Metabolism
Types of energy
Kinetic Energy
energy of motion (moving objects perform work by causing other matter to move)

Subtopic
Potential Energy
stored energy (energy that is available but not yet released)
Bond Energy
the energy required to break (or form) a chemical bond
endothermic
A Endothermic Reaction is a reaction or process accompanied by or requiring the absorption of energy in the form of heat
/endothermic-and-exothermic-reactions-602105_final-c4fdc462eb654ed09b542da86fd447e2.png)
Exothermic Reactions are reactions or processes accompanied by the released of energy in the form of heat
Metabolic pathways
Anabolism
process of using energy to build large molecules
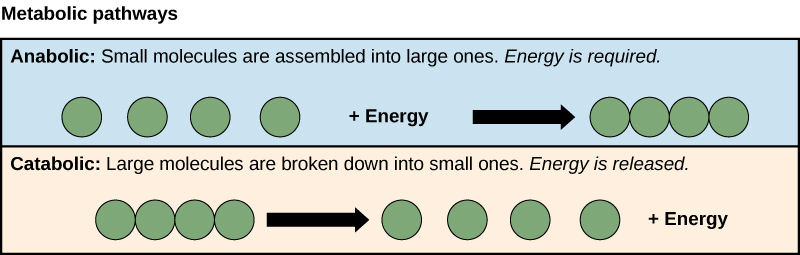
Catabolism
process of breaking down compounds into smaller molecules to release energy
Main topic
Laws of Thermodynamics
Law #1
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be transformed from one type into another and transferred from one object to another
Ex. Chemical energy stored in food molecules, then transformed into Kinetic energy in your muscles so you can move
Law #2
During any process, the universe tends toward disorder
Ex. It is more likely that a stack of books will tumble over that a pile of books will stack themselves up again
Thermodynamis
System
can be a whole organism, a group of cells, or a set of substrates/products - whatever object is being studied
Open systems
system and its surroundings can exchange matter and energy (example: biological systems like the human body)
Surroundings
everything in the universe outside of the system
Thermodynamics and Metabolism
ATP
Energy from catabolic reactions is used to power anabolic reactions and the source of energy that links these sets of reactions is called ATP
ATP also known as adenosine triphosphate is referred to as the energy of the cell, this is because so many cellular activities depend on it! ATP is composed off Nitrogenous base ,Adenine, Ribose sugar and three Phosphate Groups
electron carriers
compounds that pick up electrons from energy-rich compounds and donate them to low-energy compounds
Examples
NAD⁺ (oxidized form), NADH (reduced form)
FAD (oxidized form), FADH₂ (reduced form)
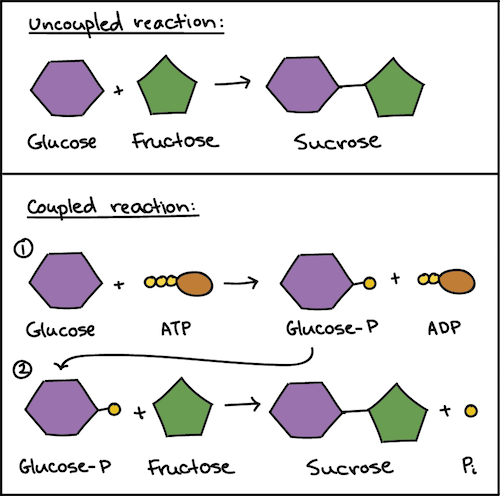
Coupled Reactions
Use the energy from hydrolysis as input for the build up of ATP
Subtopic