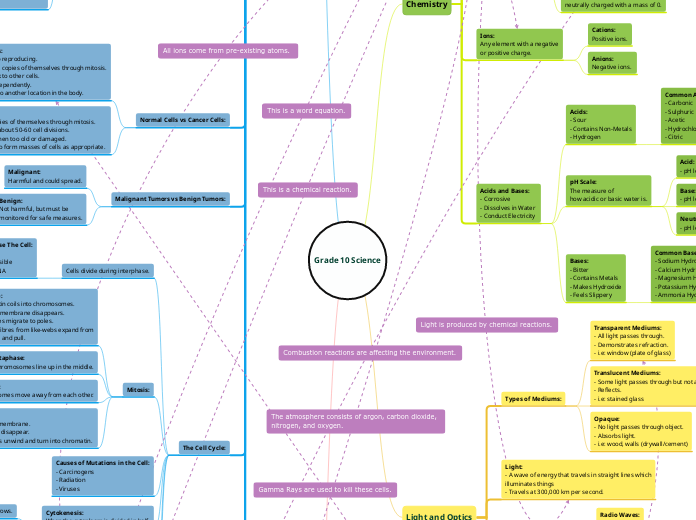
Chemical Reactions
Hints A Chemical
Reaction Has
Occurred:
- Smell
- Colour
- Precipitate
- Hard to Reverse
- Sound
- Gas
Ways to Represent A Chemical Reaction:
- Word Equation
- Skeletal Equation
- Balanced Equation
Types of Chemical Reactions:
Synthesis: Two elements combined into one.
( i.e - A + B > AB )
Decomposition: To break a compound into two elements.
( i.e - AB > A + B )
Single Displacement: To replace another element in a compound. ( i.e - A + BC > B + AC )
Double Displacement: When the cations in two ionic compounds switch places. ( i.e - AB + CD > AD + BC )
Combustion: When a substance reacts with oxygen gas, releasing energy in the form of light and heat.
( i.e - CxHy +O2 > CO2 +H2O )
Neutralization: When an acid and a base react to form a salt and involves a combination of hydrogen and hydroxide ( OH- ) ions to generate water. ( i.e - HB + XOH > XB + H2O )
The Law of Conservation of Mass states
that mass is neither created,
nor destroyed during chemical reactions.
Parts of An Atom:
Protons:
positively charged with a mass of +1.
Electrons:
negatively charged with a mass of -1.
Neutrons:
neutrally charged with a mass of 0.
Ions:
Any element with a negative
or positive charge.
Cations:
Positive ions.
Anions:
Negative ions.
Acids and Bases:
- Corrosive
- Dissolves in Water
- Conduct Electricity
Acids:
- Sour
- Contains Non-Metals
- Hydrogen
Common Acids:
- Carbonic
- Sulphuric
- Acetic
- Hydrochloric
- Citric
pH Scale:
The measure of
how acidic or basic water is.
Acid:
- pH levels are under 7.
Base:
- pH levels are above 7.
Neutral:
- pH levels are exactly at 7.
Bases:
- Bitter
- Contains Metals
- Makes Hydroxide
- Feels Slippery
Common Bases:
- Sodium Hydroxide
- Calcium Hydroxide
- Magnesium Hydroxide
- Potassium Hydroxide
- Ammonia Hydroxide
Types of Mediums:
Transparent Mediums:
- All light passes through.
- Demonstrates refraction.
- i.e: window (plate of glass)
Translucent Mediums:
- Some light passes through but not all.
- Reflects.
- i.e: stained glass
Opaque:
- No light passes through object.
- Absorbs light.
- i.e: wood, walls (drywall/cement)
Light:
- A wave of energy that travels in straight lines which
illuminates things
- Travels at 300,000 km per second.
Different Wave Uses:
Radio Waves:
- TV Signals
- Cell Phones
Micro Waves:
- Microwaves
- Radar Guns
Infrared Waves:
- Burgular Alarms
Visible Waves:
- Rainbows
UltraViolet Waves:
- Disinfect Drinking Water
X-Rays:
- Customs at Airports
Gamma Rays:
- To Kill Cancerous Cells
Cell Organelles and Their Functions:
Mitochondria:
- Makes the energy for the cell.
- Self-replicating.
- Distributes the energy it creates evenly throughout the cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum:
- Transports proteins around the cell.
- Stores proteins.
- Modifies molecules if needed.
Golgi Apparatus:
- Produces the membranes and proteins.
- Packages proteins and carbohydrates and prepares
them to be exported.
- Modifies molecules produced by the cell if necessary.
Nucleus:
- Controls what's going on in the cell.
- Contains, stores, and protects DNA.
- Directs activities in the cell.
Vacuole:
- Collects the waste from the other organelles.
- Collects large amounts of water.
- Digests the food materials in the cell.
Ribosomes:
- Produces proteins.
- Clings onto the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Scattered throughout the cytoplasm.
Nuclear Membrane:
- The membrane surrounding the nucleus.
- Allows proteins to pass in and out of the nucleus.
- Defines and decides the boundaries that surround
the nucleus.
Cytoplasm:
- Where the organs are located.
- Made of salts, minerals, and nutrients.
- Can change the cells shape.
Cell Membrane:
- Protects the cell.
- Decides what comes in and out of the cell.
- Lets the good in, and gets rid of the bad.
Organ Systems:
Animal Organ Systems:
The Respiratory System:
Functions:
- To exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- Respiration consists of 2 processes: inhalation and expiration, which operates on the principle that air moves from high to low pressure.
Inhalation and Expiration:
- Diaphram:
Inhalation - contracts and moves down.
Exhalation - relaxes and moves up.
- Ribcage:
Inhalation - lifts and pulls out.
Expiration - falls and pushes in.
- Chest Cavity:
Inhalation - expands and volume increases.
Expiration - shrinks and volume decreases.
- Air Pressure:
Inhalation - low pressure inside enlarged lungs.
Expiration - high pressure inside lungs as they shrink.
- Air Movement:
Inhalation - oxygen moves in.
Expiration - carbon dioxide moves out.
Circulatory System:
Functions:
- Transports in oxygen, nutrients, and hormones.
- Transports out carbon dioxide and wastes.
- Distributes heat.
- Fights against disease.
Consists Of:
- Blood
- Blood Vessels
- The Heart
Blood:
- 4-6 L in your body.
Plasma Component:
- 55% of blood.
- 90% water, 10% proteins, nutrients,
and wastes.
- Maintains temperature, fights diseases, and
transports vitamins.
Cellular Component:
- 45% of blood.
Red Blood Cells:
- Carry oxygen then carbon dioxide
and are produced in bone marrow.
- Live 100-120 days.
White Blood Cells:
- Guard against infection.
- Produced in bone marrow.
- Live for many years.
- Fight foreign invaders.
Platelets:
- Proteins that release blood clotting factor.
- Fibrin forms scabs to heal cuts.
Blood Vessels:
- Provide pathway of blood and all its components.
Arteries:
- Carry pressurized blood away from the heart to tissues.
- Branch into small vessels called arterioles or capillaries.
Veins:
- Unpressurized blood returns to heart through valves.
Capillaries:
- Microscopic
- Only one cell can travel through at a time
- Where nutrients and wastes are exchanged.
The Heart:
- Structure of your heart enables it to pump deoxygenated
blood to your lungs and oxygenated blood to your entire body.
- Heart contracts, and blood pumps out, heart releases and blood goes into the heart.
- Size of a clenched fist.
- Nestled between your lungs in the chest cavity.
The Digestive System:
Function:
- Breaks down food into nutrients.
- Absorb nutrients for growth, maintenance, and repair.
- Removes solid waste.
Stages of the Digestive System:
1. Indigestion
2. Digestion
3. Absorption
4. Egestion
Included Organs:
- Oral Cavity
- Pituitary Gland
- Stomach
- Pharynx
- Esophagus
- Gall Bladder
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Large Intestine
- Small Intestine
- Rectum
- Anus
The Lymphatic System:
Function:
- Acts as the bodies "sewage system".
- Helps move lymph through the body.
- Protects body against disease.
- Maintains fluid levels in body tissues by removing
all fluids that leak out of blood vessels.
Urinary System:
Function:
- Eliminates liquid waste.
- Regulates blood volume and pressure.
Reproductive System:
Function:
- Produces egg and sperm cells.
- Creates life.
- Produces hormones.
Integumentary System:
Function:
- Protection
- Controls body temperature.
- Helps remove waste from body.
Muscular System:
Functions:
- Produces body movement.
Skeletal System:
Functions:
- Gives structure to organism.
- Protection for organs.
- Produces stem cells.
- Helps movement occur.
Nervous System:
Functions:
- Sends signals.
- Receives information.
- Helps body parts communicate.
Endocrine System:
Functions:
- Hormonal release and control.
- Controls growth, mood, development,
and metabolism.
Plant Organ Systems:
Root:
- Below ground.
- Roots take up water and nutrients
and send them up to stem.
Shoot:
- Above ground.
- Stem, leaves, buds, fruit, and flowers grow and reproduce.
- Pulls up water through the xylem.
- Where transpiration occurs.
Organ:
A structure composed of different tissues
specialized to carry out a specific function.
Animal Organs:
Skin:
- The largest organ in your body.
- Serves protect the inner cells from damage,
as a defense against disease organisms, insulates,
releases heat and excretes bodily wastes.
Included Tissues:
- Epithelial
- Connective
- Nervous
- Muscle
Made up of Two Different Layers:
1. Epidermis
2. Dermis
Lungs:
- Pair of organs involved in respiration
- Breathe in oxygen, breathe out carbon dioxide.
Included Tissues:
- Connective
- Nervous
- Epithelial
Heart:
- A muscular pump that supplies blood to all parts
of the body, moves nutrients, oxygen, and waste.
Included Tissues:
- Epithelial
- Connective
- Nervous
- Muscle
Separated Into 4 Chambers:
- Left Ventricle
- Right Ventricle
- Right Atrium
- Left Atrium
Ventricles - Lower Chambers
Atriums - Upper Chambers
Stomach:
- Physically breaks down food into a liquid mixture called chyme.
- Enzymes, hydrochloric acid, and other chemicals are released into the stomach to help break down nutrients.
Included Tissues:
- Epidermal
- Connective
- Nervous
- Muscular
Plant Organs:
Roots:
- Anchors plant.
- Collects water from soil and transports to stem.
- Stores food that is made in other parts of plant.
Included Tissues:
- Epidermal
- Meristematic
- Ground
- Vascular
Leaf:
- Works together to carry out photosynthesis.
Included Tissues:
- Vascular
- Epidermal
- Ground
Stem:
- Transports water and nutrients through plants.
- Supports and protects the leaves and flowers.
Included Tissues:
- Epidermal
- Ground
- Vascular
Flower:
- Reproductive structure of the plant.
- Produces seeds through sexual reproduction.
Included Tissues:
- Meristematic
- Vascular
- Ground
Tissue:
A group of cells that work
together to perform a task.
Animal Tissues:
Epithelial:
- Lines body cavities and outer
surface of body.
- Protects structures.
- Forms glands that produce hormones,
enzymes, and sweat.
Connective:
- Supports and protects structures.
- Forms blood.
- Stores fat.
- Fills empty space.
Muscle:
- Allows for movement.
Three Types:
- Skeletal
- Smooth
- Cardiac
Skeletal:
Attached to bones and allows movement.
Smooth:
Located in internal structures such as the digestive tract.
Cardiac:
Muscle specific to the heart.
Nervous:
- Responds to stimuli.
- Transmits and stores information.
Plant Tissues:
Meristematic:
- Unspecialized tissue capable of dividing mitosis.
- Found in several locations in the plant.
- Responsible for growing new parts of the plant.
Epidermal:
- Forms the protective outer covering.
- Allows the exchange of materials and gases into
and out of the plant.
Ground:
- Provides strength and support.
- Stores food and water.
Vascular:
- Moves substances from the roots to the leaves.
- Transports sugars form the leaves to other parts
of the plant.
Xylem:
Conducts water and minerals from the roots
upward and throughout the plant.
Phloem:
Transports dissolved nutrients in all directions
within the plant.
Normal Cells vs Cancer Cells:
Cancer Cells:
- Do not stop reproducing.
- Make exact copies of themselves through mitosis.
- Do not stick to other cells.
- Behave independently.
- Can move to another location in the body.
Normal Cells:
- Make exact copies of themselves through mitosis.
- Reproduce for about 50-60 cell divisions.
- Self-destruct when too old or damaged.
- Stick together to form masses of cells as appropriate.
Malignant Tumors vs Benign Tumors:
Malignant:
Harmful and could spread.
Benign:
Not harmful, but must be
monitored for safe measures.
The Cell Cycle:
Cells divide during interphase.
During Interphase The Cell:
- Grows
- The nucleus is visible
- Replication of DNA
Mitosis:
Prophase:
- Chromatin coils into chromosomes.
- Nuclear membrane disappears.
- Centrioles migrate to poles.
- Spindle fibres from like-webs expand from
centrioles and pull.
Metaphase:
- Chromosomes line up in the middle.
Anaphase:
- Chromosomes move away from each other.
Telophase:
- New nuclear membrane.
- Spindle fibres disappear.
- Chromosomes unwind and turn into chromatin.
Causes of Mutations in the Cell:
- Carcinogens
- Radiation
- Viruses
Cytokenesis:
When the cytoplasm is divided in half.
In an animal cell, a cleavage furrows.
In a plant cell, the pre-mature cell wall forms.
Why do Cells Divide:
- Growth
- Repair
- Replace
- Reproduction
- ALL living things are made of cells.
- The cell is the smallest functional unit of life.
- ALL cells come from pre-existing cells.
Stem Cells:
All stem cells have the potential to be specialized cells.
Sources of Stem Cells:
- Embryonic stem cells
- Umbilical cord
- Adult stem cells
All cells start their lives as identical cells called stem cells.
Cell Specialization:
- All cells begin alike and differentiate into specialized cells.
- They have a different structure and ability to perform their specific functions.
- Group of cells work together to perform functions.
- There are 200 different types of cells in the human body.
Microscope:
- An optical instrument used for viewing very small objects, such as animal or plant cells, typically magnified several hundred times.
Parts:
- Eyepiece
- Eyepiece Tube
- Objective Lenses
- Nose Piece
- Adjustment Knobs
- Stage
- Aperture
- Microscopic Illuminator
- Condenser
- Diaphragm
- Condenser Focus Knob
Incomplete Combustion:
Occurs when burning happens, but
there is not enough oxygen.
Combustion:
Fast reaction of a substance
with oxygen to produce oxides.
Fuel + Oxygen > Oxides + Water Energy
Combustion in Cars:
1. Intake
2. Compression
3. Powerstroke
4. Exhaust
Greenhouse Gases (GHG):
A natural way for the Earth to
stay warm.
Contributors to Greenhouse Gases (GHG):
- Water Vapour
- Carbon Dioxide
- Methane
- Nitrous Oxide
Earth naturally keeps these
in balance so the atmosphere keeps
the temperature ideal for the biosphere.
Earth's Spheres:
Each of these spheres receive
the sun's energy, traps it, stores it
and transports it until it all radiates
back out to space.
Atmosphere:
Gas surrounding Earth.
Hydrosphere:
Liquid water, water vapour, and ice.
Lithosphere:
Solid rock, minerals (Earth's crust).
Biosphere:
All plants, animals, bacteria, etc.
The darker the surface, the more the sun will reflect it back.
Difference Between Climate And Weather:
Climate Is:
- Long-Term
- The average after a long period
- Average wind speed
- Average wind direction
Weather Is:
- Short-Term
- Immediate (happening at the moment)
- Weather conditions at a particular time and place
Adaptation:
- Adjusting lifesyles and activities to our changing climate.
- Preparing for future.
- i.e : storing water for emergencies.
Mitigation:
- Activites to reduce Greenhouse Gases (GHG)
emissions
- i.e : walking, biking, energy efficiency in home, eating less meat.
Natural Causes of Climate Change:
- Volcanic Activity
- Meteorites
- Orbital Variation
- Methane Producing Animals
- Water Cycle
- Wildfires
- Carbon Sinks
- Carbon Dioxide
- Methane
- Water Vapour
- Nitrous Oxide
- Chloroflourcarbon
Climate Change Effects:
- The Environment
- Habitats
- Overall Health of Humans and Animals
- Economics
Human Causes of Climate Change:
- Pollution
- Overpopulation
- Burning Fossil Fuels
- Combustion
- Clearcutting
- Industrial Processes
- Land Use
- Landfills
- Carbon Dioxide
- Methane
- Water Vapour
- Nitrous Oxide
- Chloroflourcarbon
Anthropogenic Greenhouse Effect:
- The process that warms the earth due to the human
production of greenhouse gases and other actions.