Metabolism
Laws of Thermodynamics
The transfer and transformation of thermal energy
First Law

Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be transformed from one type into another
Second Law

During any process, the universe tends toward disorder
(law pertains to the transformation of potential energy into heat or molecular motion)
Thermodynamics and Metabolism
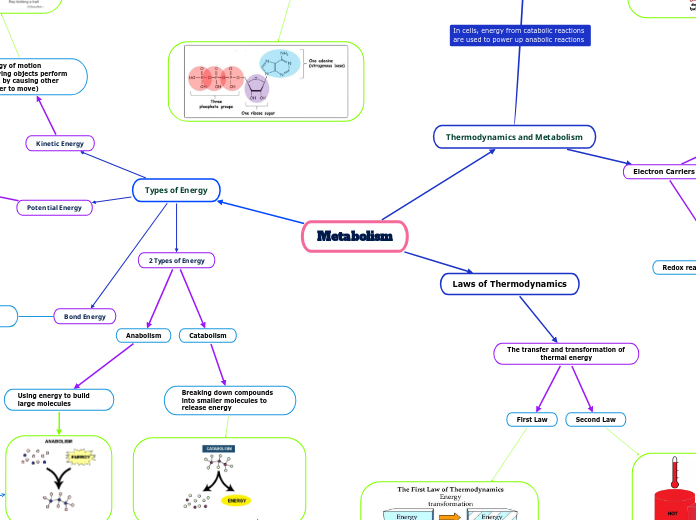
ATP
(Energy of the cell)
Composed of:
Nitrogenous base Adenine
Ribose sugar
Three Phosphate Groups

Phosphates are negative
Releases energy when hydrolyzed
ADP is released when 1 bond is broken
Electron Carriers
Compounds that pick up electrons from energy-rich compounds and donate them to low-energy compounds

Redox reactions are coupled reactions

Reduced molecules (gained electrons) have higher energy levels compared to oxidized molecules
Types of Energy
Kinetic Energy

Potential Energy
Bond Energy
Energy required to break (or form) a chemical bond
Exothermic Reaction:
a reaction accompanied by the release of energy in the form of heat

Endothermic Reaction:
a reaction or process accompanied by or requiring the absorption of energy in the form of heat
Example:
-photosynthesis
2 Types of Energy
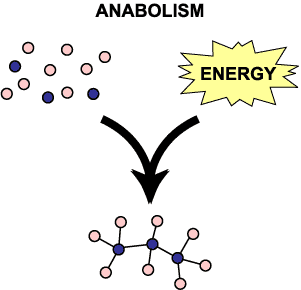
Anabolism
Using energy to build large molecules
Catabolism
Breaking down compounds into smaller molecules to release energy