Body Systems
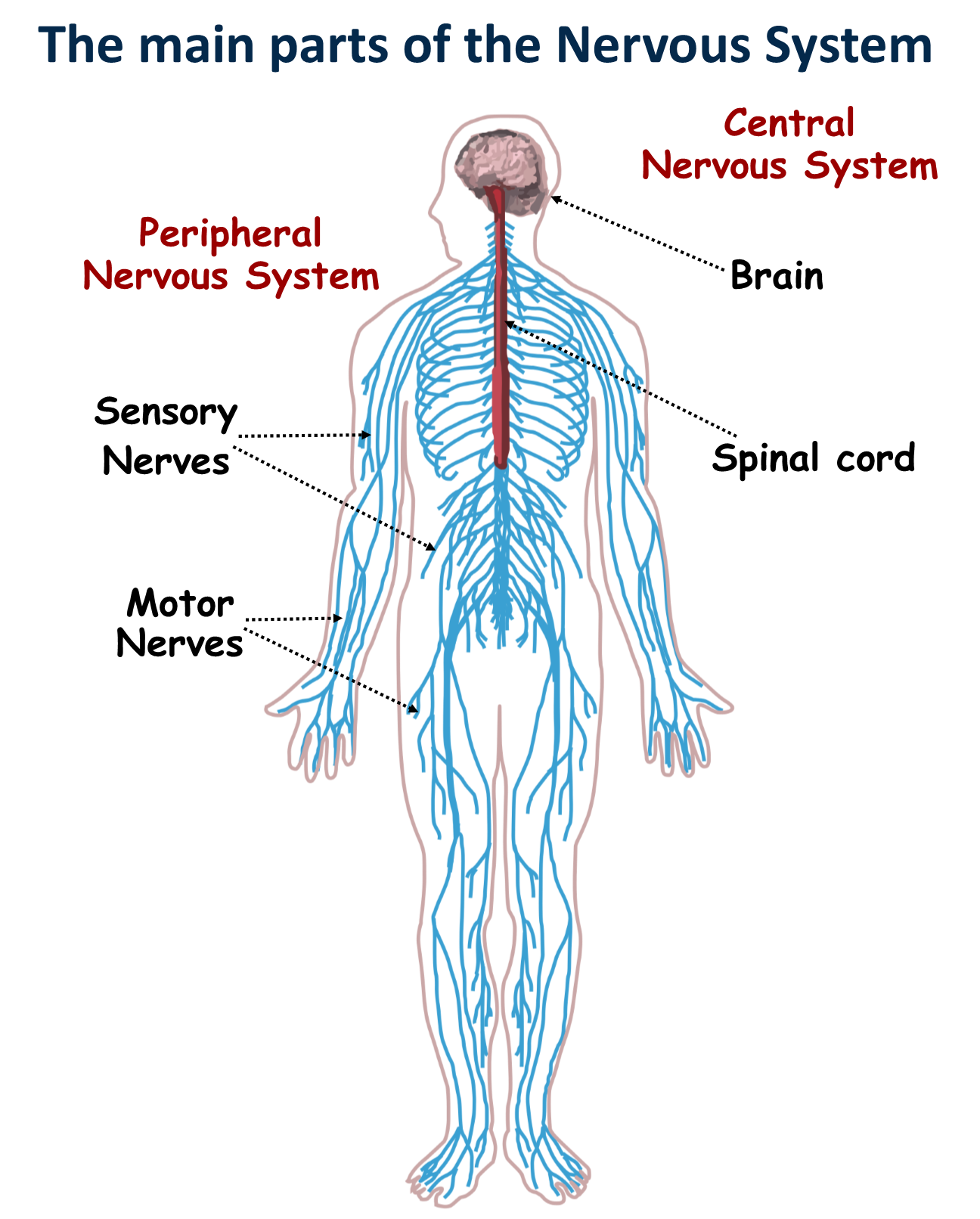
Nervous system
cope with stress
Functions
Sends messages back and forth between the brain and body.
Controls all of the body’s functions such as breathing, reflex and seeing
Controls learning and memory
Controls the voluntary movement of the body
brain tumour
Abnormal cells in the brain tissue
to grow
can cause loss of cognitive abilities
problem solving, memory and learning
Treatment
Radiation therapy
A high of dose of radiation
used to kill cancer cells
Radiosurgery
Focused beams of radiation using X-rays and protons
Organs
The Brain
Every process in the human body
Breathing, Learning and movement
The brain stem
The brain to the spinal cord
Nerves
neurons from the brain
to the body
contain information
Allows the body to move and use it senses
The cardiovascular system
Functions
- Pumps up blood throughout the body
- Makes sure the body gets its oxygen and nutrients
- Gets rids of waste such as carbon dioxide
Malfunctions
heart attack
When blood supply
The Heart
Severely reduced or blocked
can cause shortness of breath,
heartburn
Death
treated
Thrombolytic drugs
are used to dissolve
Clots that cause the heart attack
Balloon angioplasty
a tiny balloon
placed in the blood vessel
remove the blockage
the blood vessel
Organs
The Heart
Up and Moves blood
the body
Capillaries
the veins
the arteries
Veins
Blood to
heart
Arteries
Blood away
the heart
giving nutrients from food to the blood in the cardiovascular System
carries those nutrients where they need to go.
make red blood cells
remove excess liquid from blood
Urinary system
Organs
Kidneys
the waste from the human body
a hormone called erythropoietin that
renal pelvis
a funnel that transports the urine
the kidney to the ureters
ureters
urine in to the bladder
bladder
role is to store and empty urine into the urethra
urethra
the passage of urine
the penis
the passage of semen
Functions
filter blood and create urine as a waste by-product to empty
Malfunctions
cystitis
bladder infection usually caused by bacteria
causes inflammation in the bladder
spread to and damage the kidneys
treatment
urinary alkalisers
drug that reduces the acidity of the urine
help relieve pain and inflammation
Nitrofurantoin
antibiotic used to treat cystitis
remove watse
the urethra
Respiratory Systems
Malfunctions
asthma a malfunction
wheezing and breathlessness are caused
caused by a narrowing of the airways.
treatment
Inhalers
small, handheld device used
deliver medication to your lungs to
open up airways in your lungs
prevent symptoms of asthma such as
Inflammation
Fuctions
Delivers oxygen into cells
clean out waste gasses like carbon dioxide.
Organs
Lungs
Oxygen and gets rids of
Carbon dioxide
nose
air to enter the body
Trachea
air in and out of your lungs
diaphragm
and flattens to allow air to enter the lungs
pharynx
air from the nose
larynx
the respiratory system
preventing food from
entering the system
bronchi
distributes air across the lungs
The reproductive systems
Functions
Producing sperm and egg cells
Transport the sperm and egg cells
Nurture and develop offspring
Organs
the female reproductive system
ovaries
fallopian tubes
the sperm cells
the ovaries to the uterus
uterus
and protects the fetus
cervix
Vagina to the uterus
Vagina
a passageway for blood
The menstrual cycle
the Male reproductive system
prostate
semen with sperm cells and
fluids from other glands
testes
job is to produce sperm and egg cells
Penis
used for sexual intercourse
Malfunctions
Endometriosis
disease where the lining of the uterus
outside of the uterus
can cause pain during sexual intercourse
Other diseases such as nausea and
Chronic pelvic pain
treatment
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
medicines used to reduce inflammation
pain caused by Endometriosis
GnRH-analogues
medicines that affect sex hormones
and gonadotropins
are used to control pain in cause by Endometriosis
The skeletal system
Absorbing Vitamin d
Crucial for bone growth
malfunctions
Arthritis
Organs
the bones
organs
the body's its shape
tendons
the body to move its limbs
Cartilage
the bones and joints
Ligaments
tissues that hold the bones together
Joints
the body to move
functions
Gives the body its shape
Allows movement
Makes blood cells
Provides protection for organs e.g the brain and lungs
stores minerals like calcium and vitamin d
Digestive System
Organs
Stomach
and breaks down food
gallbladder
stores
liquid, bile
pancreas
an enzyme for the body
break down the food
liver
the nutrients from the waste
the food and is
for metabolism in the human body
a thick liquid called bile
is used to break down fat
intestines
small intestine
digests further food from the stomach
large intestine
nutrients such as minerals and electrolytes
feces from food and pushes the feces
the rectum
rectum
the feces
its time for it to release
anus
the feces as waste roduct
Functions
breaks down food into nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
Malfuctions
lactose intolerance
where is the intestines can't digest Lactose
cause vomiting, diarrhea and bloating
digesting lactose in the stomach
treatment
lactase tablets
drug that is taken before eating food that contain lactose
help digesting lactose
reducing the chances of getting lactose symptoms
Lymphatic System
organs
lymph nodes
filers substances in the lymph fluid
spleen
white and red blood cells
stores and filter blood
Thymus
white and red blood cells
Peyer’s patches
regulate intestinal flora
pathogens to prevent diseases and
Infections
Appendix
where blood cells to fight infections
Functions
regulates the body's fluid levels
Fights off illnesses
absorbs digestive tract
removes cellular waste
Mafuctions
Lymphedema occurs when a blocked or damaged lymphatic system causes fluid to build up in the limbs, and lymph can't flow through the body as normal
Endocrine system
Organs
Glands
Pituitary gland, Hypothalamus, Thyroid, parathyroid gland, Adrenal glands, Pineal gland, Pancreas
secretes chemicals
Hormones
Insulin and estrogen
coordinate different functions
sending messages to organs and tissues
tells your body what to do
Functions
Regulates Metabolism
Regulates Energy level
Regulates Reproduction
Regulates Sleep
Regulates Blood pressure
Regulates Growth and development
Controls response to injury, stress, and mood
Malfunctions
diaebets
Malfunction
THe glands
Make enough insulin
blood sugar
Clogged in blood
can lead to heart disease
damage to the nervous system
Medications
Insulin pumps
small, portable device
to inject insulin
the body
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
Medicine that
The body
Starchy foods and table sugar
lowers blood sugar levels
hormones that help the immune
system
Muscular system
Organs
Smooth Muscle fiber
responsible for blood flow and pressure
control the flow of air
Cardiac muscle fiber
Responsible for the contractility of the heart
Skeletal muscle fiber
responsible for body posture
and joint stability
Functions
Is responsible for almost of the movement in the body
Produces 85% of heat for the body
Allows posture and joint stability
Allow for facial expression
Malfucntions
Myositis
inflammation of the
voluntary muscles
can cause trouble breathing, moving
muscle damage
treated using medicines
Prednisone
drug that is used
suppress the immune system
Steriods
Integumentary systen
Organs
Nails
Toes and fingers
Hair
keep heat
Protect your eyes
Skin
The body
UV light
Hazardous substances
Glands
Liquids like milk and water
Sudoriferous glands, Sebaceous glands, ceruminous glands, mammary glands
Functions
- Helps fight against bacteria,
- Protects the body from UV sunlight and sunburn
- Protects and heals injuries
- Produces vitamin D using synthesis
- keeps heat
- protect your eyes from dirt and water using eyelashes and eyebrows
- Regulates body temperature
- Releases sweat, sebum and other waste products from your body
- Stores fat, water, glucose, vitamin d
Malfunctions
Cellulitis
Bacterial skin infection
Redness, swelling, and tissue damage
and can spread to and damage other systems
Treatment
Oral antibiotics
Treat skin diseases
Killing the bacteria
Stopping it from spreading
Cryotherapy
process
Applies extreme cold
Treat skin diseases
