Tangent
|AB|
/|BC| use this to estimate slope.
MPQ = x^2-1/x-1
Velocity
Average Velocity = Change in Position / Time Elasped
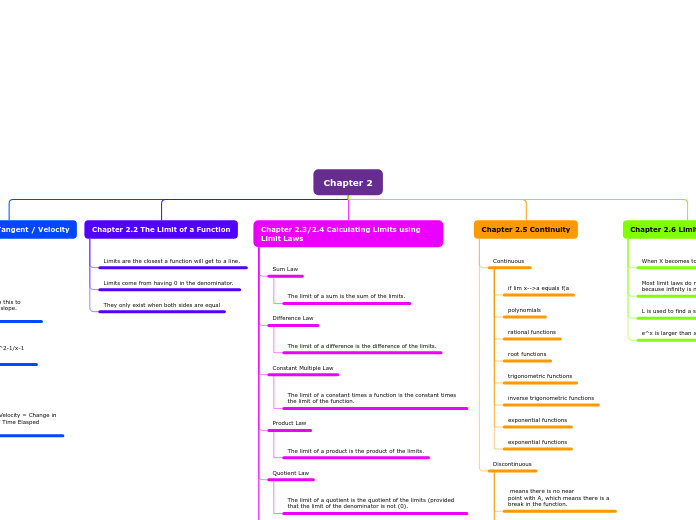
Limits are the closest a function will get to a line.
Limits come from having 0 in the denominator.
They only exist when both sides are equal
Sum Law
The limit of a sum is the sum of the limits.
Difference Law
The limit of a difference is the difference of the limits.
Constant Multiple Law
The limit of a constant times a function is the constant times the limit of the function.
Product Law
The limit of a product is the product of the limits.
Quotient Law
The limit of a quotient is the quotient of the limits (provided that the limit of the denominator is not (0).
Power Law
Makes an equation able to spread the power throughout equation.
Root law
Same as power law but for roots.
Direct Substitution Property
Continuous
if lim x-->a equals f(a
polynomials
rational functions
root functions
trigonometric functions
inverse trigonometric functions
exponential functions
exponential functions
Discontinuous
means there is no near
point with A, which means there is a
break in the function.
Infinite discontinuity
Jump discontinuity
removeable discontiniuty
Can be fixed into continuous
When X becomes too large, it becomes infinity.
Most limit laws do not apply to limits at infinity
because infinity is not a number.
L is used to find a specific interval on graph, also a.
e^x is larger than x^3 when x is larger.