How efficient is Mindomo for education and learning?
Over the years, many pieces of research and publications written by authorities in this area mentioned Mindomo and detailed how this visual tool is efficient for learning. Many situations were evaluated, and many studies were conducted on this topic (how efficient are mind maps for kids and for students, or as an assistive technology tool). These studies determined that Mindomo is an efficient tool for learning and education.
Students process information easier and better synthesize basic and clinical sciences with the help of Mindomo’s concept maps.
In 2010 the State University of New York (SUNY) College of Optometry conducted a pilot project in order to demonstrate the utility and acceptance of concept maps among selected groups of students. This project had three stages, all of them used Mindomo as a concept mapping tool, and each focus group was selected from different years: first, second, and third.
The results show that this method improved students’ ability to integrate didactic knowledge and clinical care clearly and cohesively.
Some specific benefits pointed out during this pilot project are:
-
Teachers can easily notice which concepts the students consider essential learning points. Any gaps in understanding are also made easily noticeable.
-
Concept map presentations are an excellent tool for students to clarify misinterpretations and questions before the final examination.
-
62% of the students who participated and created concept maps with Mindomo affirm that it helped them see the bigger picture and have an overview of their clinical case presentations.
-
About half of the students consider that concept maps helped them connect information from the course to other courses from their curriculum.
The faculty concluded that Mindomo’s concept mapping is a valuable tool to demonstrate students’ knowledge, organize and present thoughts, and integrate fundamental concepts of a course. Moreover, they suggested introducing concept mapping as early as possible in the curriculum before students adopt different study methods on their own.
The faculty considers that using the concept mapping method across multiple courses would improve their comfort and efficiency, recognizing good results over this pilot project (the students’ first contact with this technique).
Some students continued to use Mindomo in other courses from the curriculum and apply the concept mapping technique to their learning. You can read the research paper for more details.
Concept maps are an effective tool to enhance students’ performance and understanding in an e-learning environment.
The paper “Blending Concept Maps with Online Labs for STEM Learning” describes how concept maps blend with online labs (OLabs) to enhance secondary students’ performance in biology (read the full research paper).
The problem brought to our attention by this paper is the need for more understanding of the complex concepts of Biology and the challenge of providing a framework where the concepts can be linked to each other. The paper analyzes the concept mapping technique and concludes that concept maps are an excellent solution for enhancing students’ comprehension.
Concept maps are a versatile tool for education, having multiple uses when it comes to learning: providing accurate instructions, learning objectives, and evaluation criteria. Moreover, it is concluded to be an effective productivity booster and a quick accomplisher for both teachers and students.
Many educational practitioners believe concept mapping is a great way to strengthen academic understanding. This technique is integrated into teacher training programs to help them/allow them to keep up with the principles of the modern education culture.
Why are concept maps efficient for learning?
-
Concept maps are a versatile tool for education, having multiple uses when it comes to learning: providing accurate instructions, learning objectives, and evaluation criteria.
-
It is concluded to be an effective productivity booster and a quick accomplisher.
-
Research suggests that visual learning is the best method for teaching and learning. When students start to organize knowledge graphically, they draw the ideas learned and easily see the connections between them.
-
When students efficiently use it, concept mapping can enhance retention and test scores compared to other study techniques.
-
Concept maps reduce the complexity of the material and also minimize students’ misconceptions.
Concept mapping enhances teaching quality in Higher Education.
While the above papers and studies showed how concept mapping applies in K12, it is important to note that this technique is also valuable for Higher Education. It helps turn abstract knowledge into concrete visual representations. Concept maps are great for teaching and for measuring the quality of learning.
Concept mapping is a powerful tool that can be thought out in 10-20 minutes. Most students think 20-30 additional minutes are enough to create the first concept map.
Uses of concept maps in a Higher Education academic environment:
-
assessing change in the course of learning
-
identifying students’ misconceptions
-
teaching practice (concept mapping can enhance the quality of the dialog between teacher and students by creating an exchange of knowledge between them)
-
lesson planning
-
assessment (testing knowledge)
-
cognitive typology (observing different structures people use to organize their thinking)
-
identification of expertise (show measurable differences between experts and novices)
-
team working
The article “Making learning visible: the role of concept mapping in Higher Education” (read the whole paper) describes four educational uses of concept mapping:
- Identification of prior knowledge – it is important to measure newly acquired and prior knowledge, to integrate new concepts, and connect them to the ones you were already familiar with.
- Presentation of new materials in ways that facilitate meaningful learning – the authors suggest that involving students directly in the construction of new understanding should be part of all university-level teaching. They also suggest the following exercise: students should create concept maps about their existing knowledge, and then teachers can ask them to add the new knowledge and evaluate if the new one can be linked to the prior one. If the new knowledge is not integrated into the existing one, it is likely to be quickly forgotten.
- Sharing of “expert” knowledge and understanding among educators and learners – reduce abstract knowledge to concrete diagrammatic representation.
- The documentation of knowledge changes to show the integration of students’ prior knowledge and teaching.
According to the above article, concept mapping is considered important in the future development of Higher Education and its research. H
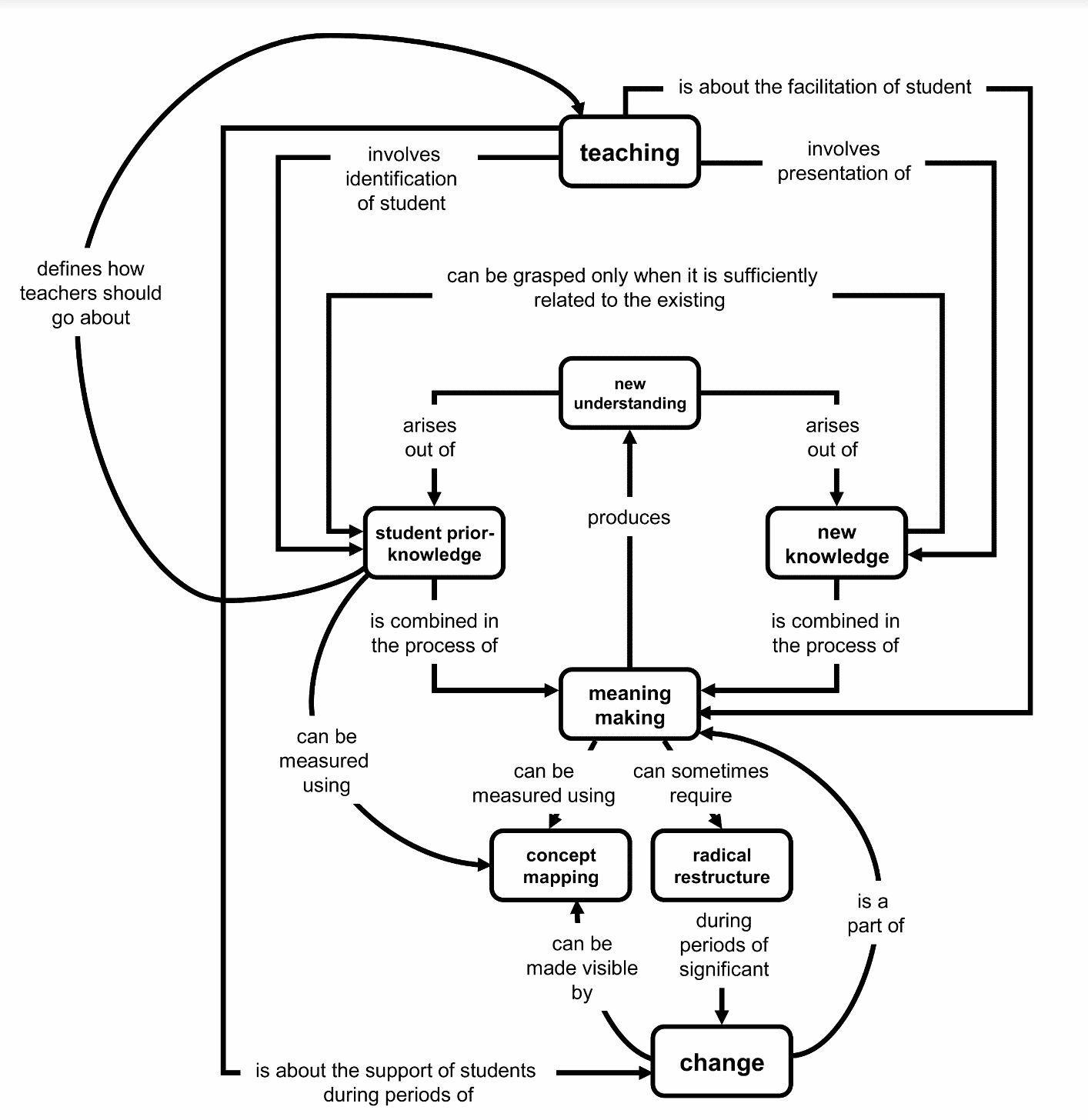
A model of university teaching practice.
(Source: Making learning visible: The role of concept mapping in Higher Education)
Mindomo’s concept maps are a great pedagogical tool that engages students in higher-order thinking
Brandon M. Sabourin, a teacher from the University of Windsor, Canada, wrote about his experience using Mindomo’s concept maps with his students in “Using Mindomo to engage students in higher-order thinking” (read the paper).
This paper explains how and why Mindomo’s concept maps are helpful as a teaching tool. Concept maps promote creativity, encourage deep learning, and support finding connections between concepts. It’s a great pedagogical tool for any age, level of study, or subject (discipline).
The paper points out the unique characteristic of a concept map vs. a mind map. The first one supposes a depth to the levels and types of relationships depicted. It is explained that mind mapping focuses on lower-order thinking skills like summarizing, defining, memorizing, or classifying, while concept mapping engages learners in high-order thinking actions, such as justifying, analyzing, defending, or hypothesizing.
The instructor’s perspective on Mindomo highlights the importance of concept mapping as a tool that supports meaningful learning and highlights Mindomo as one of the solutions he found for developing students’ critical thinking.
The students assessed Mindomo as a tool that allowed them to engage with the courses, where they participated more meaningfully. Moreover, the general opinion supports Mindomo as a pedagogical mind map software in their courses.
Mind mapping helps students memorize vocabulary and motivates them to learn a foreign language
Besides the concept mapping mentioned above, mind mapping is another very well-known type of diagram used for education by Mindomo users.
The “Memorizing Vocabulary through Mind Mapping Technique” (read the research paper) study analyzed 40 first-year students from Bangkok University in Bangkok, Thailand, during a 6-week experiment on learning a foreign language. After the experiment, the University chose mind mapping as a specific technique for memorizing vocabulary.
Students learned in the first week using conventional methods and were then tested. In the third week, the teacher introduced the mind mapping method, and they were tested again at the end of this study (sixth week). The difference between the results significantly increased after using mind mapping as a learning method.
The study clearly revealed the benefits of using the mind mapping technique for learning a new language and emphasized the differences between this method and conventional ones:
-
Mind mapping enhanced students’ motivation, attention, comprehension, and recall.
-
This technique allowed learners to use the left and right brain in the memorizing process, and it incorporated a variety of memory strategies such as grouping, associating, using imagery, and elaborating, which are essential for improving both memory and comprehension of new vocabulary items.
-
This study proves that mind maps are an excellent tool for both storing and expanding vocabulary size, helping learners utilize and rely on their long-term memory.
-
The positive effect of using mind maps was pronounced for learners as well, not only for teachers; students stopped feeling overwhelmed by the limited amount of “storage” attributed to vocabulary items in their memory.
-
Students had a very high opinion of the benefits of memorizing words through the mind mapping technique. Consequently, they felt motivated to learn vocabulary using these diagrams.
-
Visualisation using colors, pictures, and curvy lines helped learners make associations. They were attracted to this method because they could express their style by using art and imagination to the fullest.
-
Mind mapping is considered one of the best tools for constructing and sharing knowledge.
-
Learners considered mind mapping an enjoyable way of absorbing knowledge, which attracted their brain, becoming more interested in mastering vocabulary items.
-
Mind mapping is also a creative note-taking solution.
Mindomo is a helpful tool for reading lessons, helping the readers understand the text better.
The study called “Mindomo: a digital mind mapping in primary ESL reading skills” (read the paper here) investigated the efficiency and the perception of students using Mindomo as a digital mind map maker in their reading lessons.
The research had 30 participants that were Primary Year 6 students. The study started from the already proven ideas related to the efficiency of the mind mapping technique, such as:
-
Mind mapping aids students in structuring and organizing their thoughts in a simple yet comprehensive manner, which helps them present their ideas easily and meaningfully to their listeners.
-
Students retain information faster using visual learning.
-
Creating visual connections and associations between concepts increases comprehension.
-
The Mind mapping strategy does not limit learners and teachers to visual and linear structure. On the contrary, it gives them freedom and supports their creativity.
The results of the study support the fact that Mindomo is a great tool for reading lessons, being used with pleasure and excitement by students during their reading time. Moreover, Mindomo motivates students to be avid readers.
-
Students affirmed that they want to read more books after discovering how Mindomo helped them understand the text they read. 90% of participants stated that the use of Mindomo assisted them in understanding the ideas in the texts read.
-
Reading became more enjoyable for students as they started using Mindomo at home, and their motivation increased. 63% of the students said that the process of creating mind maps using Mindomo was enjoyable, whereas 67% of them claimed that they enjoyed the overall process of using Mindomo in their reading lessons.
-
Students improved their reading skills by using Mindomo’s mind maps to summarize ideas from the text and add visual elements such as images, fonts, styles, icons, etc.
-
Students better categorize main and supporting ideas from texts they read, and they are able to understand the structure of a text. (100% of participants concurred that Mindomo aids them in identifying the main ideas and supporting ideas).
-
Using the mind mapping technique while reading increased readers’ vocabulary knowledge.
Seventh-grade students are excited, interested, and motivated to use Mindomo for writing descriptive text
A recent study conducted in 2021 called “Students’ response toward the implementation of Mindomo in writing descriptive text at the seventh grade the students in Cimahi” (read the paper here) analyzed how diagramming helped learners develop writing skills in a foreign language.
The study, conducted in Junior High School in Cimahi, and having 33 students who actively participated, showed that the implementation of Mindomo was successful and had a positive response to learning a foreign language, especially in writing descriptive text.
- 81.80% of students agree with the implementation of Mindomo in the learning process of writing.
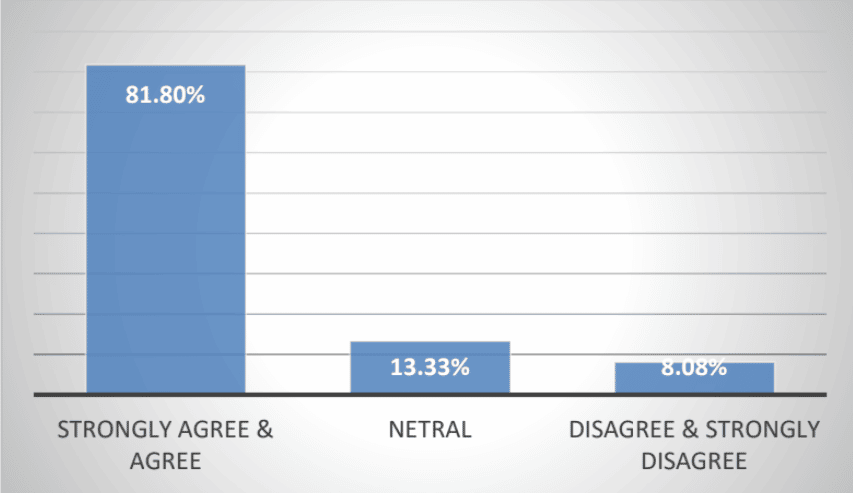
The average response of students about the use of Mindomo in the process of writing descriptive texts
(Source: Students’ response toward the implementation of Mindoro in writing descriptive text at the seventh grade the students in Cimahi)
+ Students shared their feedback regarding the experience of using Mindomo expressed into 4 indicators: attention, relevance, confidence, and satisfaction. The results show that attention during the learning process is the highest.
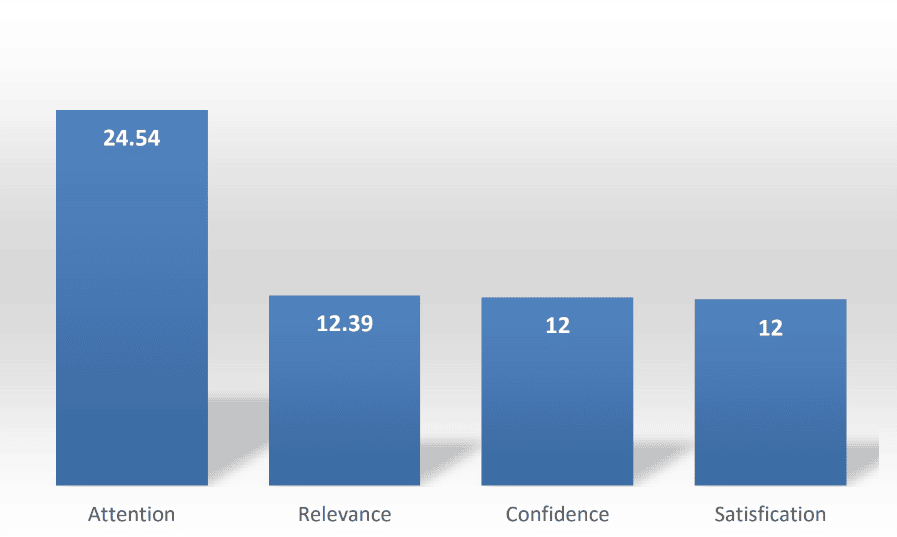
Average of participants’ responses on each indicator.
(Source: Students’ response toward the implementation of Mindoro in writing descriptive text at the seventh grade the students in Cimahi)
The conclusion of this study highlights that Mindomo made students happy, creative, motivated, and excited about writing descriptive texts. They were focused on understanding and learning the material and were happy to share their ideas using Mindomo’s diagrams.
Mind mapping is embraced by students and they like to use it for organizing and generating ideas when they write
During the pandemic, teaching writing skills was more challenging, and it required extra effort. A recent study written in 2022 called “Application of Digital Mind Mapping (MINDOMO) in Improving Weak Students’ Narrative Writing Performance” (read the full study), aimed to investigate how mind mapping could make a difference in students’ narrative writing performances.
Sixteen students took part in this research. They were pre-tested, introduced to the mind mapping technique, and encouraged to use it. Afterward, they were post-tested and interviewed.
The differences between pre-test and post-test scores are obvious, showing that mind mapping significantly improved the students’ understanding and learning.
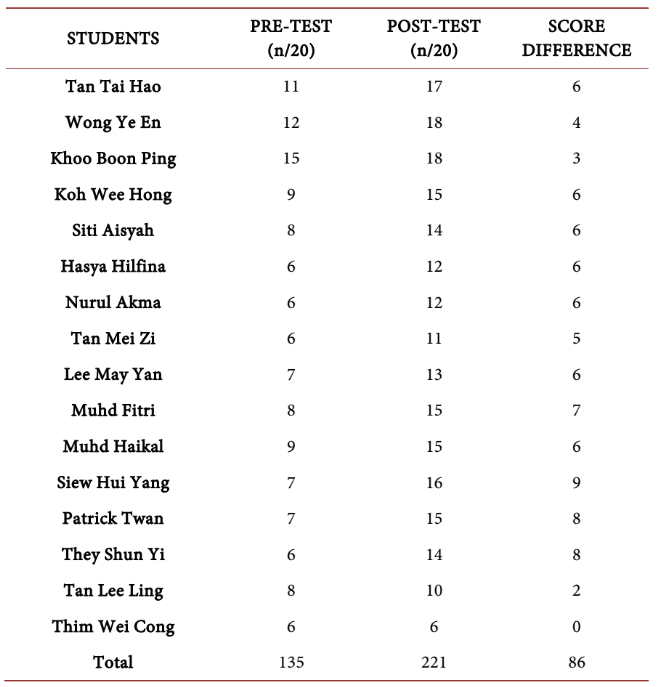
Pre-test and post-test scores of the students before and after using mind mapping
(Source: Application of Digital Mind Mapping (MINDOMO) in Improving Weak Students’ Narrative Writing Performance)
After the tests, students answered what benefits of using mind mapping they observed, and they had positive opinions regarding this method:
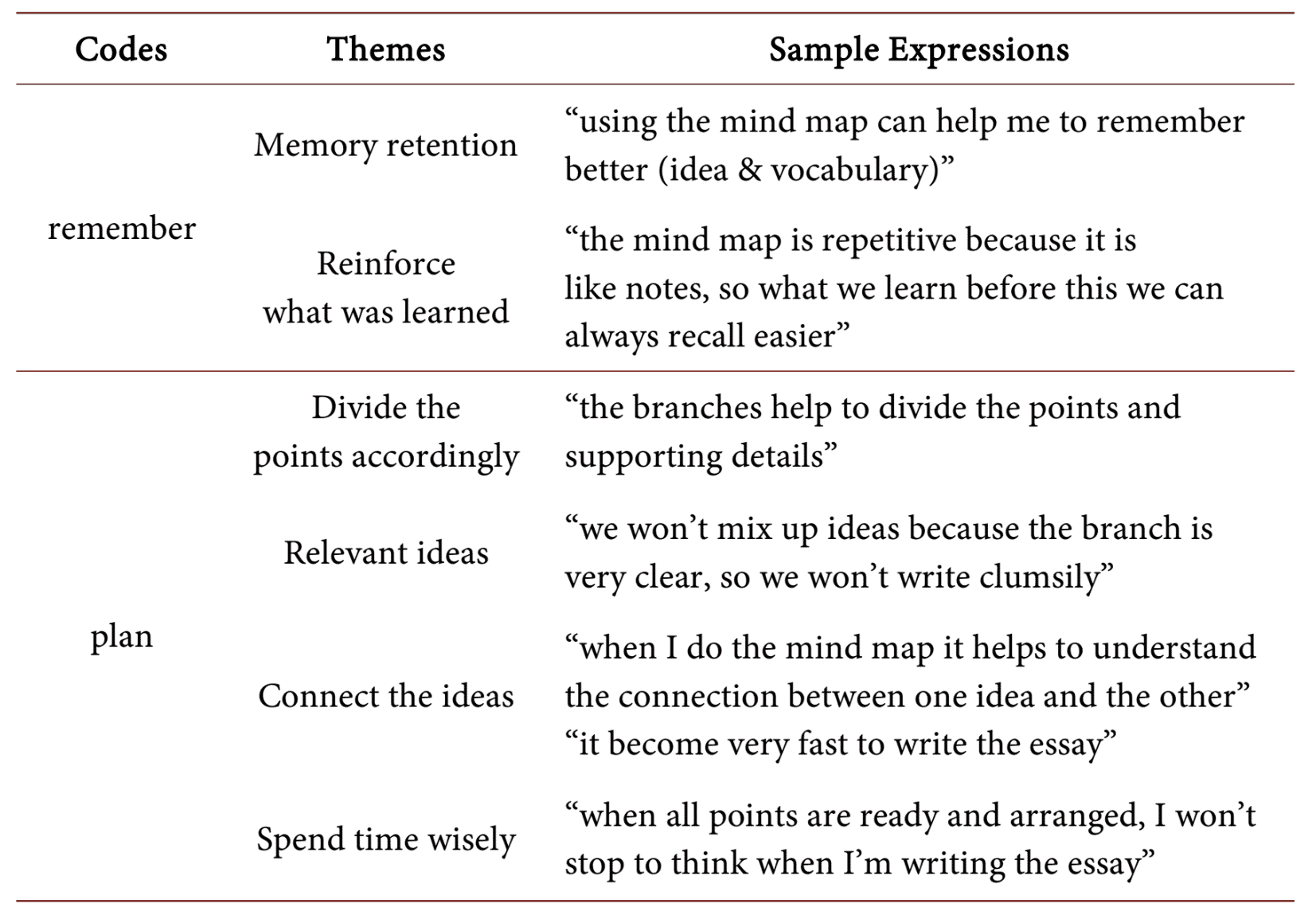
Students opinion about the benefits of mind mapping
(Source: Application of Digital Mind Mapping (MINDOMO) in Improving Weak Students’ Narrative Writing Performance)
Mindomo is an efficient tool for learning
Gathering all this research and all the studies made over time, Mindomo’s usability for teaching and learning is confirmed. Both educators and learners noticed significant benefits when they introduced Mindomo’s mind mapping and concept mapping as learning techniques. The efficiency of these methods is established by the examples presented above.
The numerous benefits include better comprehension, deep learning, organizing knowledge and creating connections, boosting retention and recall, and improving creativity.
References
Find all the mentioned documents and research on how Mindomo is an efficient tool for learning in the following external sources:
- Jean Pak, MSEd, Elaine Wells, MA, MLS, AHIP(D), David Libassi OD, Susan Schuettenberg, OD, and Kathryn Richdale, PhD, OD: Concept Mapping as a Tool for Didactic Learning and Case Presentation in an Optometric Curriculum(2016)
- Raghu Raman, Mithun Haridas, and Prema Nedungadi: Blending Concept Maps with Online Labs for STEM Learning (2015)
- David Hay, Ian Kinchin, and Simon Lygo-Baker: Making learning visible: the role of concept mapping in Higher Education (2008)
- Brandon M. Sabourin: Using Mindomo to engage students in higher-order thinking (2020)
- Nuttanuch Munsakorn: Memorizing Vocabulary through Mind Mapping Technique (2012)
- Denish Sevakumaran, Jamaludin Badushah: Mindomo: a digital mind mapping in primary ESL reading skills (2017)
- Annisa Novianti, Evie Kareviati: Students’ response toward the implementation of Mindoro in writing descriptive text at the seventh grade the students in Cimahi (2021)
- Vejayan, L., & Yunus, M. M. : Application of Digital Mind Mapping (MINDOMO) in Improving Weak Students’ Narrative Writing Performance, (2022)
