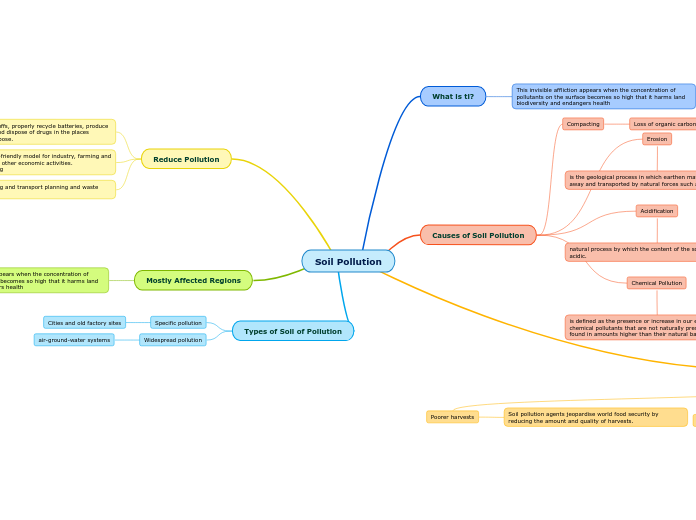
Soil Pollution
What is ti?
This invisible affliction appears when the concentration of pollutants on the surface becomes so high that it harms land biodiversity and endangers health
Causes of Soil Pollution
Compacting
Loss of organic carbon
Increased salt content
Erosion
is the geological process in which earthen materials are worn away and transported by natural forces such as wind or water.
Acidification
natural process by which the content of the soil becomes more acidic.
Chemical Pollution
is defined as the presence or increase in our environment of chemical pollutants that are not naturally present there or are found in amounts higher than their natural background values.
Consecuences of Soil Pollution
Poorer harvests
Soil pollution agents jeopardise world food security by reducing the amount and quality of harvests.
Climate change
In the first decade of the 21st century, soil degradation released between 3.6 and 4.4 billion tonnes of CO2 into the atmosphere.
Dmage to gealth
Soil pollutants enter our body through the food chain, causing illnesses to appear. Moreover, the spread of antibiotics in the environment increases the pathogens' resistance to these drugs.
Reduce Pollution
Eat sustainable foodstuffs, properly recycle batteries, produce homemade compost and dispose of drugs in the places authorised for this purpose.
Encourage a more eco-friendly model for industry, farming and stock breeding, among other economic activities.
Improve urban planning
Improve urban planning and transport planning and waste water treatment.
Mostly Affected Regions
This invisible affliction appears when the concentration of pollutants on the surface becomes so high that it harms land biodiversity and endangers health
Types of Soil of Pollution
Specific pollution
Cities and old factory sites
Widespread pollution
air-ground-water systems