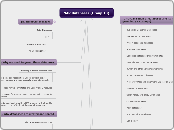
NAR Databases (Group 13)
Nucleotide Sequence Databases
RNA sequence databases
Protein sequence databases
Structure Databases
Genomics Databases (non-vertebrate)
Metabolic and Signaling Pathways
Human and other Vertebrate Genomes
Human Genes and Diseases
Microarray Data and other Gene Expression Databases
Proteomics Resources
Other Molecular Biology Databases
Organelle databases
Plant databases
Immunological databases
Cell biology
(c) Criteria for selection into NAR databases
Directory organized by biological subject
subcategory are of common task relevant
Resources
static resource whose intention is to convey bioinformatics information
Tool
bioinformatics software or server that can analyse, extract and modify input data to particular databases
Database
biological data store that can be queried
(e) Why some databases are no longer in the databases and dropped from it
Commercialization Purposes
The databases are no longer free
Databases Evolution
Some of the smaller groups of databases have being merge to form a ne database which is more relevant in today's context
Redundancy
Databases having the same or way similar datas and information regarding a specific topic
Diverted from the original objective and purpose of the databases which should be a public-free databases
Databases are not updated and no longer accessible
Total Databases
1512
14 Major Categories
41 Subcategories
(d) Why we need to group these databases
Incresing numbers of information
scientist, biologists, researchers unable to track tools, databases, methods and their specialty information easily
need for well annotated and user-friendly resource
make it easier for users to search by narrowing or specify their search
due to significant growth in NAR web server that lead to change in type of tool, databases and resources
(f) Why databases are created and shared
Pivotal Reference Resources
Providing literature for further research
Up-to-date Databases Resources
To notify the researchers of newly-discovered information