Structural Strength and Stability
Stability
Base of Support
Bases of supports help make a structure more stable
as seen on this photo the three legs are the bases of
support on this structure, which helps hold up the
stools center of gravity.

Unstable
Unstable is when a structure, the building blocks
can not hold themselves up and eventually they
fall over.

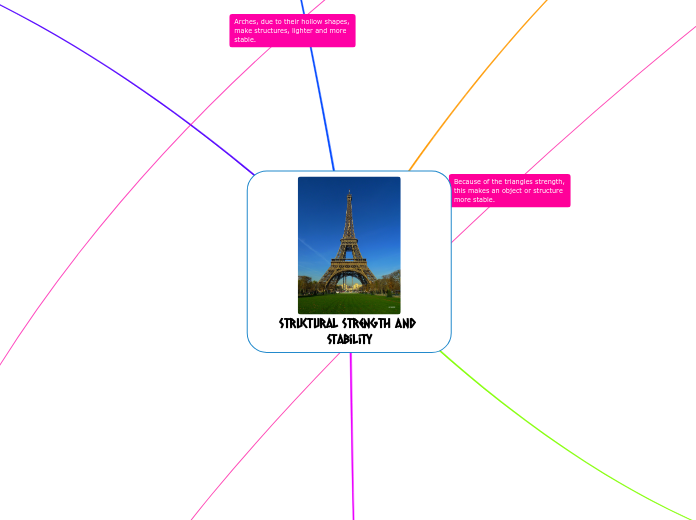
Stable
Stable is when a structure, the Eiffel tower
can hold itself up due to it's wide triangular
shaped base and it will not fall over.

Center of Gravity
Center of gravity is what every single thing is
supposed to have, on a human the center of
balance is your belly button, on a pencil the
center of gravity is closer to the eraser because
the eraser is heavier.

Internal Forces
Torsion
Torsion is the movement of twisting an object
like the rag or a water bottle, torsion is applied
to structures like the rag, so the person can
remove the water in the rag or to unscrew the
cap of a bottle. There are two types of torsion
two way torsion and one way torsion.
Two way torsion is when you hold an object
in two hands and twist it in opposite directions
like the rag shown below.

One way torsion is when you hold a structure
example a water bottle and twist the cap off of
the bottle.


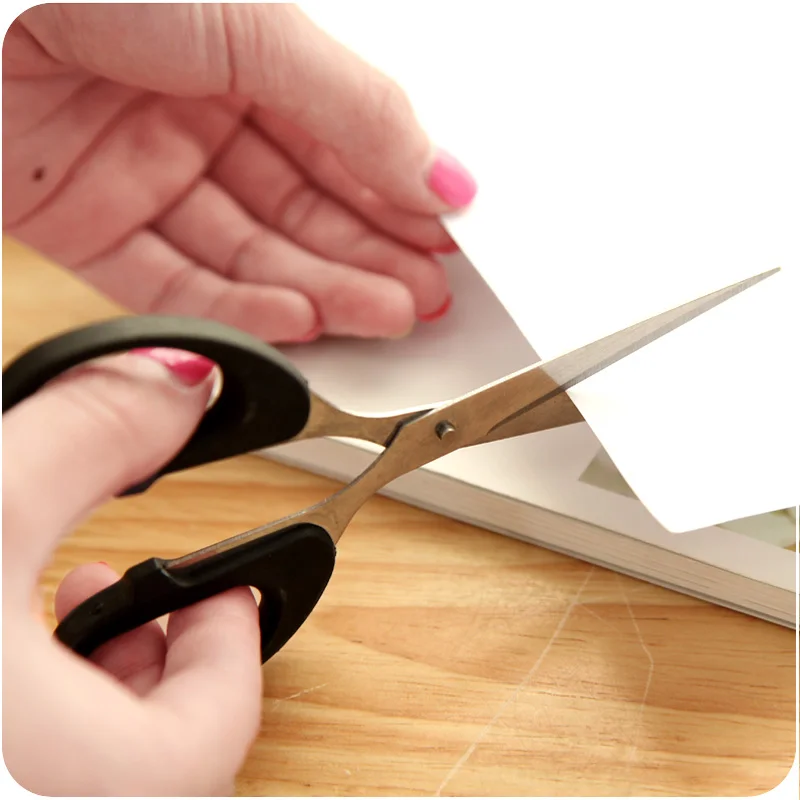
Shear
Shearing is when to sides example of those on
scissors move parallel to each other causing a
shearing motion.

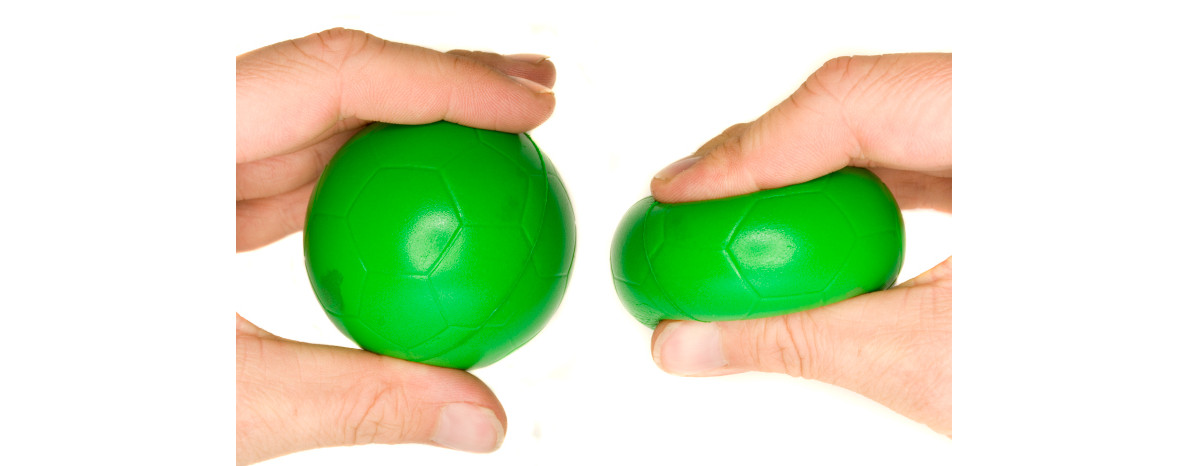
Compression
Compression is the force when an object is being
pushed down forcefully and continuously, which,
like the foamy ball will be squeezed smaller.

Tension
Tension is when a structure example a rubber band
is being pulled on both ends causing it to stretch
out further till the point it snaps in two.

Loads
Static Load
Live Load
Live load is the object/living thing that is not a
permanent part of the structure it is on an
example is the cars on this bridge since they
are not attached to the bridge so they are live
loads.

Dead Load
Dead load is the main structure or anything
permanently attached to the structure itself
an example is this bridge it is permanently
attached to the supports and the railings on
the sides.

Dynamic Load
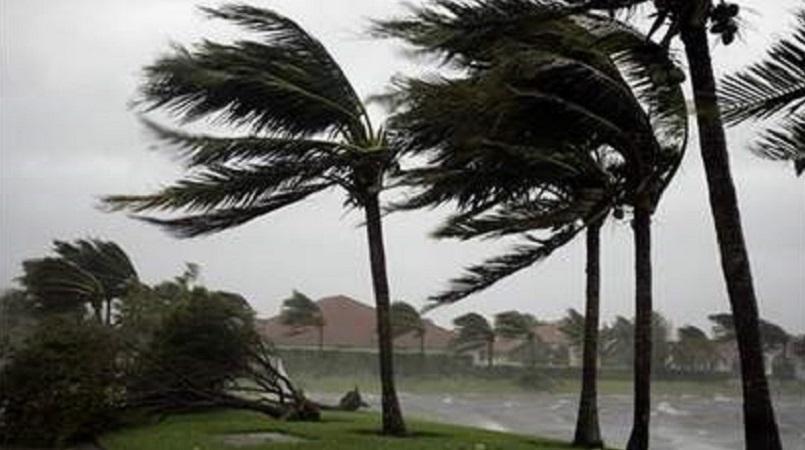
Dynamic load is the force that is forcefully applied
forcefully and continuously on a structure, that
means engineers need to build structures to withstand
dynamic loads like hurricanes, wind and Tornadoes.

External Forces
Plane of Application
Plane of application is the angle at which an
object is pushed. If a structure example a
water bottle is pushed at a lower angle it
won't fall, if you push the water bottle
at a higher angle it will fall.

Point of Application
Point of application is where the structure is pushed
example if you push a water bottle close to the top
the water bottle will fall over, if the water bottle
is pushed at the bottom then it will not fall but,
instead just move forward.

Direction
Direction is the way a structure is moving example
if you roll a ball forward the ball will move
forward, if you roll it on an angle that is where
the ball will roll.

Magnitude
Magnitude is the force of which you push something
lets say you shove your sibling in a light, playful
way you are using less magnitude, but, if you shove
your sibling in a hard, mean way you use more
magnitude and your sibling will likely fall.

Strengthening Structures
Triangles
Triangles are the cause of making structures stronger
because they are stronger shapes than squares, that's
why bridges and stools have triangular shape, to
make a structure be able to hold whatever live loads
are held on it.
Truss
A truss is a frame of triangles that help a structure
keep its stability and strength, an example is when
the roof of your house is made or a bridge is started
builders use trusses to hold live loads and not
collapse, there are 3 types of truss, Pratt truss, warren
truss and Howe truss.
Pratt truss
Pratt truss is a series of diagonal beams that move
outwards, unlike the Howe truss it is used in bridge
building, this give a structure strength because of
its triangular pattern.

Warren truss
Warren truss is a series of equilateral or isosceles
triangles forming the shape of shark teeth jags,
which, also help give a structure strength, mainly
bridges.
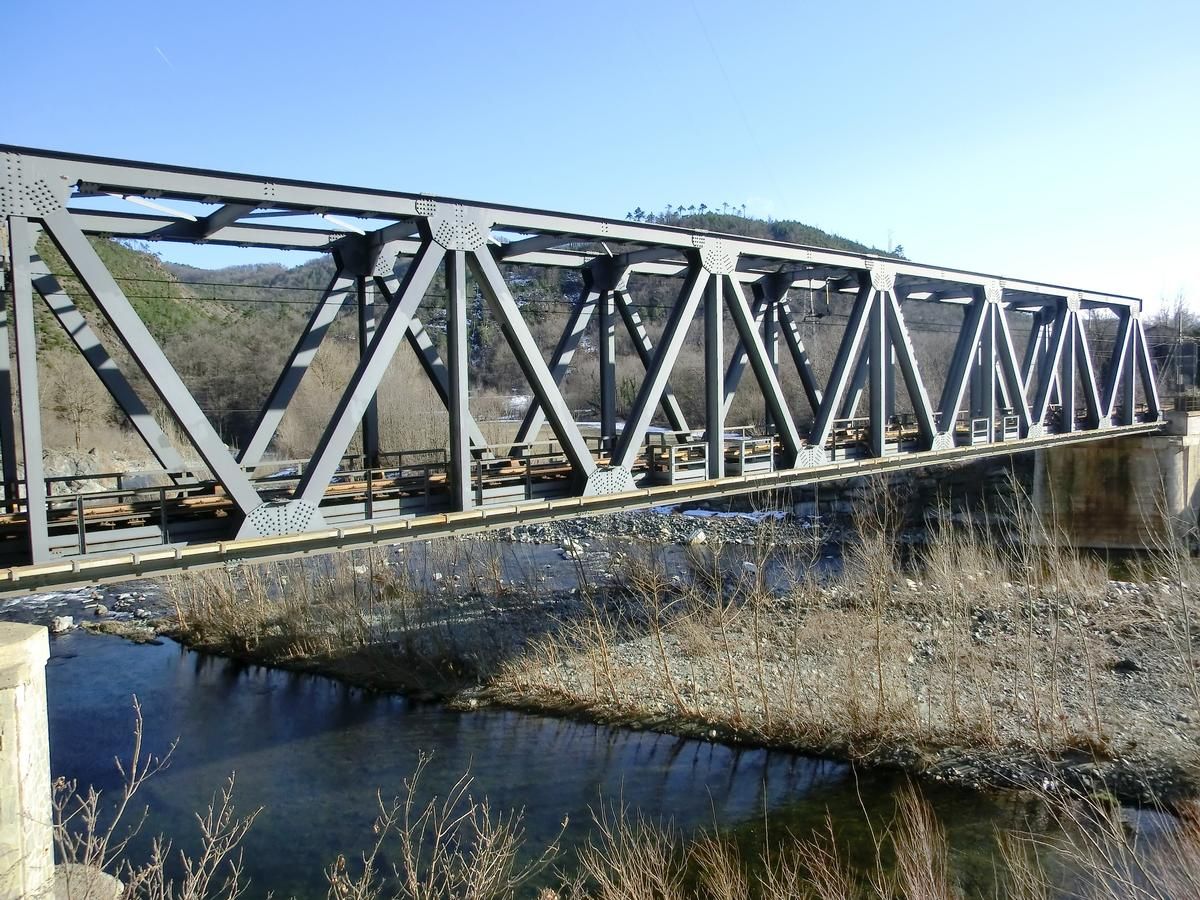

Howe truss
Howe truss is a series of triangles in odd directions
mainly used for house building, unlike the Pratt
truss it can't be used for bridges.



Gusset
Gussets are the connectors of trusses and keep the
trusses in place without them moving, gussets are
made of a solid, tough material.

Curves
Curves are shapes that have an upside down "U" shape
which can be used very well in structures and any
other places.
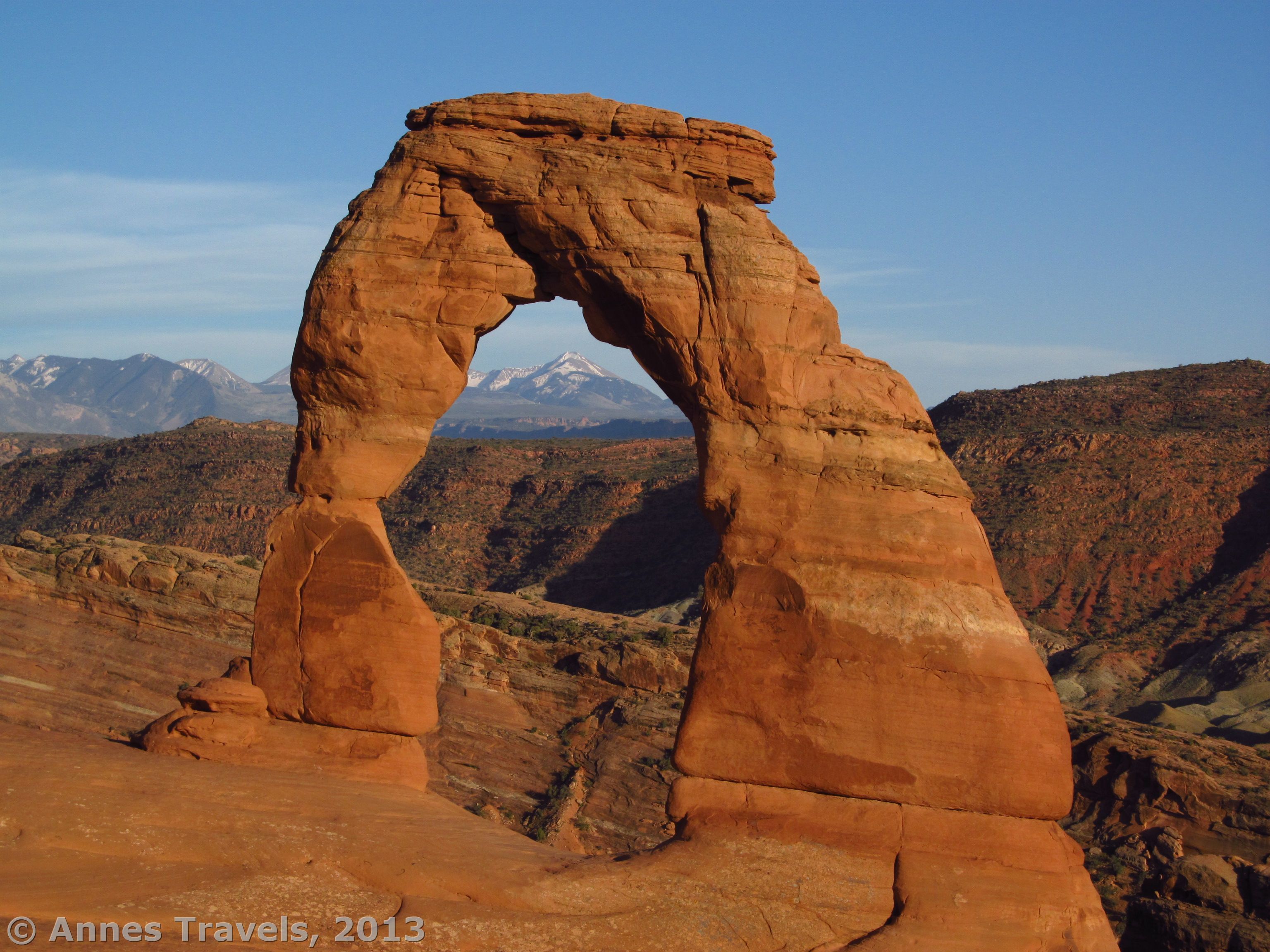
Arch
Arches which are curves can hold heavy objects better
than normal shapes, they are almost like triangles,
that is because of their hollow inside, the are more
stable.


Ties
Ties hold objects up but deal with the force of
tension in between the beam and the wall.
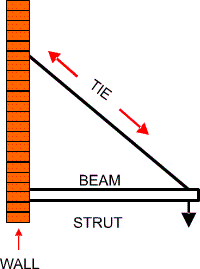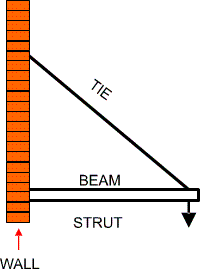
Struts
Struts also hold things up and have to deal with
the force of compression in between the beam and
the wall.

Corrugation
Due to its hollow arch like insides corrugation
makes a structure example cardboard lighter
and cheaper and easy to stack.

Lamination
Lamination is when you have a paper stuck in a plastic
that keeps the paper bend and water free this also
makes a laminated beam of wood cheaper and lighter
than a normal beam of wood.