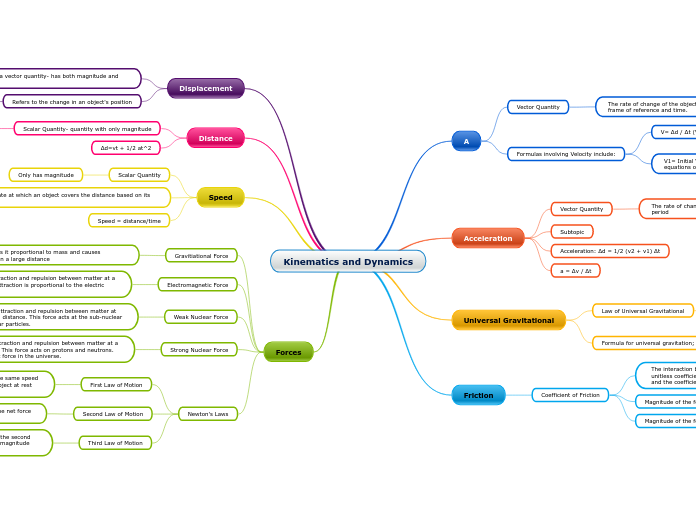
Kinematics and Dynamics
A
Vector Quantity
The rate of change of the object's position with respect to a frame of reference and time.
Formulas involving Velocity include:
V= Δd / Δt (Velocity formula/uniform motion)
V1= Initial Velocity, V2= Final Velocity, part of the five equations of kinematics
V2 = v1 + aΔt
v2^2 = V1^2 + 2 aΔd
Acceleration
Vector Quantity
The rate of change in speed/velocity over the given time period
Subtopic
Acceleration: Δd = 1/2 (v2 + v1) Δt
a = Δv / Δt
Universal Gravitational
Law of Universal Gravitational
There exists a force of gravitational attraction between every two objects in the universe. This force varies inversely as the square of the distance between the objects and directly as the product of their masses. The force's direction is towards the centre of the attracting object.
Formula for universal gravitation; Fg=Gm1m2/d ^2
Friction
Coefficient of Friction
The interaction between two surfaces is quantified with unitless coefficients called the coefficient of static friction (mS) and the coefficient of kinetic friction (mK).
Magnitude of the force of Static Friction
FS = mSFN
Magnitude of the force of Kinetic Friction
FK = mKFN
Displacement
Displacement is a vector quantity- has both magnitude and direction
Direction is represented in terms of direction in square brackets, [N], [S], [E], [W].
Refers to the change in an object's position
Δd= Final displacement - initial displacement
Distance
Scalar Quantity- quantity with only magnitude
The total length of the path traveled by an object in motion
Typically represented in m, km, etc.
Δd=vt + 1/2 at^2
Speed
Scalar Quantity
Only has magnitude
The rate at which an object covers the distance based on its unit
Examples: m/s, km/h, etc.
Speed = distance/time
Forces
Gravitiational Force
The force where is it proportional to mass and causes attraction between a large distance
Electromagnetic Force
This force causes attraction and repulsion between matter at a large distance. The attraction is proportional to the electric charge.
Weak Nuclear Force
This force causes attraction and repulsion between matter at an extremely small distance. This force acts at the sub-nuclear level on sub-nuclear particles.
Strong Nuclear Force
This force causes attraction and repulsion between matter at a very small distance. This force acts on protons and neutrons. This is the strongest force in the universe.
Newton's Laws
First Law of Motion
An object at motion tends to stay in motion at the same speed and direction unless acted upon by a force. An object at rest stays at rest.
Net Force: Fnet= F1 + F2 + F3 ...
Second Law of Motion
The acceleration of the object depends based on the net force applied and inversely to the mass of an object
F = ma
Third Law of Motion
When an object exerts a force on another object, the second body exerts a force on the first body of the same magnitude but in the opposite direction.
Fab = - Fba