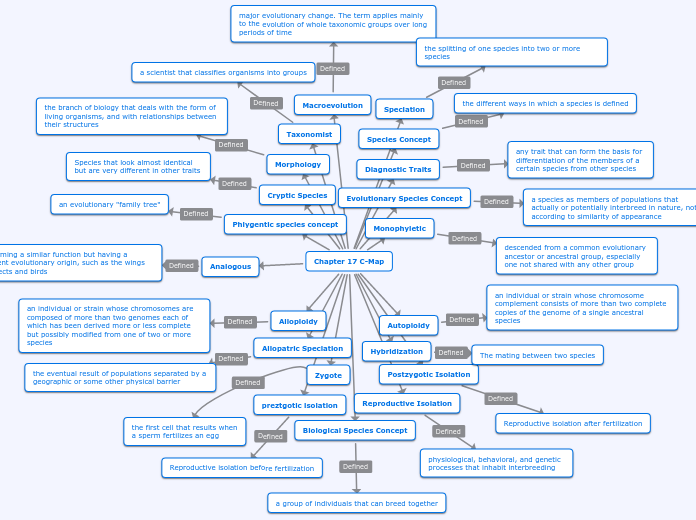
Chapter 17 C-Map
Macroevolution
major evolutionary change. The term applies mainly to the evolution of whole taxonomic groups over long periods of time
Speciation
the splitting of one species into two or more species
Taxonomist
a scientist that classifies organisms into groups
Species Concept
the different ways in which a species is defined
Morphology
the branch of biology that deals with the form of living organisms, and with relationships between their structures
Diagnostic Traits
any trait that can form the basis for differentiation of the members of a certain species from other species
Cryptic Species
Species that look almost identical but are very different in other traits
Evolutionary Species Concept
a species as members of populations that actually or potentially interbreed in nature, not according to similarity of appearance
Phlygentic species concept
an evolutionary "family tree"
Monophyletic
descended from a common evolutionary ancestor or ancestral group, especially one not shared with any other group
Biological Species Concept
a group of individuals that can breed together
Reproductive Isolation
physiological, behavioral, and genetic processes that inhabit interbreeding
preztgotic isolation
Reproductive isolation before fertilization
Postzygotic Isolation
Reproductive isolation after fertilization
Zygote
the first cell that results when a sperm fertilizes an egg
Hybridization
The mating between two species
Allopatric Speciation
the eventual result of populations separated by a geographic or some other physical barrier
Autoploidy
an individual or strain whose chromosome complement consists of more than two complete copies of the genome of a single ancestral species
Alloploidy
an individual or strain whose chromosomes are composed of more than two genomes each of which has been derived more or less complete but possibly modified from one of two or more species
Analogous
performing a similar function but having a different evolutionary origin, such as the wings of insects and birds