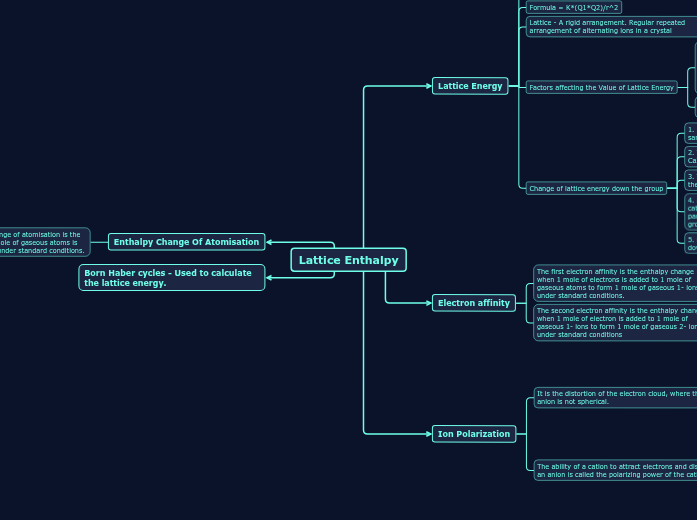
Lattice Enthalpy
Lattice Energy
Is the Enthalpy change when 1 mole of an ionic compound is formed from its gaseous ions under standard conditions.
Formula = K*(Q1*Q2)/r^2
Lattice - A rigid arrangement. Regular repeated arrangement of alternating ions in a crystal
Factors affecting the Value of Lattice Energy
1.Ion size - As the size of the ion increases, the lattice energy becomes less exothermic (Applies to both anions and Cations). Ions with the same ionic charge have a lower charge density if their radius is larger. This occurs because the same charge is spread out over a larger volume.
2. Charge of the ion - As the ionic charge increases, the lattice energy becomes more exothermic.
Change of lattice energy down the group
1. Lattice energy is greater if the ions (with the same charge) forming the lattice are small
2. The lattice energy decreases in the order Mg2+> Ca2+> Sr2+> Ba2+
3. The lattice energy is also inversely proportional to the sum of the radii of the anion and cation
4. As a sulfate ion is much larger than the group 2 cation, the sulfate ion contributes a relatively greater part to the change in the lattice energy down the group
5. Decrease in the lattice energy is relatively small down the group.
Electron affinity
The first electron affinity is the enthalpy change when 1 mole of electrons is added to 1 mole of gaseous atoms to form 1 mole of gaseous 1- ions under standard conditions.
Cl(g) + e- = Cl-(g)
The second electron affinity is the enthalpy change when 1 mole of electron is added to 1 mole of gaseous 1- ions to form 1 mole of gaseous 2- ions under standard conditions
O-(g) + e- = O2-(g)
Ion Polarization
It is the distortion of the electron cloud, where the anion is not spherical.
The degree of polarization of anion depends on
1. The charge density of the cation
2. The ease with which the anion can be polarized (Polarizabilty)
The anion is more likely to be polarized if
1. Cation is small
2. Cation has a charge of 2+ or 3+
3. Anion is large
4. The anion has a charge of 2- or 3-
The ability of a cation to attract electrons and distort an anion is called the polarizing power of the cation.
Enthalpy Change Of Atomisation
The standard enthalpy change of atomisation is the enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous atoms is formed from its elements under standard conditions.