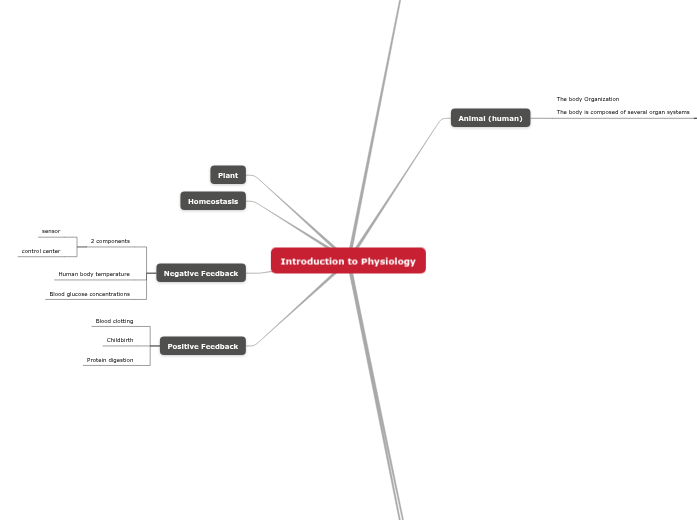
Introduction to Physiology
Introduction
Definition
Physiology (Greek, physis, meaning "nature") refer either to the parts or functions (mechanical, physical & biochemical) of living organisms
the branch of biology that deals with the study of all the parts of living organisms
Scientific Method
Determine how organisms, organ systems, organs, tissues, cells and bio- molecules (molecules & atoms) carry out the chemical or physical function that they have in a living system.
Animal (human)
The body Organization
The body is composed of several organ systems
Cells
Tissues
Tissues are composed of cells
Organs
An organ is composed of tissues
Organ are composed of one or more tissues
Organs integrate the function of different tissues, providing functions that the individual tissues lack.
The function of organ system is similarly dictated by the organ present
Organ System
An organ system is composed of one or more organs
Transport of f luids
cardiovascular system
consist of
heart
blood vessels
carries blood through the body to
deliver nutrients
remove wastes
lymphatic system
consist of
lymph nodes
lymph fluid
lymphatic vessels
collects excess fluid and fat
from the body
returns it to the heart
Body maintenance
deliver and remove substances from the body's tissues
the digestive system
composed of the organs of the digestive tract and peripheral components
teeth
liver
pancreas
processes and extracts nutrients from food
the respiratory system
provides gas exchange for the cardiovascular system
lungs
tubes - through which air moves
the urinary system
removes excess water and salts from the blood and excretes them in the urine
kidneys
bladder
urine conducting tubes
Control of the body systems
nervous system
brain
spinal cord
nerves
endocrine system
the glands secrete chemical that serve as messengers between body parts
hormonal glands
these messages help control bodily functions
Sensory input and motor output
integumentary system
the sensory receptors of this system sense external stimuli
skin
accessory systems
skeletal system
provides support and works with the muscular system to provide movement
bones
muscular system
the contraction of these muscles moves the skeletal system to provide movement
body's muscles
Reproduction
reproductive system
Main topic
Main topic
Plant
Homeostasis
Negative Feedback
2 components
sensor
control center
Human body temperature
Blood glucose concentrations
Positive Feedback
Blood clotting
Childbirth
Protein digestion