Central Nervous System

Telencephalon
Cerebral hemispheres
The left hemisphere is dominant with regard to language and logical processing, while the right hemisphere handles spatial perception. The brain is separated into the frontal, temporal, occipital, and parietal lobes. The frontal lobe is associated with executive functions and motor performance.
Lateral ventricles
Lateral ventricles. The right and left lateral ventricles are structures within the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid, a clear, watery fluid that provides cushioning for the brain while also helping to circulate nutrients and remove waste.
Youtube: Brain 4 -Telencephalon: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7AP6V6GUVeY

Diencephalon
Thalamus
The thalamus (from Greek, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter in the dorsal part of the diencephalon of the brain with several functions such as relaying of sensory signals, including motor signals to the cerebral cortex, and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness
Third ventricle
Third ventricle. The third ventricle is one of the four ventricles in the brain that communicate with one another. As with the other ventricles of the brain, it is filled with cerebrospinal fluid, which helps to protect the brain from injury and transport nutrients and waste.
Youtube: Brain 6 - Diencephalon: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h1c5oIVMH64
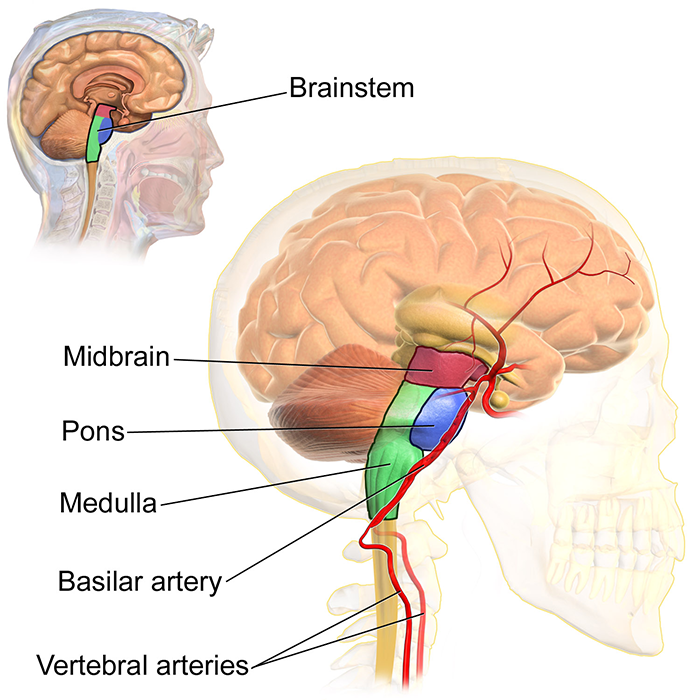
Mesencephalon
Midbrain
Midbrain, also called mesencephalon, region of the developing vertebrate brain that is composed of the tectum and tegmentum. The midbrain serves important functions in motor movement, particularly movements of the eye, and in auditory and visual processing.
Cerebral aqueduct
Cerebral aqueduct contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and connects the third ventricle in the diencephalon to the fourth ventricle within the region of the mesencephalon and metencephalon, located dorsal to the pons and ventral to the cerebellum.
Youtube: Brain 7 - Mesencephalon: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FVEqE-idruQ

Metencephalon
Pons
Location: Area of the hindbrain that sits directly above the medulla. Function: Connects upper and lower parts of the brain. The Pons serves as a message station between several areas of the brain. It helps relay messages from the cortex and the cerebellum.
Cerebellum
The cerebellum is a vital part of the brain and is primarily responsible for motor control. This includes muscle tone, equilibrium, and balance as it relates to movement. Additionally, it seems the cerebellum may actually have additional functions, including some cognitive and emotional functions.
Fourth ventricle
The main function of this ventricle is to protect the human brain from trauma (via a cushioning effect) and to help form the central canal, which runs the length of the spinal cord. This ventricle has a roof and a floor.
Youtube: Brain 8 - Metencephalon: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rWnNreKwR-c

Myelencephalon
Medulla
The medulla oblongata helps regulate breathing, heart and blood vessel function, digestion, sneezing, and swallowing. This part of the brain is a center for respiration and circulation. Sensory and motor neurons (nerve cells) from the forebrain and midbrain travel through the medulla
Fourth ventricle
The main function of this ventricle is to protect the human brain from trauma (via a cushioning effect) and to help form the central canal, which runs the length of the spinal cord. This ventricle has a roof and a floor.
Youtube: Brain 9 - Mylencephalon:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=su9VFTlq8Ro
SOURCES
Cerebral hemispheres and lobes of the brain. Lumen. Retrieved on February 15, 2019 from: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/teachereducationx92x1/chapter/cerebral-hemispheres-and-lobes-of-the-brain/
Fourth ventricle. Healthline. Retrieved on February 15, 2019 from: https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/fourth-ventricle#1
Lateral venticles. Healthline. Retrieved on February 15, 2019 from: https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/lateral-ventricles
Medulla Oblangata. Healthline. Retrieved on February 15, 2019 from: https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/medulla-oblongata
Roger, K. Midbrain. Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved on February 15, 2019 from: https://www.britannica.com/science/midbrain
The Pons. The Brain Made Simple. Retrieved on February 15, 2019 from: http://brainmadesimple.com/pons.html
Third ventricle. Healthline. Retrieved on February 15, 2019 from: Healthline. Lateral venticles. Retrieved on February 15, 2019 from: https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/lateral-ventricles
Wikipedia contributors. (2019, February 1). Thalamus. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved February 16, 2019 from: https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Thalamus&oldid=881263225
Williams, J. Cerebellum: definition & function. Study.com. Retrieved February 15, 2019 from: https://study.com/academy/lesson/cerebellum-definition-function-quiz.html
Riggs, W. [Wendy Riggs]. (2014, September 28). Brain 6 - Diencephalon [Video File]. Retireved on February 16, 2019 from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h1c5oIVMH64
Riggs, W. [Wendy Riggs]. (2014, September 28). Brain 7 - Mesencephalon [Video File]. Retireved on February 16, 2019 from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FVEqE-idruQ
Riggs, W. [Wendy Riggs]. (2014, September 28). Brain 8 - Metencephalon [Video File]. Retireved on February 16, 2019 from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rWnNreKwR-c
Riggs, W. [Wendy Riggs]. (2014, September 28). Brain 9 - Myelencephalon [Video File]. Retireved on February 16, 2019 from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=su9VFTlq8Ro
Riggs, W. [Wendy Riggs]. (2014, September 28). Brain 4 - Telencephalon [Video File]. Retireved on February 16, 2019 from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7AP6V6GUVeY&t=55s