Waves
Vibrations:
-a vibration is the cyclical motion of an object around an equilibrium point.
-all vibrations need a medium to transfer waves
-a mechanical wave is a transfer of energy through a medium by particle vibration. Particle vibration is caused by a disturbance to the medium (
-a medium is a material that allows the transmission of energy due to vibrations; can be a solid, liquid, or gas.
-the particles of an elastic medium return to their original location after a wave passes through.
-The speed of a wave and the distance it can travel depend on the composition of the medium. A rigid medium allows a wave to travel longer and faster than a less rigid medium. A less rigid medium disperses more energy, thus reducing the speed and distance that a wave can travel.
Characteristics of Waves:
Wave forms: the shape of a wave when graphed
Crest: the maximum point of a transverse wave
Trough: the minimum point of a transverse wave.
Phase shift: the shift of an entire wave across the x-axis.
Frequency (f): the number of complete cycles that occur in unit time, usually 1 s; measured in hertz (Hz)
Period (T): the time for a wave to complete one cycle, usually in seconds.

Wave speed (v): the rate at which a wave is travelling through a medium; also a measure of how fast the energy in the
wave is moving

Equation to calculate wave speed.
Linear Density (m):the mass per unit distance of a string; units are kilograms per metre (kg/m)

Factors that affect wave speed and how to calculate them.
Simple Harmonic Motion: any motion that repeats itself at regular intervals
Interference of Waves:
Interference: the process of generating a new wave when two or more waves meet.
Principle of Superposition: at any point the amplitude of two interfering waves is the sum of the amplitudes of the individual waves.
Constructive Interference: the process of forming a wave with a larger amplitude when two or more waves combine.
Destructive Interference: the process of forming a wave with a smaller amplitude when two or more waves combine.
Subtopic
Beats:
Beats: periodic change in sound intensity caused by the interference between two nearly identical sound waves.
Beat Frequency: the frequency of beats produced by the interference of two waves with slightly different frequencies; equal to the difference in the frequencies of the interfering waves.
-Many musical instruments can be tuned using beats.
Types of Mechanical Waves:
-In transverse waves, the particles of the medium move perpendicular to thedirection of the flow of energy.
-In longitudinal waves, the particles of the medium move parallel to thedirection of the flow of energy.
-In a fluid, longitudinal waves transfer energy through regions of higher and lower pressure. These regions are called compressions and rarefactions, respectively.
-Sound, an important example of a longitudinal wave, is a form of energy produced by rapidly vibrating objects.
-Many wave motions in nature are a combination of longitudinal and transverse motion.
Properties of Sound Waves:
-Sound waves are audible to humans between 20 Hz and 2 kHz. Sound waves < 20 Hz are called infrasonic waves. Sound waves > 2 kHz are called ultrasonic waves.
Echo: the sound energy reflected off a surface back to the producer of the sound
The speed of sound is 331.4 m/s + (0.606 m/s/°C)T where T is the temperature in celsius.
Mach number (M): the ratio of the airspeed of an object to the local speed of sound.
(M) = the airspeed of the object divided by the local speed of sound.
Decibel (dB): the unit of sound level used to describe sound intensity level
Waves at Media Boundaries:
Free-end Reflection: a reflection that occurs at a media boundary where the second medium is less dense than the first medium; reflections have an amplitude
with the same orientation as the original
wave.
Fixed-end Reflection: a reflection that occurs at a media boundary where one end of the medium is unable to vibrate; reflections are inverted.
Transmission: the motion of a wave through a medium, or motion of a wave from one medium to another medium.
Standing Wave: an interference pattern produced when incoming and reflected waves interfere with each other; the effect is a wave pattern that appears to be stationary.
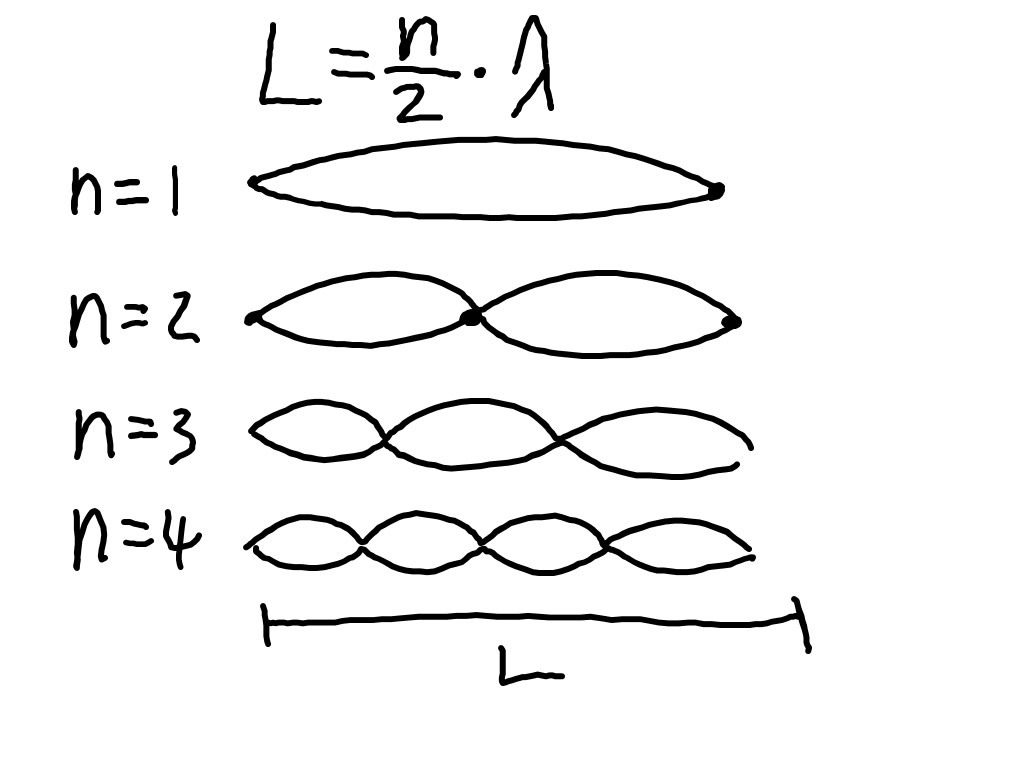
Subtopic
Node: in a standing wave, the location where the particles of the medium are at rest.
Antinode: in a standing wave, the location where the particles of the medium are moving with greatest speed; the amplitude
will be twice the amplitude of the original wave.
Fundamental Frequency or First Harmonic (f0): the lowest frequency that can produce a standing wave in a given
medium.
Doppler Effect
Doppler Effect: when a source of sound approaches an observer, the observed frequency of the sound increases; when the source moves away from an observer, the observed frequency of the sound decreases.

An example of this occurring is when a car honks while it moves at a fast speed past you; the honk will sound like it is changing pitch.