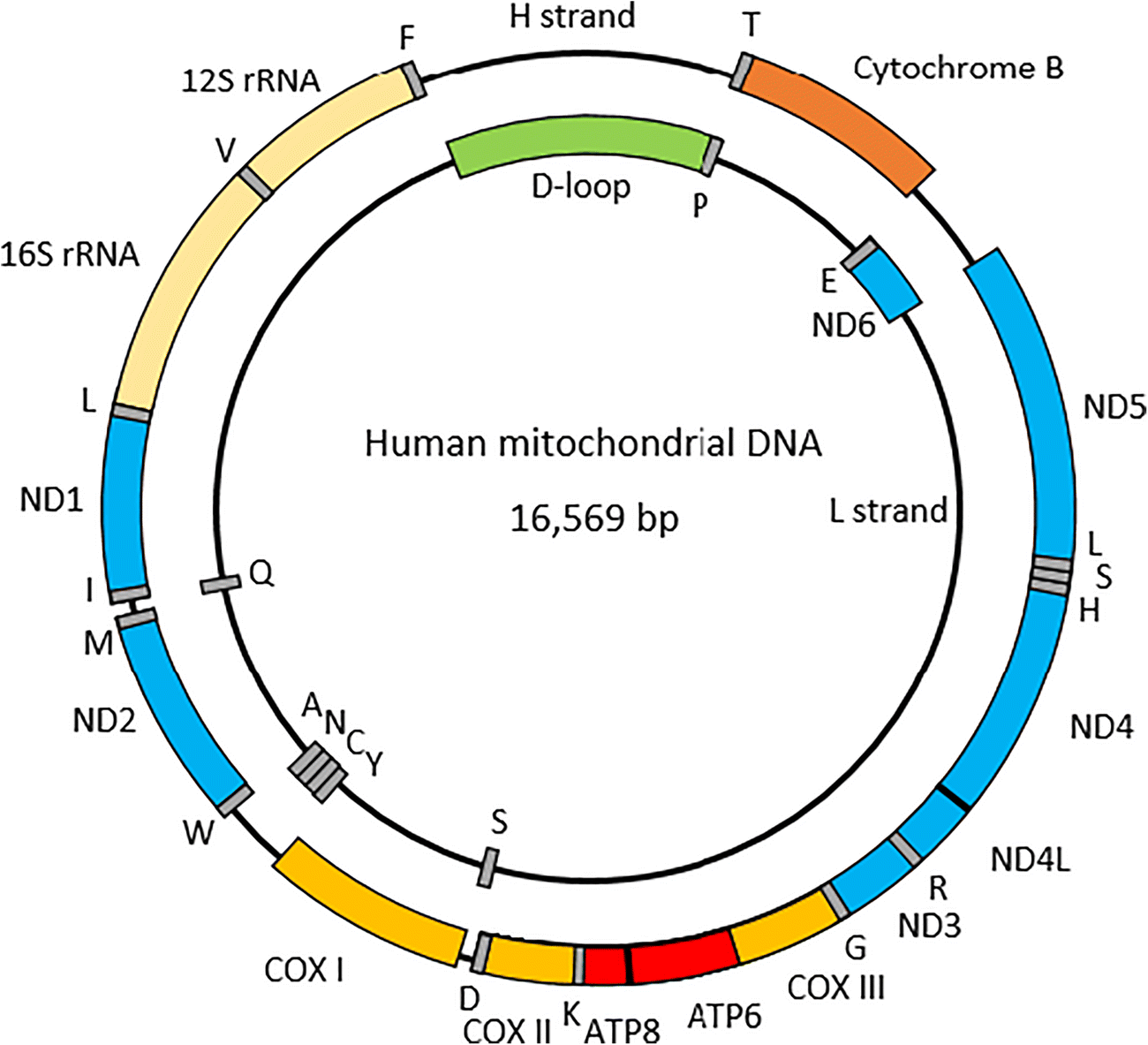
Mitochondrial DNA
Chloroplast DNA
can be divided into two, based on location
coding region
the region that code for protein
most studied part of the human genome
constitute only 2-3%
e.g. BRCA1 gene, TP53 gene, TNF gene
non-coding region
the region that does not involve in encoding protein
classification

non-coding inside gene region
e.g. introns

non-coding outside gene region
e.g. promoters, repeats, intergenic regions
increasing interest to study this region - very hard
constitute 97-98%
What is RNA?
similar to DNA but
mostly single-stranded
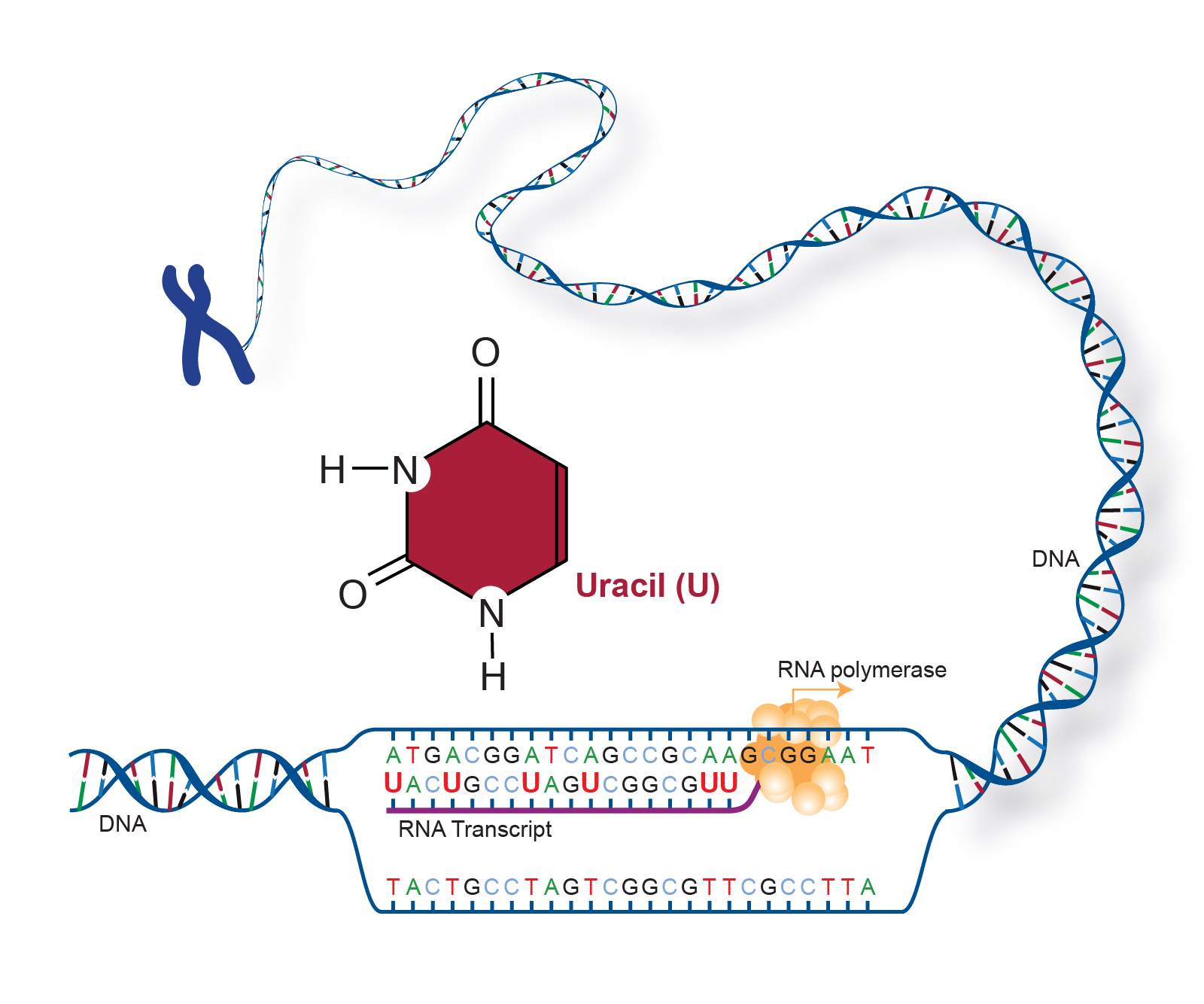
Uracil (U) instead of Thymine (T)
so it has 4 nitrogen bases
Uracil (U)
Adenine (A)
Guanine (G)
Cytosine (C)
can be classed into
coding RNA
encode protein
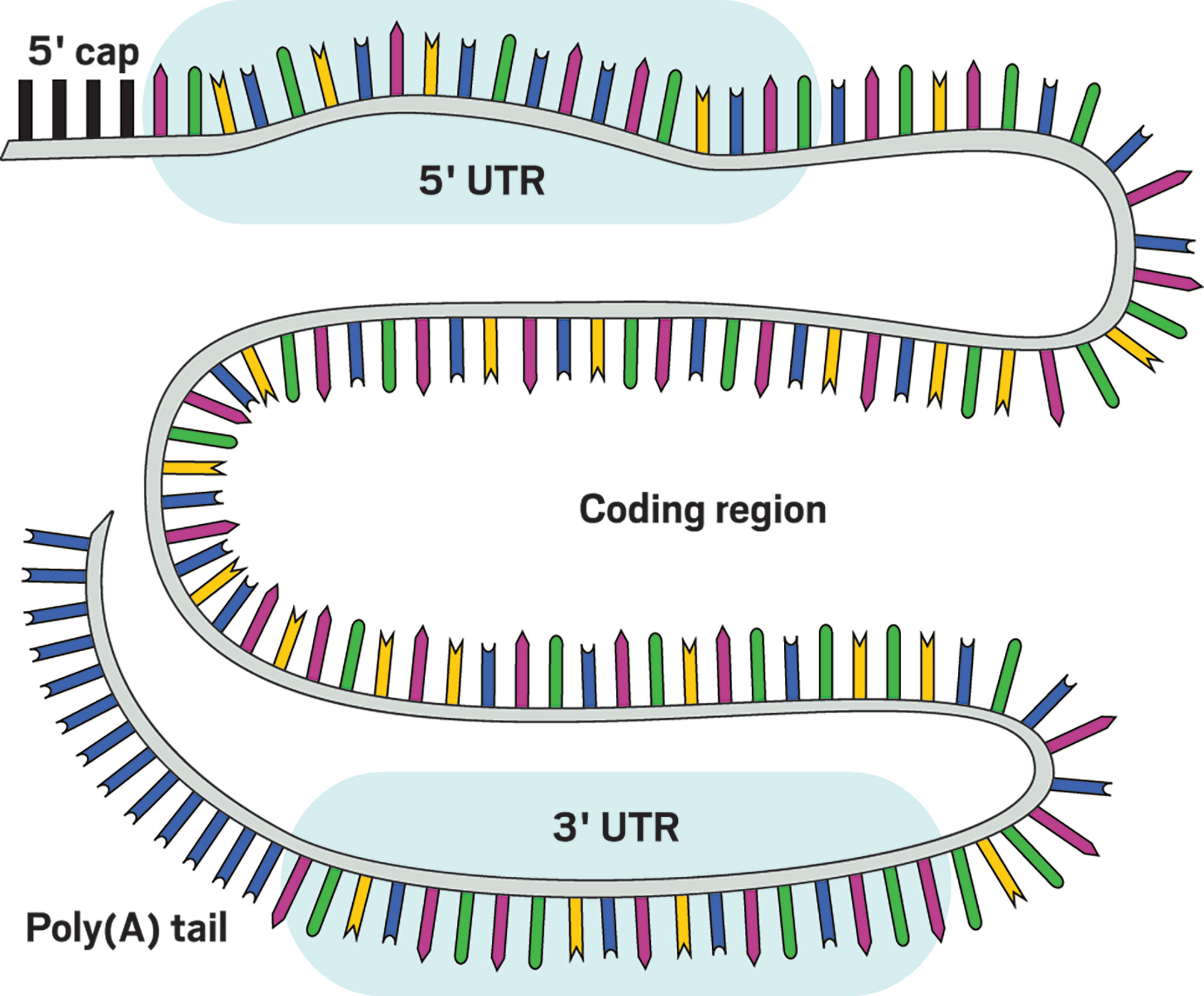
e.g. Messenger RNA (mRNA)
non-coding RNA (ncRNA)
does not encode protein
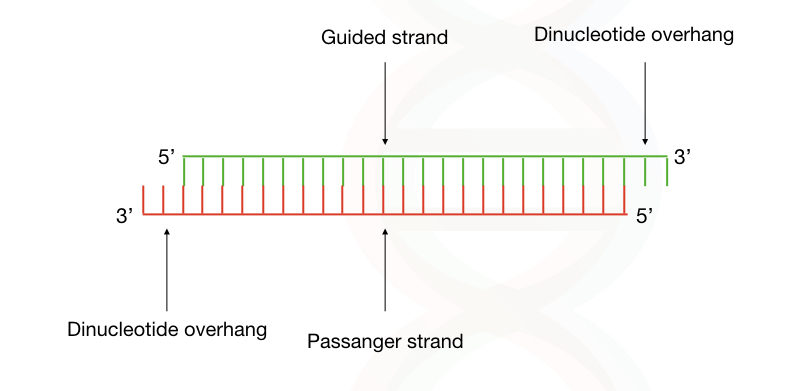
Small interfering RNA (siRNA)
double stranded
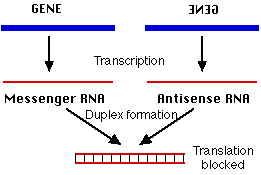
Antisense RNA

Transfer RNA (tRNA)
function is to transfer the amino acids from cytoplasm to the ribosome
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) - http://www.bio.miami.edu/dana/250/250SS16_8print.html
merge with other proteins and tRNA to form the ribosome complex
function of a ribosome is to catalyze the assembly of amino acids into polypeptide chains (i.e. protein)
in eukaryotes, a ribosome consist of two subunits
large subunit & small subunit
chromosome
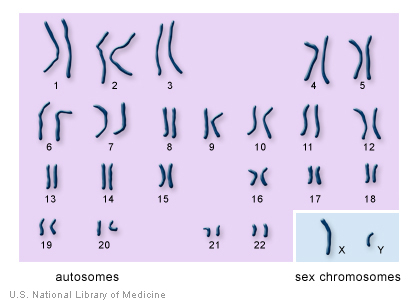
23 paired chromosomes (human)
classification
autosome
chr1 until chr22
sex chromosome
labelled as chromosome chrX and chrY
Male = chrX + chrY
Female = Two chrX

from 24 chromosomes
human is a diploid organism
what is diploid ?
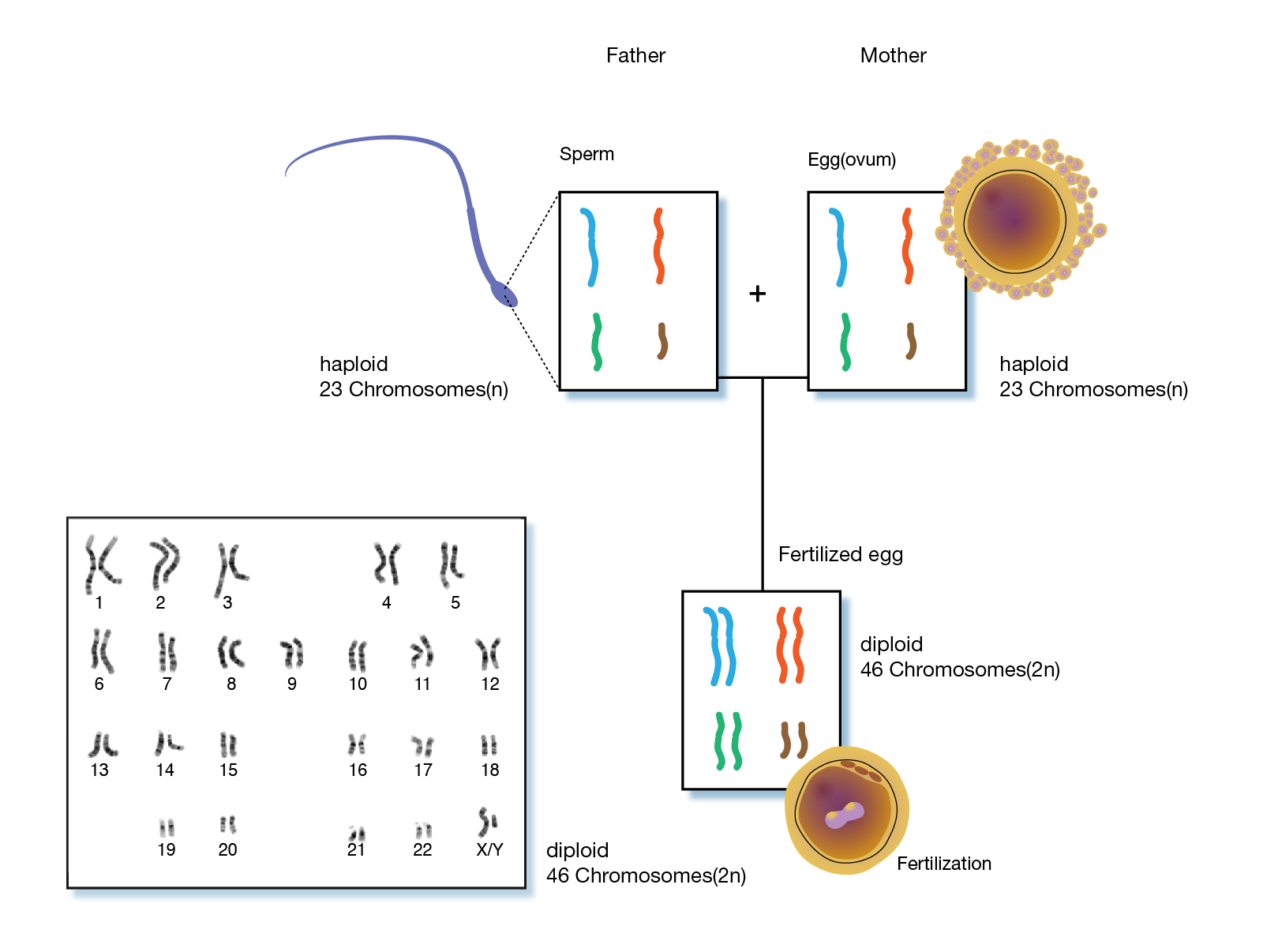
two copies of a chromosome inherited from each parent
chr17 from mother & father
humans have two versions of a gene e.g. P53
haploid
only one copy of a chromosome
in human, chromosome is packaged in chromatin
what is chromatin?
a complex consisting of double helix DNA packed with protein histone (nucleosome)

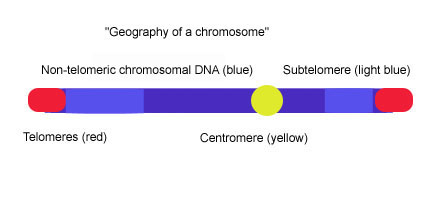
structure
telomere
subtelomere
centromere
what is phenotype?
the observable trait

hair colour, skin color, height, glucose level, disease, etc ...
what is genotype?
genetic makeup that determine the phenotype of an individual organism
determined by
allele
what is allele?
different forms of a gene
type
recessive
dominant

type
Homozygous dominant (e.g. BB)
Heterozygous (e.g. Bb)
Homozygous recessive (e.g. bb)