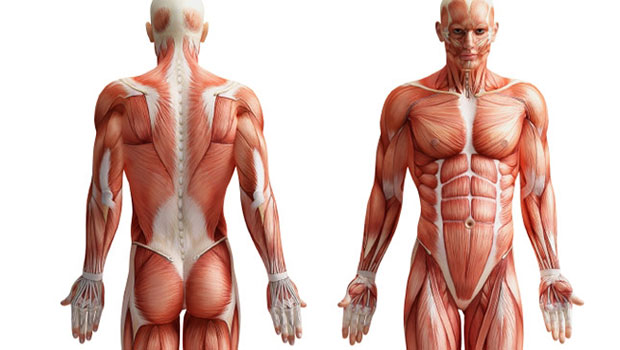
BASICS BIOMECHANICS

MARCH
Human march is a process of movement in which the human body in an upright position, moves forward, a supported weight being alternately by both legs

POSTURE
The position is one in which act the different segments of the body and will be aligned correctly, generating a minimum of stress on the body's tissues and involves an expenditure of energy, minimum
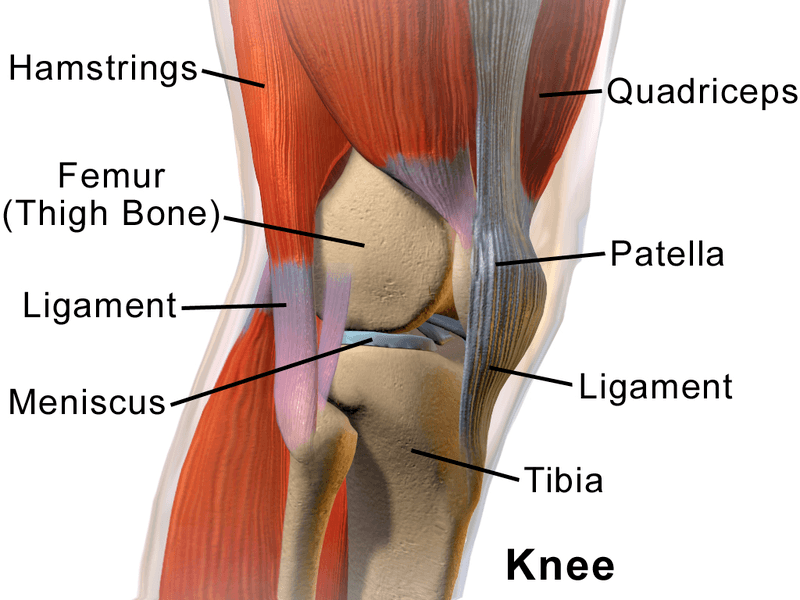
KNEE
the knee is a synovial joint with a mechanical architecture that includes two joints one patellofemoral formed between the femur and patella and tibiofemoral between the femur and the tibia
SURFACES
The joint surfaces are the distal femoral epiphysis, femoral trochlea or patella facet on the front, femoral condyles, proximal tibial epiphysis

Subtema
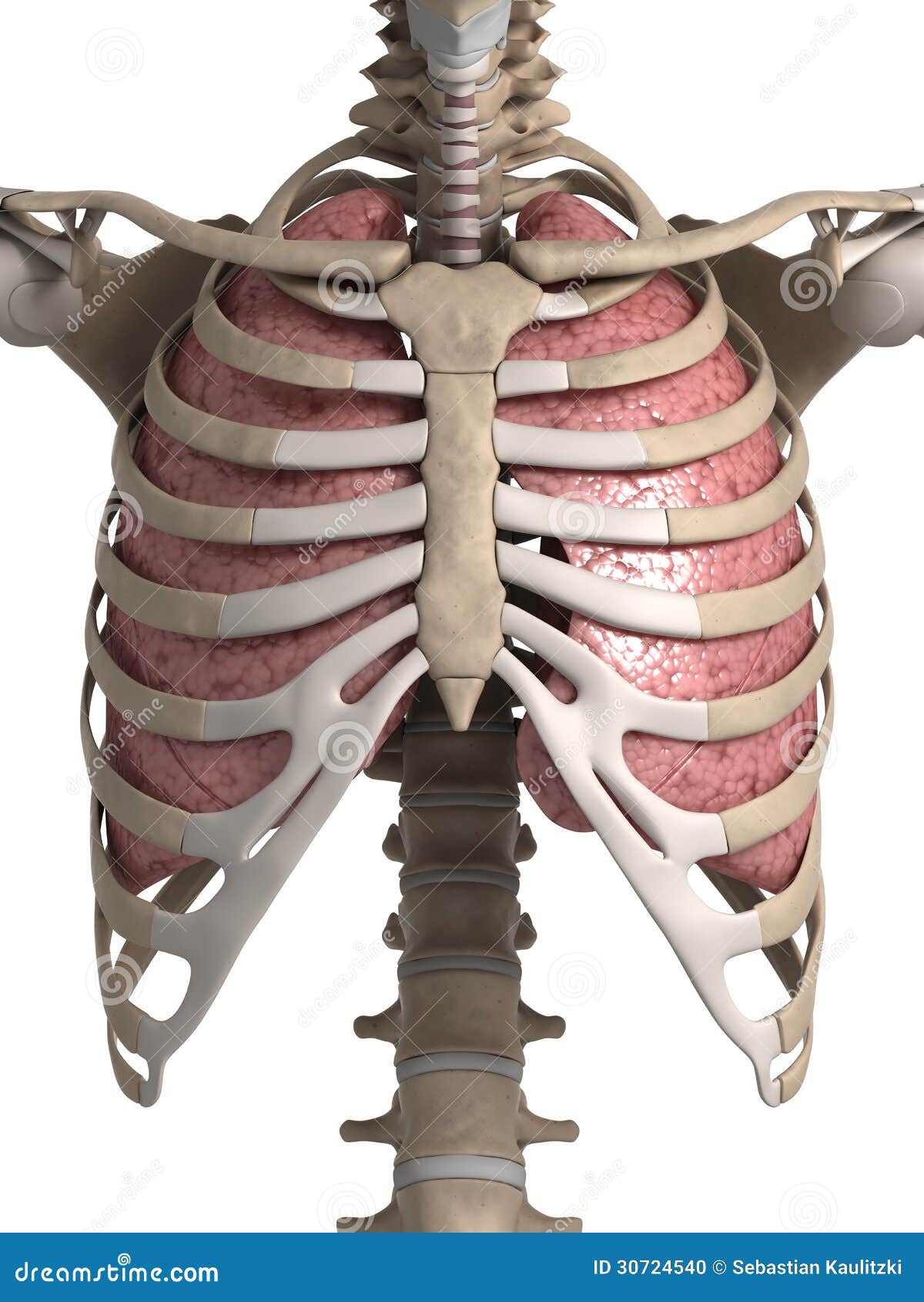
CHEST
Is a bony box formed by the sternum, ribs, costal cartilages, ribs, and the bodies of the thoracic vertebrae
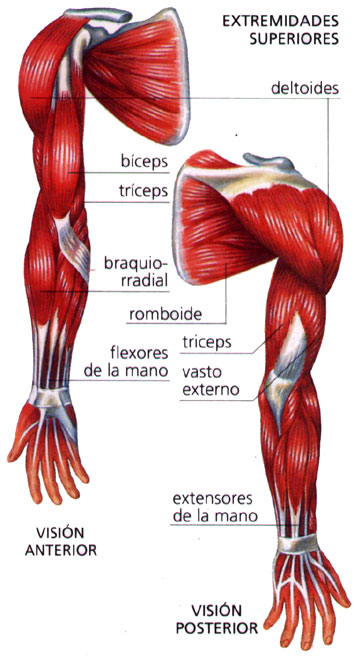
UPPER EXTREMITY
It is each of the tips are fixed to the upper body. It consists of four segments: shoulder girdle, arm, forearm and hand.
COMPONENTS
It is offering a total of 32 bones and 42 muscles; vascularization is the responsibility primarily of the branches of the axillary artery, the main veins are the cephalic, basilica and axillary; most of its innervation is in charge of the brachial plexus.
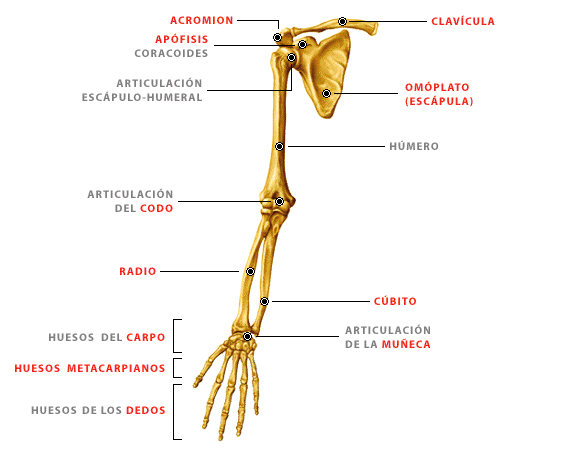
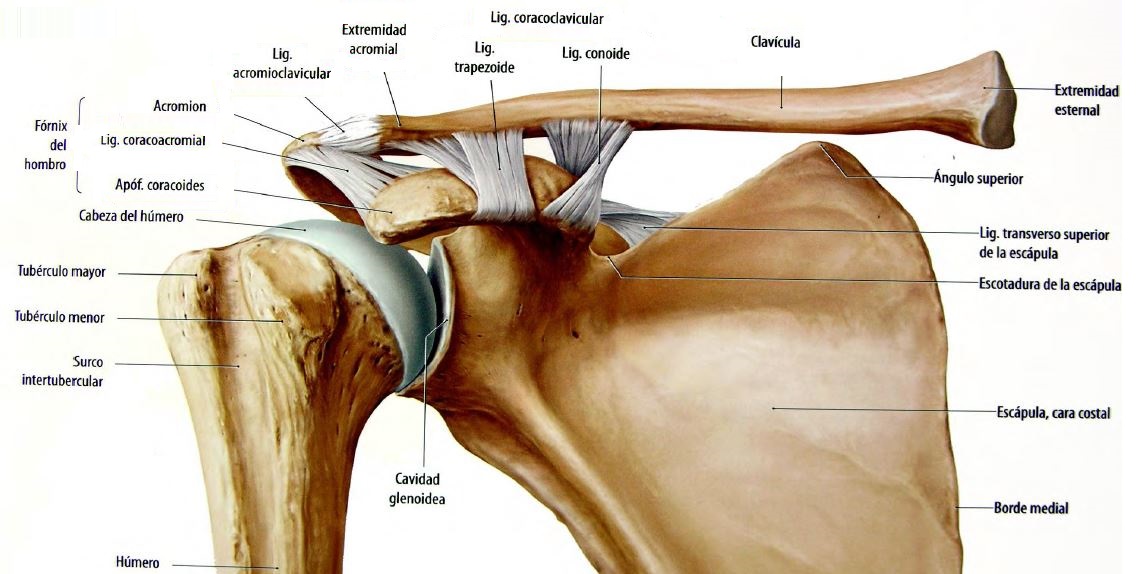
GLENOHUMERAL JOINT
it is a ball and socket joint, joint with three axes and three degrees of freedom
COMPONENTS
transversal axis in a frontal plane movements in flexion and extension, anteroposterior axis in a sagittal plane movements of abduction and adduction and a vertical axis and retropulsión antepulsion movements with the arm abducted 90 ° and a fourth longitudinal axis of the humerus with and rotation movements internal and external rotation

The articular surfaces are the humeral head and glenoid fossa of the scapula

Its passive stabilizing elements are the capsule, middle glenohumeral ligament, upper and lower, coracohumeral ligament, tendons of the subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus and teres minor. Liabilities stabilizers are the humeral head and the muscles of the rotator cuff tendon of the biceps long and short.


MOTION ANALYSIS
elements and principles that allow the continuous changes of position of the human body


MUSCULAR CHAINS
Es la expresión de una coordinación motriz organizada para cumplir con un objetivo
muscle chains
the structural and harmonic expression of the movement culminated in freedom
closed muscular chain
keeps the two upper extremities related to a grip
muscle chains distal
origin of the body weight support
muscle chains origin
displaces proximal distal segments.
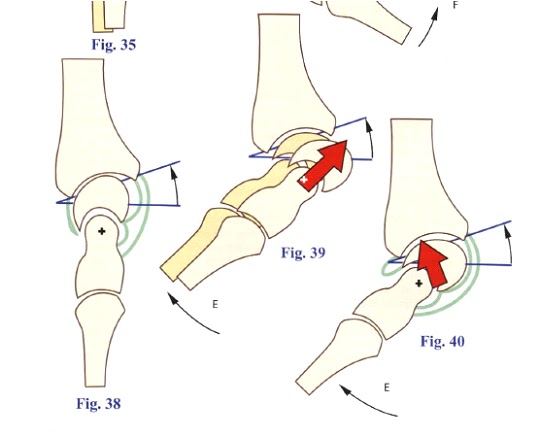
ARTHROKINEMATICS
Study of the movements at rest that occurs at the level of the joint surfaces.

OSTEOCINEMATIC
studying the movement of the bones in space regardless of muscles that contract to do so.
BIOMECHANICS

Study of the mechanic laws in living structures

STRENGTH
Modifies the amount of movement or any material form.
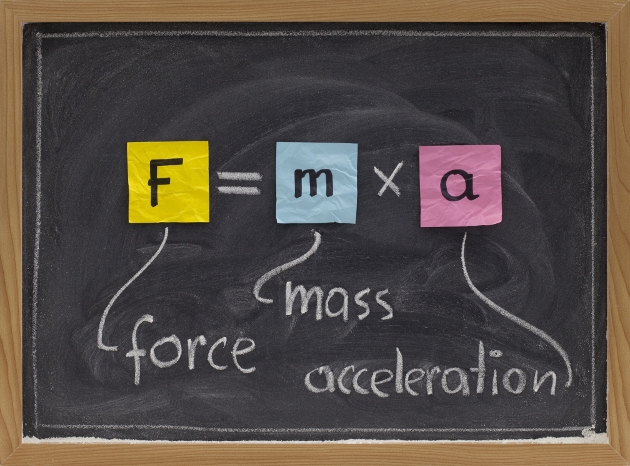
PHYSICAL LAWS
The have any direction of space and time.
INERTIA
ACCELERATION
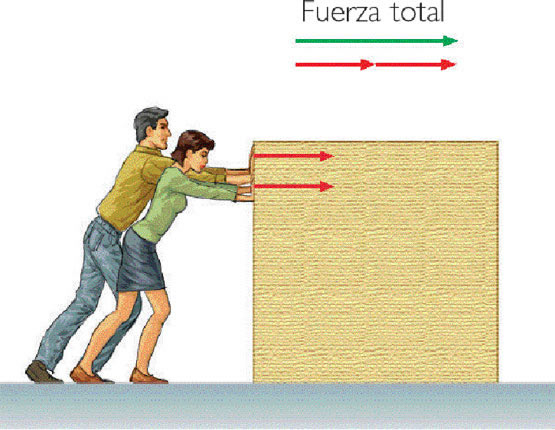
ACTION AND REACTION

Subtema

VECTORS
Segments of a straight line representing a physical quantity that can be measured

FLATS
Imaginary surface that limits the body, are named with x,y,z

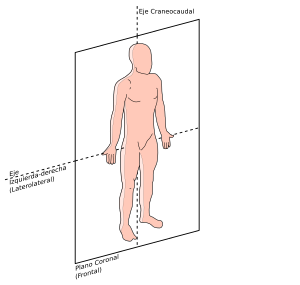


AXES
Real or imaginary lines
LEVERS AND PULLEYS
Are simple mechanisms that are used to save energy

LEVERS
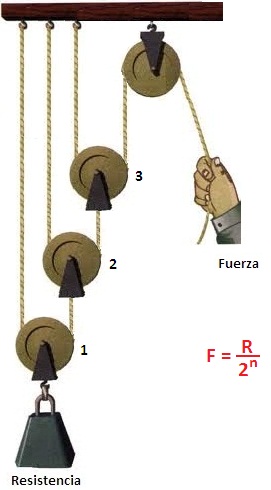
PULLEYS

EQUILIBRIUM AND BALANCE
State of a body subjected to a number of forces counteract each othe
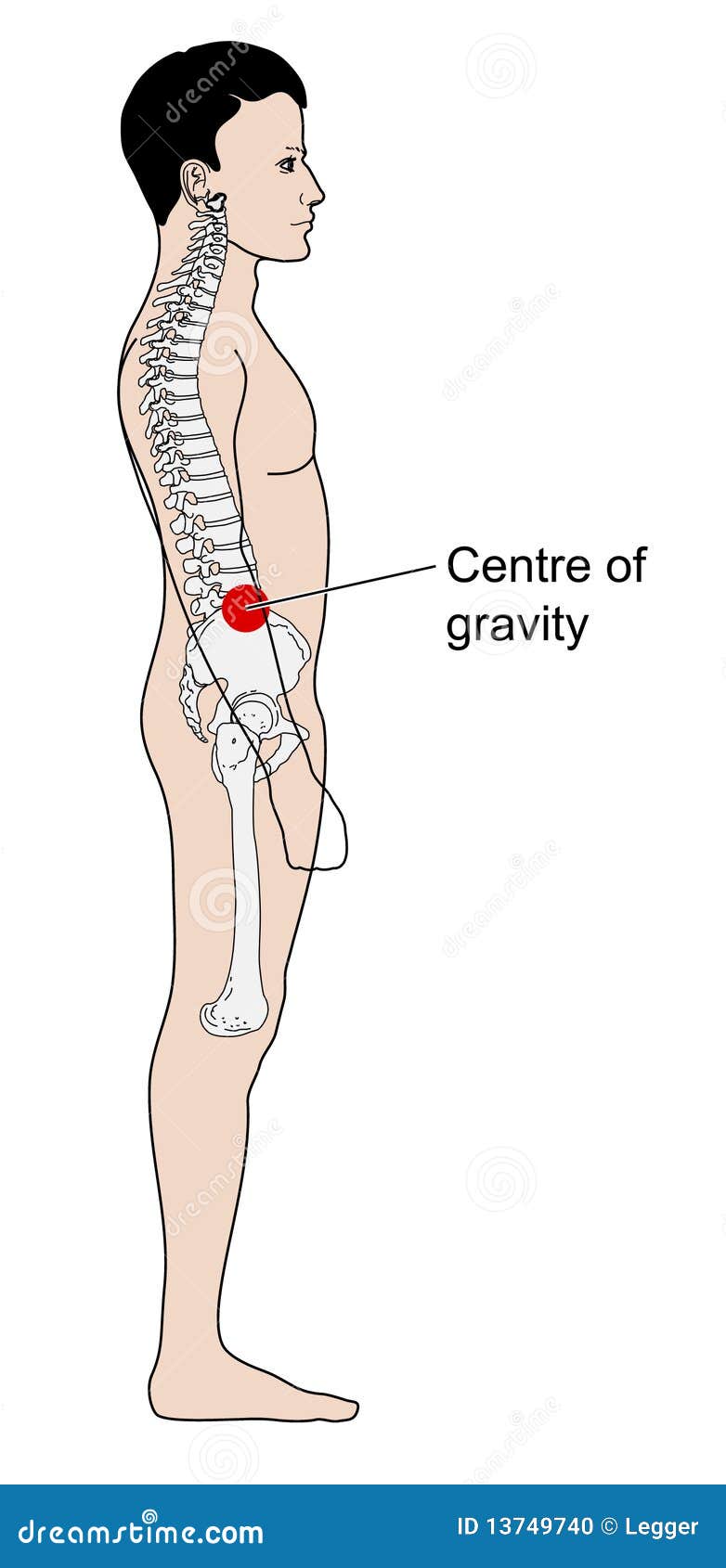
GRAVITATIONAL CENTER
Attractive force making the mass of the earth over the bodies located in the Earth's gravitational field.
SMOOTH TISSUES
Set of elements formed by organic supporting tissue