Human Body
Respiratory system
Body Parts
Lungs

Lungs are a very important part of the respiratory system. They are what allow us to breath. They take in oxygen and send it throughout the body while expelling carbon dioxide
Nose/Mouth

The Nose and Mouth take in oxygen which are then transported to the lungs. When the lungs take in the oxygen they release carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide leaves the body through the nose or mouth
Sinus

The sinuses are hollow spaces in the skull that help regulate temperature and humidity of the air we breathe in
Trachea
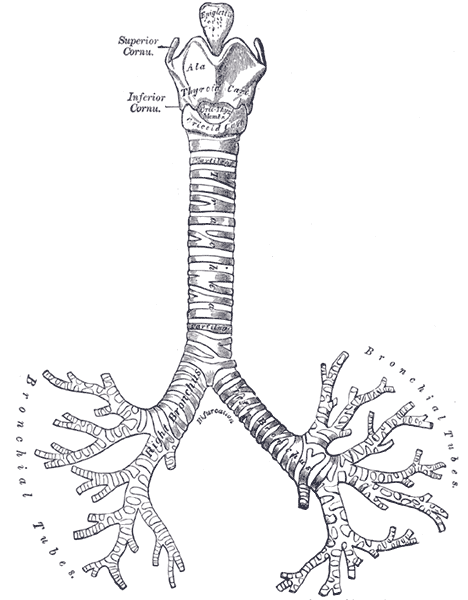
The trachea is a large tube down the throat that deliver oxygen from the upper respiratory tract to the bronchi
Bronchail Tubes

The Bronchial tubes are two tubes that take air from the trachea to the lobes of each lung. The right Bronchi Tube takes air to the right lung lobe while the left bronchi tube takes air to the left lung lobe
Lobes

Lobes have a rather simple function. They are responsible for bringing oxygen into the bloodstream and getting rid of carbon dioxide.
Alveoli

Alveoli are and important part of the respiratory system. They are in charge of exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide molecules to and from the bloodstream. They lie in clusters around the lungs.
Capillaries

These blood vessels bring
oxygen and nutrients to
tissue and remove waste products
Immune system
Body Parts

White Blood Cells
Monocytes
Monocytes are a white blood cell that fights certain infections and helps other cells remove dead or damage tissue. They also fight cancer cells and regulate immunity against foreign substances
Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are crucial to the immune system. They are some of the first cells to fight an infection. They create antibodies which stay in the blood and fight infections. The antibodies help the body get used to the the certain infection so the body can fight the infection off if it returns. They are created in bone marrow and found in blood and lymph tissue
Neutrophils
Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell that fight bacterial infections. They are produced in bone marrow and are the most numerous of cells making up about 40 to 60 percent of the cell population
Basophils
These small cells seem to sound an alarm when infectious agents invade your blood. They secrete chemicals such as histamine, a marker of allergic disease, that help control the body's immune response. They fight off allergies and using a substance called heparin, they slow down and stop blood clotting
Eosinophils
They attack and kill parasites and cancer cells, and help with allergic responses. They are responsible for combating multicellular parasites and fighting infections in vertebrae
Bone Marrow

Bone marrow is found in the bones. Bone marrow is what produces our red blood cells that carry oxygen and white blood cells that fight infections among other things
Antibodies

Antibodies produced by lymphocytes help the body fight off microbes or the poison/toxin they release. They do this by first recognizing substances produced on the microbe or in the gas they produce. These are called antigens. They then mark the cells for destruction getting rid of the infection
Complement System

The complement system is a system made of of proteins. These proteins assist the antibodies in mighting microbes and infections.
Lymphatic System

The lymphatic system is a network of delicate tubes through the body that control certain aspects. They manage the fluid levels in the body, react to bacteria, deal with cancer cells, deal with cell products that otherwise would result in disease or disorders, absorb some of the fats in our diet from the intestine among other things
The spleen is an organ that filter blood. It removes microbes and destroys old or damaged red blood cells. It also makes antibodies and lymphocytes
Thymus

The thymus filters and monitors blood content removing things that could be harmful. It also produces some white blood cells
When white blood cells malfunctions its called sepsis. Sepsis occurs when the body responds incorrectly to an infection. The body sends the wrong white blood cells leading to organ failure
Endocrine system
Body Parts
Hypothalamus Gland

The Hypothalamus is responsible for many of the bodies primary functions. This includes hunger, body temperature, moods and the release of other hormones through the body. It is small and located in center of the brain between the pituitary gland and thalamus.
Pituitary Gland
/images/library/1215/glandula_pituitaria_large_oBY3FiMMZ97OUENRoGGQUQ.png)
Considered the "Master Control Gland" this gland is what controls other glands. It is also the gland that triggers growth hormones. It sends hormones through your blood stream that effect other glands and organs. Especially the thyroid
Parathyroid Gland

The Parathyroid Gland is 4 glands in the neck that control calcium levels. They weight 30 milligrams and are 30 to 40 millimeters in diameter. When this malfunctions it causes too much calcium to be produced weakening bones and producing kidney stones
Pancreas Gland

The pancreas produces insulin and glucagon that helps control blood sugar levels.
Thyroid Gland
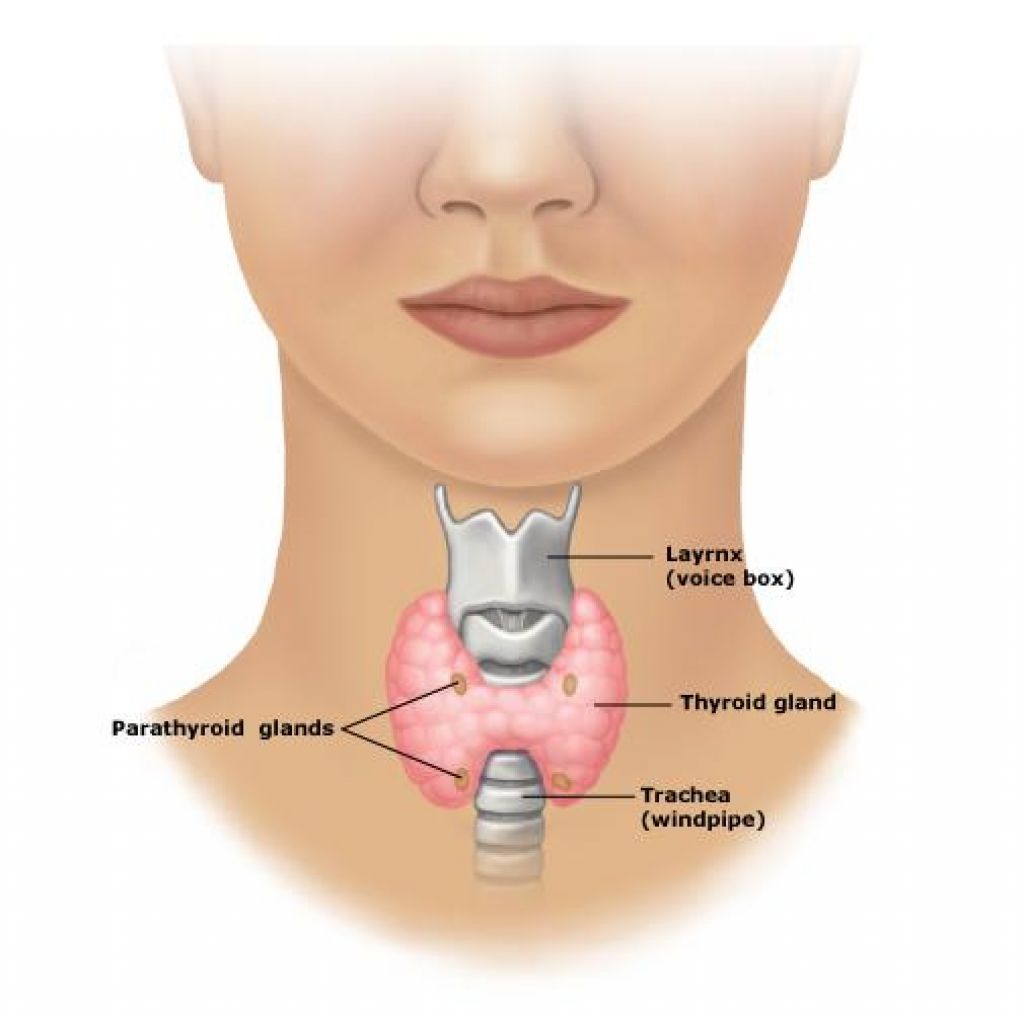
The Thyroid Gland releases hormones that control calorie burning and heart rate. It helps Brain development as well as make sure your bones are working and strong. It helps with the digestion of food as well as different muscles throughout the body
Pineal Gland
The Pineal Gland is a small gland in the brain. It produces a hormone called melatonin, which is a hormone that regulates biological rhythms like sleep and wake cycles
Problems
Failure of a gland. All the glands in this system work together. That means as soon as one gland fails a chain reaction will follow resulting in the failure of many more glands and us losing our motor functions.
Urinary system
Body Parts
Bladder

The bladder is what holds the urine. As the urine comes from the kidneys it is stored and released controlled and infrequently from the bladder.
Bladder Cancer is when cells in the bladder grow abnormally resulting in a tumor
Kidneys

The kidneys are what produces the urine. The kidneys take waste and water from the blood which it then turns into urine.
Ureters

The Ureters are two tubes that take the urine produced in the kidney to the bladder
Urethra

The male urethra connects the urinary bladder to the penis. Once the bladder becomes full, urine flows through the urethra and leaves the body
Muscular system
Body Parts
Skeletal Muscle
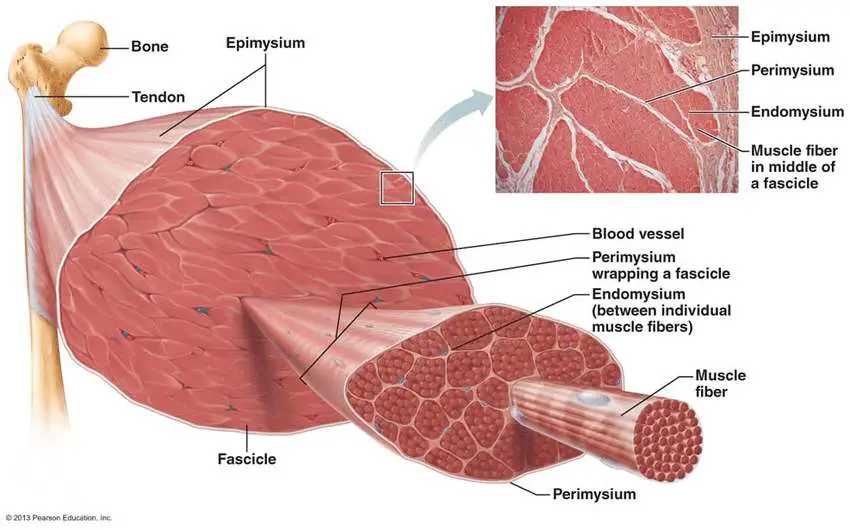
Skeletal Muscles help us maintain posture. They stabilize bones and joints and help us with internal movement. They also generate heat
If we started having problems with out skeletal system we would no lone be able to stand upright. We would have trouble moving and performing basic functions
Cardiac Muscle

Cardiac muscle is a muscle found only in the heart. It is the muscle that keeps our heart pumping and blood flowing through our heart. It responds to electric signals sent from the nervous system
Smooth Muscle

Smooth muscles are lined against the walls of hollow organs like out intestine. They work without us noticing them to digest food
Nervous system
Central Nervous System
Body Parts
Brain
The Brain is the most important part of the nervous system. The brain is what controls our thoughts, our feelings and basically everything that we do. The brain takes in information and sends a response back through the body. Think of the brain as a command center. It tels the body what to do.
Spinal Cord
The Spinal Cord is the pathway for information from the brain. The Brain give out an order and the spinal cord sends that order to wherever it needs to go. Wether it be an organ or your toe. The message travels down from the spinal cord to go where it needs to go.
Peripheral Nervous System
Body Parts
Cranial Nerves
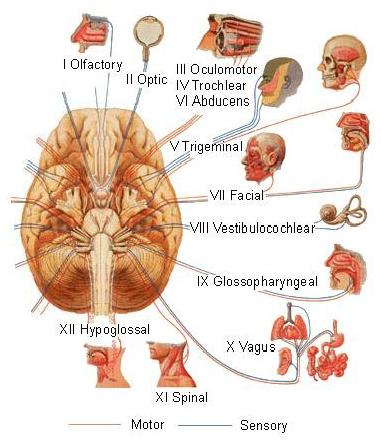
There are 12 types of Cranial Nerves. The Cranial nerves are in charge of controlling sensory functions, motor functions, or both. Sensory function are like helping the eyes see and ears hear while motor functions help control muscles in the head and neck.
Sacral Plexus
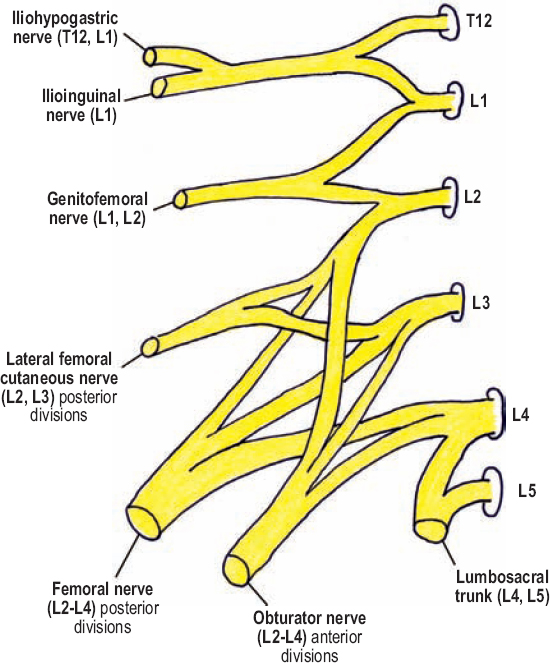
The Sacral Plexus provides motor and sensory functions for the posterior thigh and most of the lower leg, foot and pelvis. It emerges from the lumbar and sacral vertebrae
Brachial Plexus

The brachial plexus is a somatic nerve plexus formed by intercommunications among the roots of the lower 4 cervical nerves (C5-C8) and the first thoracic nerve (T1). The plexus, depicted in the images below, is responsible for the motor innervation of almost all of the muscles of the upper extremity
Thoracoabdominal Nerves

Thoracoabdominal Nerves do a number of things. they are mostly responsible for sensory functions regarding skin around the body. They also help give the skin fibers keeping it strong and healthy.
Lumbar Nerves
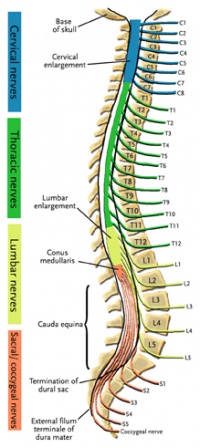
These are the nerves responsible for controlling the communication from the brain to the legs.
Disease
Brain Damage
Brain Damage affects the way the brain thinks and communicates with the rest of the body. meaning it could send incorrect responses through the body
Skeletal system
Body Parts
Bones
Bones are what give the body its shape and posture. Without bones we have o support whatsoever and would not be able to do anything. Bones protect all the organs in the body. Like the brain for example, is a organ that is incredibly delicate. So we the skull to protect it. They also give give us movement. Though they arent the part of the skeletal system that lets us moves they help move our arms.
Joints

Joints are what allow us to move. They are where two bones meet and they provide flexibility for the skeleton. Without joints we would not be able to move at all.
Cartilage

Cartilage is a connective tissue which bends a bit but not stretches. It is a connective tissue that connects bones. It is also found in the joints, the rib cage, the ear, the nose, the throat and between the bones of the back
Circulatory system
Body Parts
Heart
Right/Left ventricle
These are the two bottom chambers and they pump blood out of the heart
Right/Left Atrium
These are the top two chambers of the heart and they recieve blood entering the heart.
Tricuspid valve
The tricuspid valve separates the right atrium from the right ventricle
Mitral valve
The mitral valve separates the left atrium from the left ventricle
Pulmonic valve
The pulmonic valve is between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, which carries blood to the lungs
Aortic valve
The aortic valve is between the left ventricle and the aorta, which carries blood to the body
Pulmonary circulation

The pulmonary circulation is somewhat of a loop going through the lungs. This is where blood is oxygenated before going through the rest of the body.
systemic circulation

The systemic circulation is a loop through the rest of the body. This loop provides oxygen to the blood as it travels to different parts of the body.
Arteries

Arteries are strong blood vessels that take blood from the heart which has recieved oxygen and nutrients and take it to different blood vessels.
Viens

Veins are responsible for returning deoxygenated blood back to the heart after arteries take blood out. Veins have much thinner walls compared to arteries which is why we can see them through our skin
Vessels

Coronary vessels supply the heart with blood. they supply the heart with oxygenated blood.
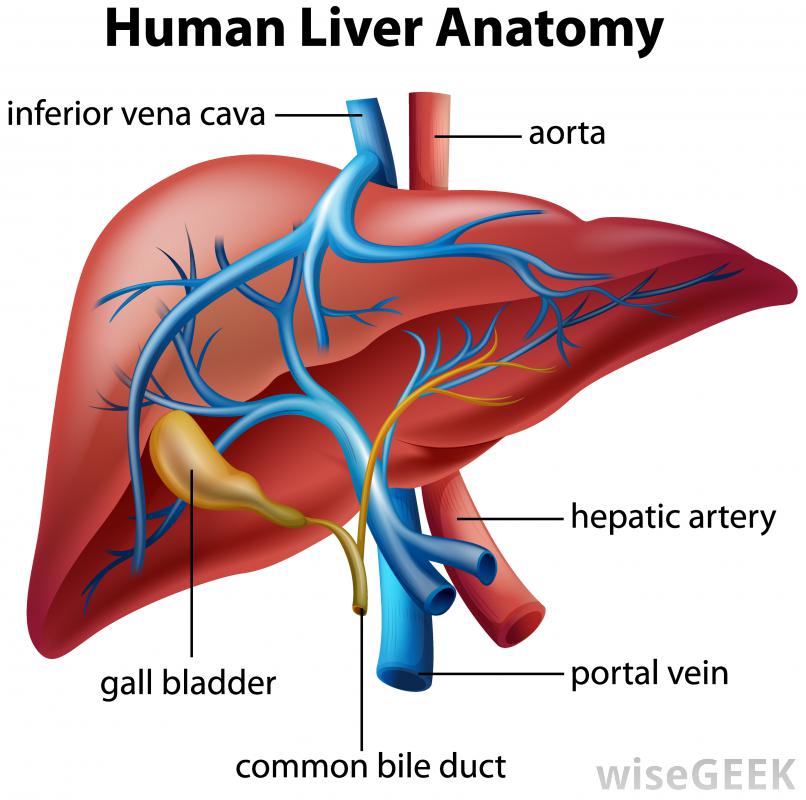
This is a vein that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, spleen and pancrease to the liver.
Integumentary system
Body Parts
Skin
Epidermis

The epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin. It provides a barrier preventing infections from getting in the body. It also regulates how much water is released from the body.
Dermis

Hypodermis
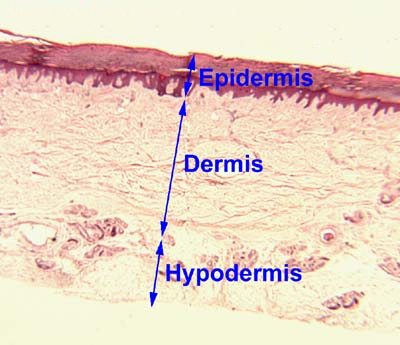
The Hypodermis acts as a layer of insulation for the body. It also cushions parts under the skin
Skin cancer occurs when the body does not repair damage to the DNA inside skin cells, allowing the cells to divide and grow uncontrollably. It can create tumors.
Hair

Hairs protect us from certain infections as well as helping us regulate body temperature. They also act as sense organs.
Nails

Nails protect the tips of fingers and toes from mechanical injury. Fingernails give the fingers greater ability to pick up small object
Digestive system
Body Parts
GI Tract

The Gi tract is a long tube that starts at the mouth and ends at the anus. The Gi tract is aligned with specific muscles that coordinate the movement of the food. There are also different cells that produce enzymes that help further break down the food.
Pancreas

The pancreas produces insulin and other important enzymes and hormones that help break down food. The pancreas has an endorcine function as it releases juices directly into the blood stream.
Liver
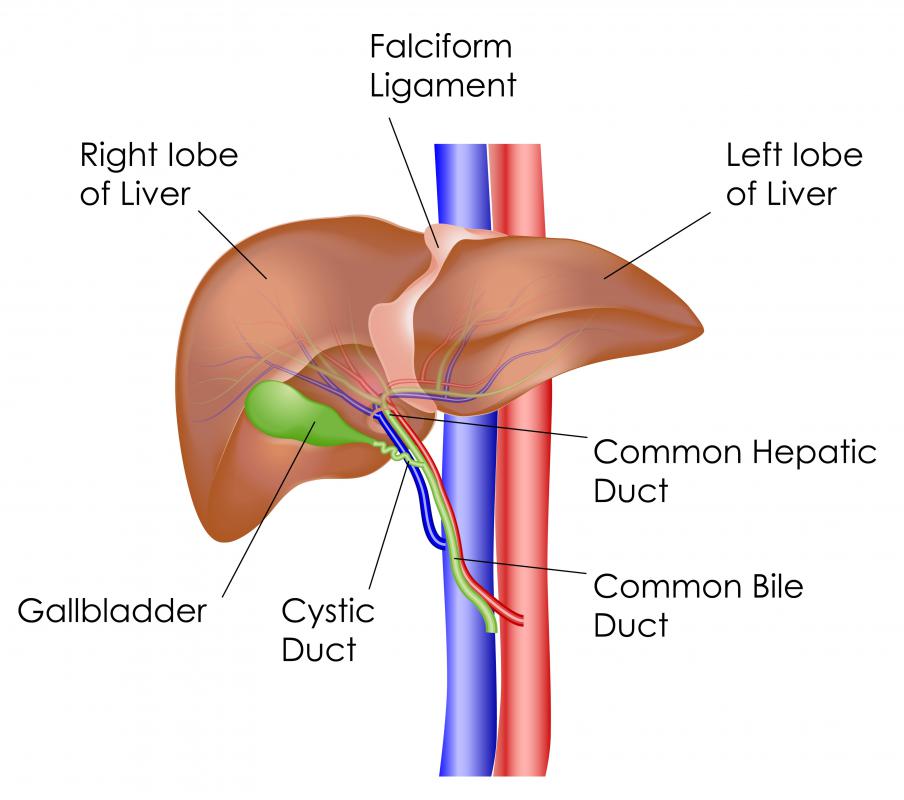
The liver has does many things in the digestive system. It creates and bile then give it to the small intestine helping to break down fats. It expels hormones, cholesterol and drugs. Metabolism fats, carbohydrates and protein. Stores witamins and minerals among other thigs.
Mouth
The mouth is what starts off the digestion track. The mouth takes food and chews it up until the food is small and soft enough to go down the esophagus smoothly
Esophagus

The Esophagus is the passage for food from your mouth to your stomach. The esophagus uses a series of muscles to move food down the body.
Stomach
The stomach produces enzymes and acids that digest food. The walls of the stomach are aligned with ridges of muscle tissue called rugae. The rugae move in certain ways that crunches up food and helping the process of digestion
Large intestine

The Large Intestine is the final stop before the rectum and anus. undigested food enters the large intestine from the small intestine. it then soaks up the water from digestion and eliminates undigested food and fibers. This causes waste to harden and form faeces
Small Intestine
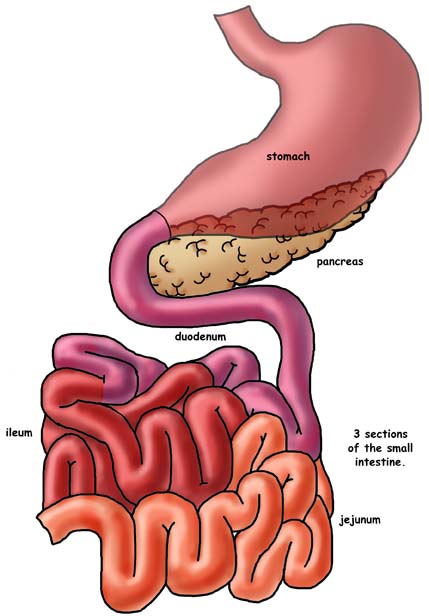
90% of digestion occurs in the small intestine. The small intestine is responsible for absorbing nutrients recieved from food. The small intestine uses enzymes from the pancreas to digest food.
Rectum

The rectum is what holds waste products after the colon. The waste then sits there until it is ready to be disposed of