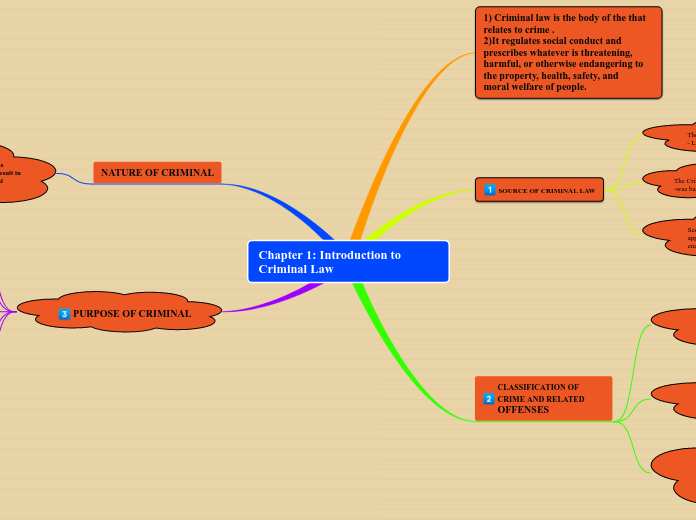
Chapter 1: Introduction to Criminal Law
1) Criminal law is the body of the that relates to crime . 2)It regulates social conduct and prescribes whatever is threatening,
harmful, or otherwise endangering to the property, health, safety, and
moral welfare of people.
SOURCE OF CRIMINAL LAW
The penal code (kanun keseksaan)
- Law that codifies most criminal and procedures in Malaysia
The Criminal Procedure Code
-was based on the Indian criminal code .
Section 5 Criminal procedure Code states English law be applied in cases where no specific legislation has been enacted .
CLASSIFICATION OF CRIME AND RELATED
OFFENSES
Against Properties
- Crimes against property are crimes of theft, where no force or threat of force is directed against an individual .
- Crime in which property is destroyeed
-Crimes in which property is stolen or taken against the owner's will .
Example: Burglary , Larceny , Robbery , Exortion and motor vehicles theft .
Against Public order
-identified as offences against public order which threaten and disturb the standard of living of the public
Against Person
-The terms "crimes against the person" refers to a board arrary of criminal offenses which usually involve bodily harm, the threat of bodily harm or other actions commited against the will of an individual .
NATURE OF CRIMINAL
Professor Henry M.Hart, Jart , Jr. defines crimes as "conduct which if shown to have taken place will result in the formal and solemn pronouncement of the moral condemnation of the community .
most people find objectionable that thipcally are not subject to stat prosecution and officially punishment .
someone who cheats on his or her spouse generally leave the solution to the individuals involved .
PURPOSE OF CRIMINAL
Maintaining Order
resolving disputes
protecting individuals and property
providing for smooth functioning of society
safeguarding civll liberties